LeetCode题解1
1. Two Sum
题目
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1]
题目大意
在数组中找到 2 个数之和等于给定值的数字,结果返回 2 个数字在数组中的下标。
解题思路
这道题最优的做法时间复杂度是 O(n)。
顺序扫描数组,对每一个元素,在 map 中找能组合给定值的另一半数字,如果找到了,直接返回 2 个数字的下标即可。如果找不到,就把这个数字存入 map 中,等待扫到“另一半”数字的时候,再取出来返回结果。
代码
- Java
- Go
package leetcode;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int another = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(another)) {
return new int[] {map.get(another), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return null;
}
}
package leetcode
func twoSum(nums []int, target int) []int {
m := make(map[int]int)
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
another := target - nums[i]
if _, ok := m[another]; ok {
return []int{m[another], i}
}
m[nums[i]] = i
}
return nil
}
2. Add Two Numbers
题目
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
题目大意
2 个逆序的链表,要求从低位开始相加,得出结果也逆序输出,返回值是逆序结果链表的头结点。
解题思路
需要注意的是各种进位问题。
极端情况,例如
Input: (9 -> 9 -> 9 -> 9 -> 9) + (1 -> )
Output: 0 -> 0 -> 0 -> 0 -> 0 -> 1
为了处理方法统一,可以先建立一个虚拟头结点,这个虚拟头结点的 Next 指向真正的 head,这样 head 不需要单独处理,直接 while 循环即可。另外判断循环终止的条件不用是 p.Next != nil,这样最后一位还需要额外计算,循环终止条件应该是 p != nil。
代码
- Go
package leetcode
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
head := &ListNode{Val: 0}
n1, n2, carry, current := 0, 0, 0, head
for l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 {
if l1 == nil {
n1 = 0
} else {
n1 = l1.Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
if l2 == nil {
n2 = 0
} else {
n2 = l2.Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
current.Next = &ListNode{Val: (n1 + n2 + carry) % 10}
current = current.Next
carry = (n1 + n2 + carry) / 10
}
return head.Next
}
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
题目
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Example 1:
Input: "abcabcbb"
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
Example 2:
Input: "bbbbb"
Output: 1
Explanation: The answer is "b", with the length of 1.
Example 3:
Input: "pwwkew"
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "wke", with the length of 3.
Note that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
题目大意
在一个字符串重寻找没有重复字母的最长子串。
解题思路
这一题和第 438 题,第 3 题,第 76 题,第 567 题类似,用的思想都是"滑动窗口”。
滑动窗口的右边界不断的右移,只要没有重复的字符,就持续向右扩大窗口边界。一旦出现了重复字符,就需要缩小左边界,直到重复的字符移出了左边界,然后继续移动滑动窗口的右边界。以此类推,每次移动需要计算当前长度,并判断是否需要更新最大长度,最终最大的值就是题目中的所求。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 位图
func lengthOfLongestSubstring(s string) int {
if len(s) == 0 {
return 0
}
var bitSet [256]bool
result, left, right := 0, 0, 0
for left < len(s) {
// 右侧字符对应的 bitSet 被标记 true,说明此字符在 X 位置重复,需要左侧向前移动,直到将 X 标记为 false
if bitSet[s[right]] {
bitSet[s[left]] = false
left++
} else {
bitSet[s[right]] = true
right++
}
if result < right-left {
result = right - left
}
if left+result >= len(s) || right >= len(s) {
break
}
}
return result
}
// 解法二 滑动窗口
func lengthOfLongestSubstring1(s string) int {
if len(s) == 0 {
return 0
}
var freq [127]int
result, left, right := 0, 0, -1
for left < len(s) {
if right+1 < len(s) && freq[s[right+1]] == 0 {
freq[s[right+1]]++
right++
} else {
freq[s[left]]--
left++
}
result = max(result, right-left+1)
}
return result
}
// 解法三 滑动窗口-哈希桶
func lengthOfLongestSubstring2(s string) int {
right, left, res := 0, 0, 0
indexes := make(map[byte]int, len(s))
for left < len(s) {
if idx, ok := indexes[s[left]]; ok && idx >= right {
right = idx + 1
}
indexes[s[left]] = left
left++
res = max(res, left-right)
}
return res
}
func max(a int, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
题目
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
You may assume nums1 and nums2 cannot be both empty.
Example 1:
nums1 = [1, 3]
nums2 = [2]
The median is 2.0
Example 2:
nums1 = [1, 2]
nums2 = [3, 4]
The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
题目大意
给定两个大小为 m 和 n 的有序数组 nums1 和 nums2。
请你找出这两个有序数组的中位数,并且要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(log(m + n))。
你可以假设 nums1 和 nums2 不会同时为空。
解题思路
-
给出两个有序数组,要求找出这两个数组合并以后的有序数组中的中位数。要求时间复杂度为 O(log (m+n))。
-
这一题最容易想到的办法是把两个数组合并,然后取出中位数。但是合并有序数组的操作是
O(m+n)的,不符合题意。看到题目给的log的时间复杂度,很容易联想到二分搜索。 -
由于要找到最终合并以后数组的中位数,两个数组的总大小也知道,所以中间这个位置也是知道的。只需要二分搜索一个数组中切分的位置,另一个数组中切分的位置也能得到。为了使得时间复杂度最小,所以二分搜索两个数组中长度较小的那个数组。
-
关键的问题是如何切分数组 1 和数组 2 。其实就是如何切分数组 1 。先随便二分产生一个
midA,切分的线何时算满足了中位数的条件呢?即,线左边的数都小于右边的数,即,nums1[midA-1] ≤ nums2[midB] && nums2[midB-1] ≤ nums1[midA]。如果这些条件都不满足,切分线就需要调整。如果nums1[midA] < nums2[midB-1],说明midA这条线划分出来左边的数小了,切分线应该右移;如果nums1[midA-1] > nums2[midB],说明 midA 这条线划分出来左边的数大了,切分线应该左移。经过多次调整以后,切分线总能找到满足条件的解。 -
假设现在找到了切分的两条线了,
数组 1在切分线两边的下标分别是midA - 1和midA。数组 2在切分线两边的下标分别是midB - 1和midB。最终合并成最终数组,如果数组长度是奇数,那么中位数就是max(nums1[midA-1], nums2[midB-1])。如果数组长度是偶数,那么中间位置的两个数依次是:max(nums1[midA-1], nums2[midB-1])和min(nums1[midA], nums2[midB]),那么中位数就是(max(nums1[midA-1], nums2[midB-1]) + min(nums1[midA], nums2[midB])) / 2。图示见下图: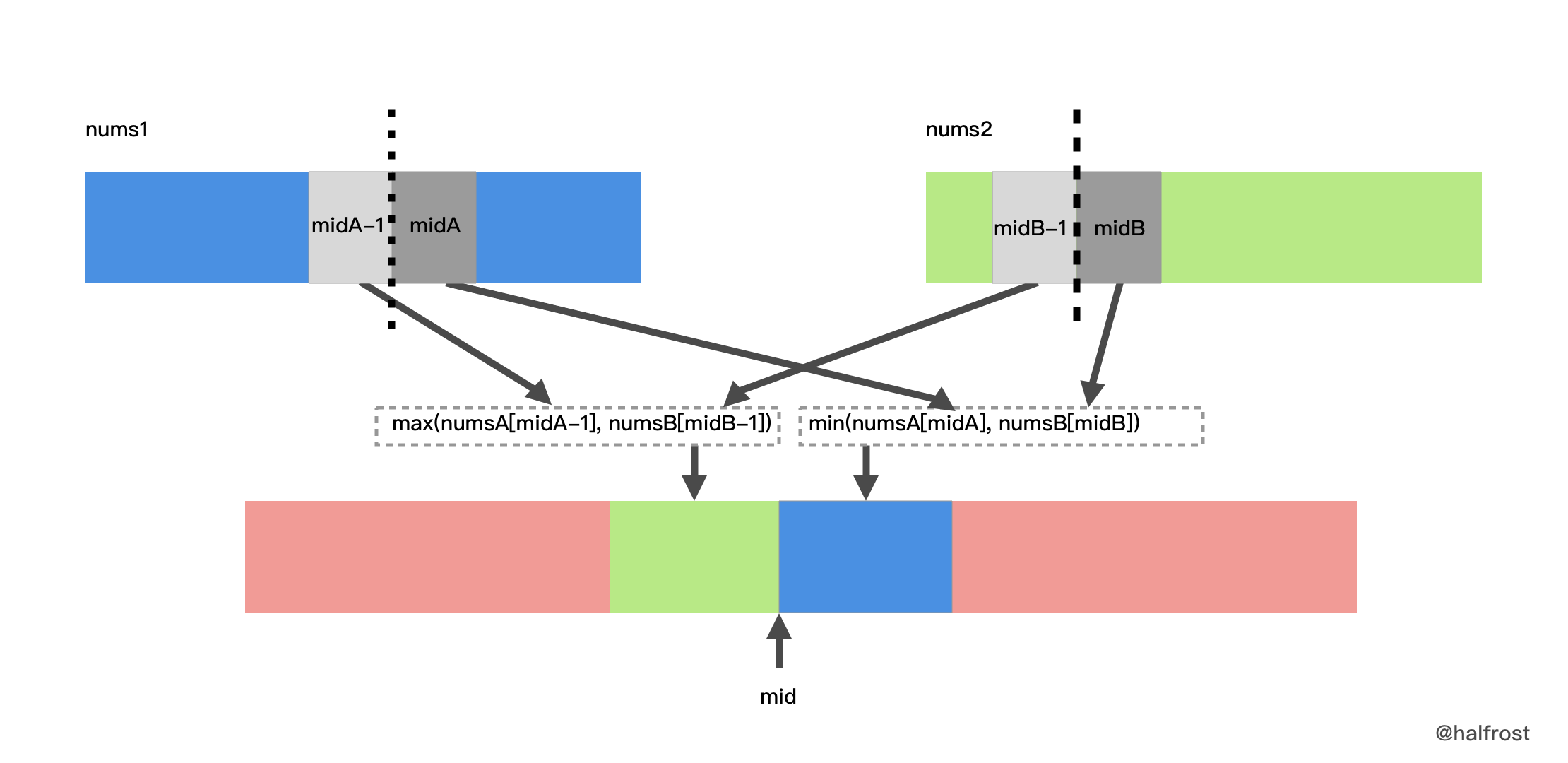
代码
package leetcode
func findMedianSortedArrays(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) float64 {
// 假设 nums1 的长度小
if len(nums1) > len(nums2) {
return findMedianSortedArrays(nums2, nums1)
}
low, high, k, nums1Mid, nums2Mid := 0, len(nums1), (len(nums1)+len(nums2)+1)>>1, 0, 0
for low <= high {
// nums1: ……………… nums1[nums1Mid-1] | nums1[nums1Mid] ……………………
// nums2: ……………… nums2[nums2Mid-1] | nums2[nums2Mid] ……………………
nums1Mid = low + (high-low)>>1 // 分界限右侧是 mid,分界线左侧是 mid - 1
nums2Mid = k - nums1Mid
if nums1Mid > 0 && nums1[nums1Mid-1] > nums2[nums2Mid] { // nums1 中的分界线划多了,要向左边移动
high = nums1Mid - 1
} else if nums1Mid != len(nums1) && nums1[nums1Mid] < nums2[nums2Mid-1] { // nums1 中的分界线划少了,要向右边移动
low = nums1Mid + 1
} else {
// 找到合适的划分了,需要输出最终结果了
// 分为奇数偶数 2 种情况
break
}
}
midLeft, midRight := 0, 0
if nums1Mid == 0 {
midLeft = nums2[nums2Mid-1]
} else if nums2Mid == 0 {
midLeft = nums1[nums1Mid-1]
} else {
midLeft = max(nums1[nums1Mid-1], nums2[nums2Mid-1])
}
if (len(nums1)+len(nums2))&1 == 1 {
return float64(midLeft)
}
if nums1Mid == len(nums1) {
midRight = nums2[nums2Mid]
} else if nums2Mid == len(nums2) {
midRight = nums1[nums1Mid]
} else {
midRight = min(nums1[nums1Mid], nums2[nums2Mid])
}
return float64(midLeft+midRight) / 2
}
5. Longest Palindromic Substring
题目
Given a string s, return the longest palindromic substring in s.
Example 1:
Input: s = "babad"
Output: "bab"
Note: "aba" is also a valid answer.
Example 2:
Input: s = "cbbd"
Output: "bb"
Example 3:
Input: s = "a"
Output: "a"
Example 4:
Input: s = "ac"
Output: "a"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000sconsist of only digits and English letters (lower-case and/or upper-case),
题目大意
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
解题思路
-
此题非常经典,并且有多种解法。
-
解法一,动态规划。定义
dp[i][j]表示从字符串第i个字符到第j个字符这一段子串是否是回文串。由回文串的性质可以得知,回文串去掉一头一尾相同的字符以后,剩下的还是回文串。所以状态转移方程是dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j]) && ((j-i < 3) || dp[i+1][j-1]),注意特殊的情况,j - i == 1的时候,即只有 2 个字符的情况,只需要判断这 2 个字符是否相同即可。j - i == 2的时候,即只有 3 个字符的情况,只需要判断除去中心以外对称的 2 个字符是否相等。每次循环动态维护保存最长回文串即可。时间复杂度 O(n^2),空间复杂度 O(n^2)。 -
解法二,中心扩散法。动态规划的方法中,我们将任意起始,终止范围内的字符串都判断了一遍。其实没有这个必要,如果不是最长回文串,无需判断并保存结果。所以动态规划的方法在空间复杂度上还有优化空间。判断回文有一个核心问题是找到“轴心”。如果长度是偶数,那么轴心是中心虚拟的,如果长度是奇数,那么轴心正好是正中心的那个字母。中心扩散法的思想是枚举每个轴心的位置。然后做两次假设,假设最长回文串是偶数,那么以虚拟中心往 2 边扩散;假设最长回文串是奇数,那么以正中心的字符往 2 边扩散。扩散的过程就是对称判断两边字符是否相等的过程。这个方法时间复杂度和动态规划是一样的,但是空间复杂度降低了。时间复杂度 O(n^2),空间复杂度 O(1)。
-
解法三,滑动窗口。这个写法其实就是中心扩散法变了一个写法。中心扩散是依次枚举每一个轴心。滑动窗口的方法稍微优化了一点,有些轴心两边字符不相等,下次就不会枚举这些不可能形成回文子串的轴心了。不过这点优化并没有优化时间复杂度,时间复杂度 O(n^2),空间复杂度 O(1)。
-
解法四,马拉车算法。这个算法是本题的最优解,也是最复杂的解法。时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)。中心扩散法有 2 处有重复判断,第一处是每次都往两边扩散,不同中心扩散多次,实际上有很多重复判断的字符,能否不重复判断?第二处,中心能否跳跃选择,不是每次都枚举,是否可以利用前一次的信息,跳跃选择下一次的中心?马拉车算法针对重复判断的问题做了优化,增加了一个辅助数组,将时间复杂度从 O(n^2) 优化到了 O(n),空间换了时间,空间复杂度增加到 O(n)。
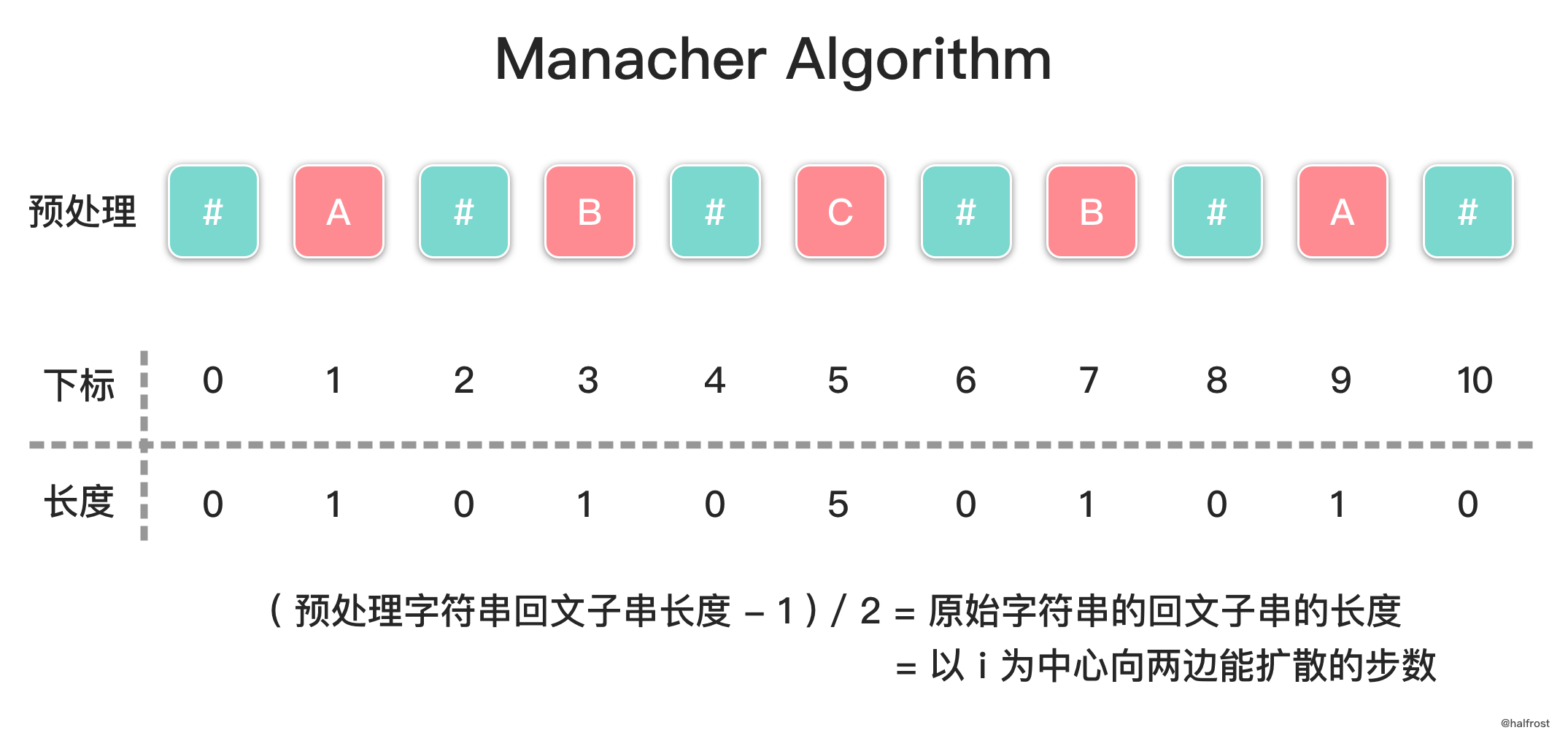
-
首先是预处理,向字符串的头尾以及每两个字符中间添加一个特殊字符
#,比如字符串aaba处理后会变成#a#a#b#a#。那么原先长度为偶数的回文字符串aa会变成长度为奇数的回文字符串#a#a#,而长度为奇数的回文字符串aba会变成长度仍然为奇数的回文字符串#a#b#a#,经过预处理以后,都会变成长度为奇数的字符串。**注意这里的特殊字符不需要是没有出现过的字母,也可以使用任何一个字符来作为这个特殊字符。**这是因为,当我们只考虑长度为奇数的回文字符串时,每次我们比较的两个字符奇偶性一定是相同的,所以原来字符串中的字符不会与插入的特殊字符互相比较,不会因此产生问题。**预处理以后,以某个中心扩散的步数和实际字符串长度是相等的。**因为半径里面包含了插入的特殊字符,又由于左右对称的性质,所以扩散半径就等于原来回文子串的长度。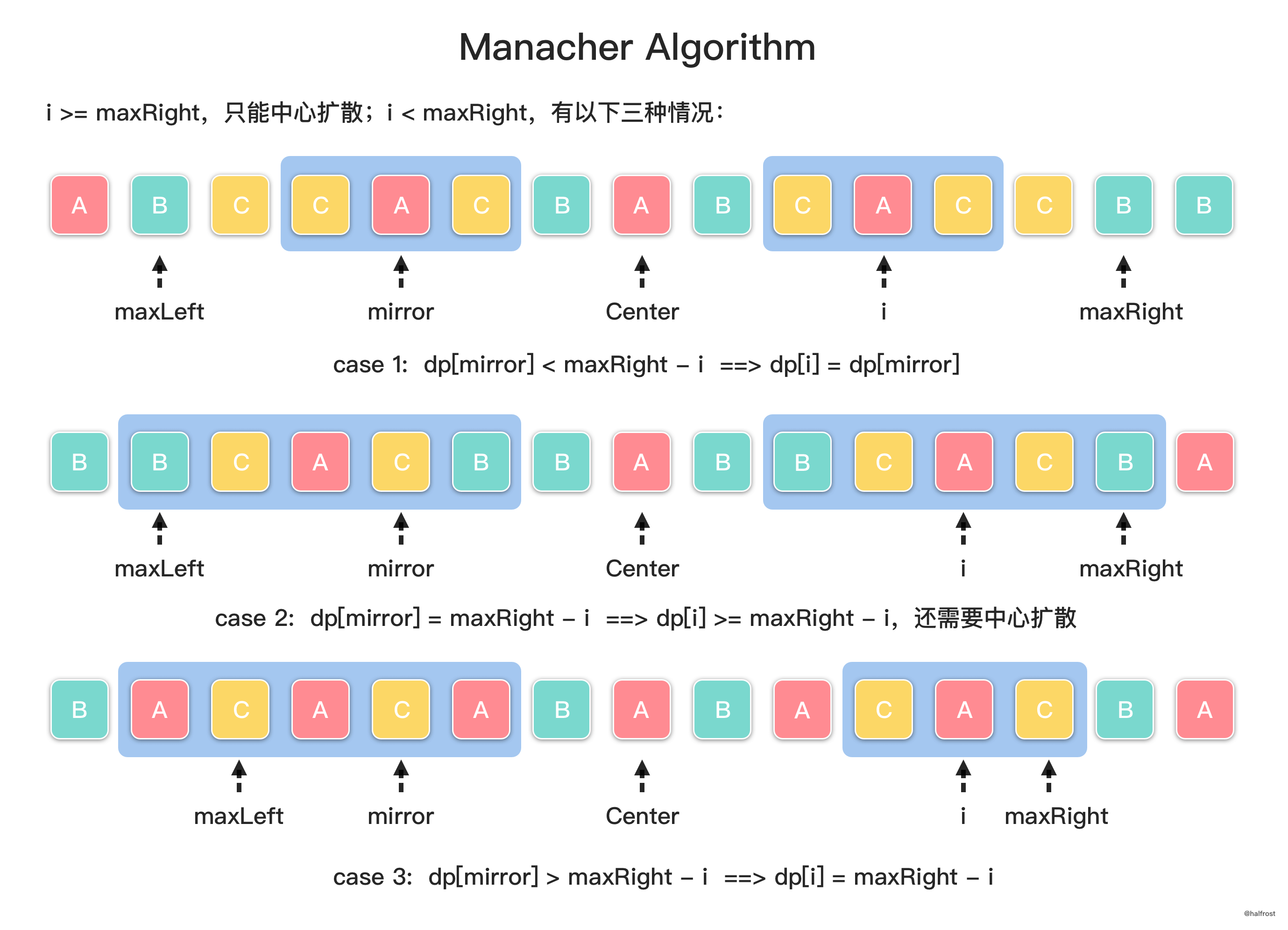
-
核心部分是如何通过左边已经扫描过的数据推出右边下一次要扩散的中心。这里定义下一次要扩散的中心下标是
i。如果i比maxRight要大,只能继续中心扩散。如果i比maxRight小,这时又分为 3 种情况。三种情况见上图。将上述 3 种情况总结起来,就是 :dp[i] = min(maxRight-i, dp[2*center-i]),其中,mirror相对于center是和i中心对称的,所以它的下标可以计算出来是2*center-i。更新完dp[i]以后,就要进行中心扩散了。中心扩散以后动态维护最长回文串并相应的更新center,maxRight,并且记录下原始字符串的起始位置begin和maxLen。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 Manacher's algorithm,时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)
func longestPalindrome(s string) string {
if len(s) < 2 {
return s
}
newS := make([]rune, 0)
newS = append(newS, '#')
for _, c := range s {
newS = append(newS, c)
newS = append(newS, '#')
}
// dp[i]: 以预处理字符串下标 i 为中心的回文半径(奇数长度时不包括中心)
// maxRight: 通过中心扩散的方式能够扩散的最右边的下标
// center: 与 maxRight 对应的中心字符的下标
// maxLen: 记录最长回文串的半径
// begin: 记录最长回文串在起始串 s 中的起始下标
dp, maxRight, center, maxLen, begin := make([]int, len(newS)), 0, 0, 1, 0
for i := 0; i < len(newS); i++ {
if i < maxRight {
// 这一行代码是 Manacher 算法的关键所在
dp[i] = min(maxRight-i, dp[2*center-i])
}
// 中心扩散法更新 dp[i]
left, right := i-(1+dp[i]), i+(1+dp[i])
for left >= 0 && right < len(newS) && newS[left] == newS[right] {
dp[i]++
left--
right++
}
// 更新 maxRight,它是遍历过的 i 的 i + dp[i] 的最大者
if i+dp[i] > maxRight {
maxRight = i + dp[i]
center = i
}
// 记录最长回文子串的长度和相应它在原始字符串中的起点
if dp[i] > maxLen {
maxLen = dp[i]
begin = (i - maxLen) / 2 // 这里要除以 2 因为有我们插入的辅助字符 #
}
}
return s[begin : begin+maxLen]
}
func min(x, y int) int {
if x < y {
return x
}
return y
}
// 解法二 滑动窗口,时间复杂度 O(n^2),空间复杂度 O(1)
func longestPalindrome1(s string) string {
if len(s) == 0 {
return ""
}
left, right, pl, pr := 0, -1, 0, 0
for left < len(s) {
// 移动到相同字母的最右边(如果有相同字母)
for right+1 < len(s) && s[left] == s[right+1] {
right++
}
// 找到回文的边界
for left-1 >= 0 && right+1 < len(s) && s[left-1] == s[right+1] {
left--
right++
}
if right-left > pr-pl {
pl, pr = left, right
}
// 重置到下一次寻找回文的中心
left = (left+right)/2 + 1
right = left
}
return s[pl : pr+1]
}
// 解法三 中心扩散法,时间复杂度 O(n^2),空间复杂度 O(1)
func longestPalindrome2(s string) string {
res := ""
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
res = maxPalindrome(s, i, i, res)
res = maxPalindrome(s, i, i+1, res)
}
return res
}
func maxPalindrome(s string, i, j int, res string) string {
sub := ""
for i >= 0 && j < len(s) && s[i] == s[j] {
sub = s[i : j+1]
i--
j++
}
if len(res) < len(sub) {
return sub
}
return res
}
// 解法四 DP,时间复杂度 O(n^2),空间复杂度 O(n^2)
func longestPalindrome3(s string) string {
res, dp := "", make([][]bool, len(s))
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
dp[i] = make([]bool, len(s))
}
for i := len(s) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for j := i; j < len(s); j++ {
dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j]) && ((j-i < 3) || dp[i+1][j-1])
if dp[i][j] && (res == "" || j-i+1 > len(res)) {
res = s[i : j+1]
}
}
}
return res
}
6. ZigZag Conversion
题目
The string "PAYPALISHIRING" is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows like this: (you may want to display this pattern in a fixed font for better legibility)
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
And then read line by line: "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
Write the code that will take a string and make this conversion given a number of rows:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
Example 1:
Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3
Output: "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
Example 2:
Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4
Output: "PINALSIGYAHRPI"
Explanation:
P I N
A L S I G
Y A H R
P I
Example 3:
Input: s = "A", numRows = 1
Output: "A"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000sconsists of English letters (lower-case and upper-case),','and'.'.1 <= numRows <= 1000
题目大意
将一个给定字符串 s 根据给定的行数 numRows ,以从上往下、从左到右进行 Z 字形排列。
比如输入字符串为 "PAYPALISHIRING" 行数为 3 时,排列如下:
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
之后,你的输出需要从左往右逐行读取,产生出一个新的字符串,比如:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"。
请你实现这个将字符串进行指定行数变换的函数:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
解题思路
- 这一题没有什么算法思想,考察的是对程序控制的能力。用 2 个变量保存方向,当垂直输出的行数达到了规定的目标行数以后,需要从下往上转折到第一行,循环中控制好方向ji
代码
package leetcode
func convert(s string, numRows int) string {
matrix, down, up := make([][]byte, numRows, numRows), 0, numRows-2
for i := 0; i != len(s); {
if down != numRows {
matrix[down] = append(matrix[down], byte(s[i]))
down++
i++
} else if up > 0 {
matrix[up] = append(matrix[up], byte(s[i]))
up--
i++
} else {
up = numRows - 2
down = 0
}
}
solution := make([]byte, 0, len(s))
for _, row := range matrix {
for _, item := range row {
solution = append(solution, item)
}
}
return string(solution)
}
7. Reverse Integer
题目
Given a 32-bit signed integer, reverse digits of an integer.
Example 1:
Input: 123
Output: 321
Example 2:
Input: -123
Output: -321
Example 3:
Input: 120
Output: 21
Note: Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 0 when the reversed integer overflows.
题目大意
给出一个 32 位的有符号整数,你需要将这个整数中每位上的数字进行反转。注意:假设我们的环境只能存储得下 32 位的有符号整数,则其数值范围为 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]。请根据这个假设,如果反转后整数溢出那么就返回 0。
解题思路
- 这一题是简单题,要求反转 10 进制数。类似的题目有第 190 题。
- 这一题只需要注意一点,反转以后的数字要求在 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]范围内,超过这个范围的数字都要输出 0 。
代码
package leetcode
func reverse7(x int) int {
tmp := 0
for x != 0 {
tmp = tmp*10 + x%10
x = x / 10
}
if tmp > 1<<31-1 || tmp < -(1<<31) {
return 0
}
return tmp
}
8. String to Integer (atoi)
题目
Implement the myAtoi(string s) function, which converts a string to a 32-bit signed integer (similar to C/C++'s atoi function).
The algorithm for myAtoi(string s) is as follows:
- Read in and ignore any leading whitespace.
- Check if the next character (if not already at the end of the string) is
'-'or'+'. Read this character in if it is either. This determines if the final result is negative or positive respectively. Assume the result is positive if neither is present. - Read in next the characters until the next non-digit charcter or the end of the input is reached. The rest of the string is ignored.
- Convert these digits into an integer (i.e.
"123" -> 123,"0032" -> 32). If no digits were read, then the integer is0. Change the sign as necessary (from step 2). - If the integer is out of the 32-bit signed integer range
[-231, 231 - 1], then clamp the integer so that it remains in the range. Specifically, integers less than231should be clamped to231, and integers greater than231 - 1should be clamped to231 - 1. - Return the integer as the final result.
Note:
- Only the space character
' 'is considered a whitespace character. - Do not ignore any characters other than the leading whitespace or the rest of the string after the digits.
Example 1:
Input: s = "42"
Output: 42
Explanation: The underlined characters are what is read in, the caret is the current reader position.
Step 1: "42" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
^
Step 2: "42" (no characters read because there is neither a '-' nor '+')
^
Step 3: "42" ("42" is read in)
^
The parsed integer is 42.
Since 42 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is 42.
Example 2:
Input: s = " -42"
Output: -42
Explanation:
Step 1: " -42" (leading whitespace is read and ignored)
^
Step 2: " -42" ('-' is read, so the result should be negative)
^
Step 3: " -42" ("42" is read in)
^
The parsed integer is -42.
Since -42 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is -42.
Example 3:
Input: s = "4193 with words"
Output: 4193
Explanation:
Step 1: "4193 with words" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
^
Step 2: "4193 with words" (no characters read because there is neither a '-' nor '+')
^
Step 3: "4193 with words" ("4193" is read in; reading stops because the next character is a non-digit)
^
The parsed integer is 4193.
Since 4193 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is 4193.
Example 4:
Input: s = "words and 987"
Output: 0
Explanation:
Step 1: "words and 987" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
^
Step 2: "words and 987" (no characters read because there is neither a '-' nor '+')
^
Step 3: "words and 987" (reading stops immediately because there is a non-digit 'w')
^
The parsed integer is 0 because no digits were read.
Since 0 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is 0.
Example 5:
Input: s = "-91283472332"
Output: -2147483648
Explanation:
Step 1: "-91283472332" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
^
Step 2: "-91283472332" ('-' is read, so the result should be negative)
^
Step 3: "-91283472332" ("91283472332" is read in)
^
The parsed integer is -91283472332.
Since -91283472332 is less than the lower bound of the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is clamped to -231 = -2147483648.
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 200sconsists of English letters (lower-case and upper-case), digits (0-9),' ','+'
题目大意
请你来实现一个 myAtoi(string s) 函数,使其能将字符串转换成一个 32 位有符号整数(类似 C/C++ 中的 atoi 函数)。
函数 myAtoi(string s) 的算法如下:
- 读入字符串并丢弃无用的前导空格
- 检查下一个字符(假设还未到字符末尾)为正还是负号,读取该字符(如果有)。 确定最终结果是负数还是正数。 如果两者都不存在,则假定结果为正。
- 读入下一个字符,直到到达下一个非数字字符或到达输入的结尾。字符串的其余部分将被忽略。
- 将前面步骤读入的这些数字转换为整数(即,“123” -> 123, “0032” -> 32)。如果没有读入数字,则整数为 0 。必要时更改符号(从步骤 2 开始)。
- 如果整数数超过 32 位有符号整数范围 [−231, 231 − 1] ,需要截断这个整数,使其保持在这个范围内。具体来说,小于 −231 的整数应该被固定为 −231 ,大于 231 − 1 的整数应该被固定为 231 − 1 。
- 返回整数作为最终结果。
注意:
- 本题中的空白字符只包括空格字符 ' ' 。
- 除前导空格或数字后的其余字符串外,请勿忽略 任何其他字符。
解题思路
- 这题是简单题。题目要求实现类似
C++中atoi函数的功能。这个函数功能是将字符串类型的数字转成int类型数字。先去除字符串中的前导空格,并判断记录数字的符号。数字需要去掉前导0。最后将数字转换成数字类型,判断是否超过int类型的上限[-2^31, 2^31 - 1],如果超过上限,需要输出边界,即-2^31,或者2^31 - 1。
代码
package leetcode
func myAtoi(s string) int {
maxInt, signAllowed, whitespaceAllowed, sign, digits := int64(2<<30), true, true, 1, []int{}
for _, c := range s {
if c == ' ' && whitespaceAllowed {
continue
}
if signAllowed {
if c == '+' {
signAllowed = false
whitespaceAllowed = false
continue
} else if c == '-' {
sign = -1
signAllowed = false
whitespaceAllowed = false
continue
}
}
if c < '0' || c > '9' {
break
}
whitespaceAllowed, signAllowed = false, false
digits = append(digits, int(c-48))
}
var num, place int64
place, num = 1, 0
lastLeading0Index := -1
for i, d := range digits {
if d == 0 {
lastLeading0Index = i
} else {
break
}
}
if lastLeading0Index > -1 {
digits = digits[lastLeading0Index+1:]
}
var rtnMax int64
if sign > 0 {
rtnMax = maxInt - 1
} else {
rtnMax = maxInt
}
digitsCount := len(digits)
for i := digitsCount - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
num += int64(digits[i]) * place
place *= 10
if digitsCount-i > 10 || num > rtnMax {
return int(int64(sign) * rtnMax)
}
}
num *= int64(sign)
return int(num)
}
9. Palindrome Number
题目
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. An integer is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
Example 1:
Input: 121
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: -121
Output: false
Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
Example 3:
Input: 10
Output: false
Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
Follow up:
Coud you solve it without converting the integer to a string?
题目大意
判断一个整数是否是回文数。回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
解题思路
- 判断一个整数是不是回文数。
- 简单题。注意会有负数的情况,负数,个位数,10 都不是回文数。其他的整数再按照回文的规则判断。
代码
package leetcode
import "strconv"
// 解法一
func isPalindrome(x int) bool {
if x < 0 {
return false
}
if x == 0 {
return true
}
if x%10 == 0 {
return false
}
arr := make([]int, 0, 32)
for x > 0 {
arr = append(arr, x%10)
x = x / 10
}
sz := len(arr)
for i, j := 0, sz-1; i <= j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
if arr[i] != arr[j] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// 解法二 数字转字符串
func isPalindrome1(x int) bool {
if x < 0 {
return false
}
if x < 10 {
return true
}
s := strconv.Itoa(x)
length := len(s)
for i := 0; i <= length/2; i++ {
if s[i] != s[length-1-i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
11. Container With Most Water
题目
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, …, an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
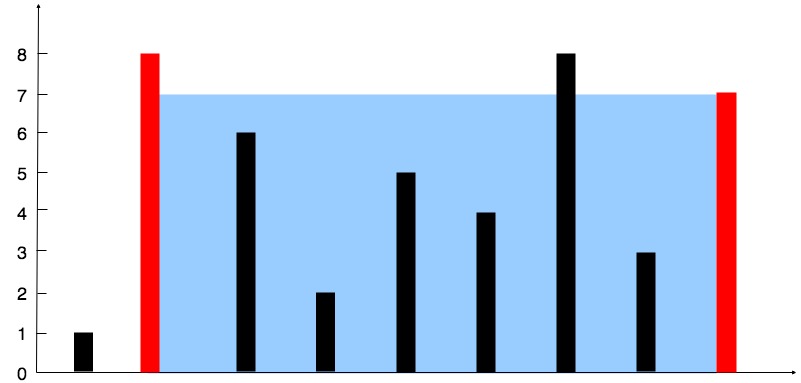
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 1:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
题目大意
给出一个非负整数数组 a1,a2,a3,…… an,每个整数标识一个竖立在坐标轴 x 位置的一堵高度为 ai 的墙,选择两堵墙,和 x 轴构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
解题思路
这一题也是对撞指针的思路。首尾分别 2 个指针,每次移动以后都分别判断长宽的乘积是否最大。
代码
package leetcode
func maxArea(height []int) int {
max, start, end := 0, 0, len(height)-1
for start < end {
width := end - start
high := 0
if height[start] < height[end] {
high = height[start]
start++
} else {
high = height[end]
end--
}
temp := width * high
if temp > max {
max = temp
}
}
return max
}
12. Integer to Roman
题目
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
For example, 2 is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one’s added together. 12 is written as XII, which is simply X + II. The number 27 is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
Ican be placed beforeV(5) andX(10) to make 4 and 9.Xcan be placed beforeL(50) andC(100) to make 40 and 90.Ccan be placed beforeD(500) andM(1000) to make 400 and 900.
Given an integer, convert it to a roman numeral.
Example 1:
Input: num = 3
Output: "III"
Example 2:
Input: num = 4
Output: "IV"
Example 3:
Input: num = 9
Output: "IX"
Example 4:
Input: num = 58
Output: "LVIII"
Explanation: L = 50, V = 5, III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: num = 1994
Output: "MCMXCIV"
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
Constraints:
1 <= num <= 3999
题目大意
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。但也存在特例,例如 4 不写做 IIII,而是 IV。数字 1 在数字 5 的左边,所表示的数等于大数 5 减小数 1 得到的数值 4 。同样地,数字 9 表示为 IX。这个特殊的规则只适用于以下六种情况:
- I 可以放在 V (5) 和 X (10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。
- X 可以放在 L (50) 和 C (100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。
- C 可以放在 D (500) 和 M (1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
给定一个整数,将其转为罗马数字。输入确保在 1 到 3999 的范围内。
解题思路
- 依照题意,优先选择大的数字,解题思路采用贪心算法。将 1-3999 范围内的罗马数字从大到小放在数组中,从头选择到尾,即可把整数转成罗马数字。
代码
package leetcode
func intToRoman(num int) string {
values := []int{1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1}
symbols := []string{"M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"}
res, i := "", 0
for num != 0 {
for values[i] > num {
i++
}
num -= values[i]
res += symbols[i]
}
return res
}
13. Roman to Integer
题目
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
For example, two is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one’s added together. Twelve is written as, XII, which is simply X + II. The number twenty seven is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
Ican be placed beforeV(5) andX(10) to make 4 and 9.Xcan be placed beforeL(50) andC(100) to make 40 and 90.Ccan be placed beforeD(500) andM(1000) to make 400 and 900.
Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
Example 1:
Input: "III"
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: "IV"
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: "IX"
Output: 9
Example 4:
Input: "LVIII"
Output: 58
Explanation: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: "MCMXCIV"
Output: 1994
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
题目大意
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。
字符 数值
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
例如, 罗马数字 2 写做 II ,即为两个并列的 1。12 写做 XII ,即为 X + II 。 27 写做 XXVII, 即为 XX + V + II 。
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。但也存在特例,例如 4 不写做 IIII,而是 IV。数字 1 在数字 5 的左边,所表示的数等于大数 5 减小数 1 得到的数值 4 。同样地,数字 9 表示为 IX。这个特殊的规则只适用于以下六种情况:
- I 可以放在 V (5) 和 X (10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。
- X 可以放在 L (50) 和 C (100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。
- C 可以放在 D (500) 和 M (1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
给定一个罗马数字,将其转换成整数。输入确保在 1 到 3999 的范围内。
解题思路
- 给定一个罗马数字,将其转换成整数。输入确保在 1 到 3999 的范围内。
- 简单题。按照题目中罗马数字的字符数值,计算出对应罗马数字的十进制数即可。
代码
package leetcode
var roman = map[string]int{
"I": 1,
"V": 5,
"X": 10,
"L": 50,
"C": 100,
"D": 500,
"M": 1000,
}
func romanToInt(s string) int {
if s == "" {
return 0
}
num, lastint, total := 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
char := s[len(s)-(i+1) : len(s)-i]
num = roman[char]
if num < lastint {
total = total - num
} else {
total = total + num
}
lastint = num
}
return total
}
14. Longest Common Prefix
题目
Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string “”.
Example 1:
Input: strs = ["flower","flow","flight"]
Output: "fl"
Example 2:
Input: strs = ["dog","racecar","car"]
Output: ""
Explanation: There is no common prefix among the input strings.
Constraints:
- 1 <= strs.length <= 200
- 0 <= strs[i].length <= 200
- strs[i] consists of only lower-case English letters.
题目大意
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 “"。
解题思路
- 对 strs 按照字符串长度进行升序排序,求出 strs 中长度最小字符串的长度 minLen
- 逐个比较长度最小字符串与其它字符串中的字符,如果不相等就返回 commonPrefix,否则就把该字符加入 commonPrefix
代码
package leetcode
func longestCommonPrefix(strs []string) string {
prefix := strs[0]
for i := 1; i < len(strs); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(prefix); j++ {
if len(strs[i]) <= j || strs[i][j] != prefix[j] {
prefix = prefix[0:j]
break
}
}
}
return prefix
}
15. 3Sum
题目
Given an array nums of n integers, are there elements a, b, c in nums such that a + b + c = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
Note:
The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example:
Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
A solution set is:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
题目大意
给定一个数组,要求在这个数组中找出 3 个数之和为 0 的所有组合。
解题思路
用 map 提前计算好任意 2 个数字之和,保存起来,可以将时间复杂度降到 O(n^2)。这一题比较麻烦的一点在于,最后输出解的时候,要求输出不重复的解。数组中同一个数字可能出现多次,同一个数字也可能使用多次,但是最后输出解的时候,不能重复。例如 [-1,-1,2] 和 [2, -1, -1]、[-1, 2, -1] 这 3 个解是重复的,即使 -1 可能出现 100 次,每次使用的 -1 的数组下标都是不同的。
这里就需要去重和排序了。map 记录每个数字出现的次数,然后对 map 的 key 数组进行排序,最后在这个排序以后的数组里面扫,找到另外 2 个数字能和自己组成 0 的组合。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"sort"
)
// 解法一 最优解,双指针 + 排序
func threeSum(nums []int) [][]int {
sort.Ints(nums)
result, start, end, index, addNum, length := make([][]int, 0), 0, 0, 0, 0, len(nums)
for index = 1; index < length-1; index++ {
start, end = 0, length-1
if index > 1 && nums[index] == nums[index-1] {
start = index - 1
}
for start < index && end > index {
if start > 0 && nums[start] == nums[start-1] {
start++
continue
}
if end < length-1 && nums[end] == nums[end+1] {
end--
continue
}
addNum = nums[start] + nums[end] + nums[index]
if addNum == 0 {
result = append(result, []int{nums[start], nums[index], nums[end]})
start++
end--
} else if addNum > 0 {
end--
} else {
start++
}
}
}
return result
}
// 解法二
func threeSum1(nums []int) [][]int {
res := [][]int{}
counter := map[int]int{}
for _, value := range nums {
counter[value]++
}
uniqNums := []int{}
for key := range counter {
uniqNums = append(uniqNums, key)
}
sort.Ints(uniqNums)
for i := 0; i < len(uniqNums); i++ {
if (uniqNums[i]*3 == 0) && counter[uniqNums[i]] >= 3 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i]})
}
for j := i + 1; j < len(uniqNums); j++ {
if (uniqNums[i]*2+uniqNums[j] == 0) && counter[uniqNums[i]] > 1 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j]})
}
if (uniqNums[j]*2+uniqNums[i] == 0) && counter[uniqNums[j]] > 1 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[j]})
}
c := 0 - uniqNums[i] - uniqNums[j]
if c > uniqNums[j] && counter[c] > 0 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], c})
}
}
}
return res
}
16. 3Sum Closest
题目
Given an array nums of n integers and an integer target, find three integers in nums such that the sum is closest to target. Return the sum of the three integers. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
Example:
Given array nums = [-1, 2, 1, -4], and target = 1.
The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
题目大意
给定一个数组,要求在这个数组中找出 3 个数之和离 target 最近。
解题思路
这一题看似和第 15 题和第 18 题很像,都是求 3 或者 4 个数之和的问题,但是这一题的做法和 15,18 题完全不同。
这一题的解法是用两个指针夹逼的方法。先对数组进行排序,i 从头开始往后面扫。这里同样需要注意数组中存在多个重复数字的问题。具体处理方法很多,可以用 map 计数去重。这里笔者简单的处理,i 在循环的时候和前一个数进行比较,如果相等,i 继续往后移,直到移到下一个和前一个数字不同的位置。j,k 两个指针开始一前一后夹逼。j 为 i 的下一个数字,k 为数组最后一个数字,由于经过排序,所以 k 的数字最大。j 往后移动,k 往前移动,逐渐夹逼出最接近 target 的值。
这道题还可以用暴力解法,三层循环找到距离 target 最近的组合。具体见代码。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"math"
"sort"
)
// 解法一 O(n^2)
func threeSumClosest(nums []int, target int) int {
n, res, diff := len(nums), 0, math.MaxInt32
if n > 2 {
sort.Ints(nums)
for i := 0; i < n-2; i++ {
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] {
continue
}
for j, k := i+1, n-1; j < k; {
sum := nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]
if abs(sum-target) < diff {
res, diff = sum, abs(sum-target)
}
if sum == target {
return res
} else if sum > target {
k--
} else {
j++
}
}
}
}
return res
}
// 解法二 暴力解法 O(n^3)
func threeSumClosest1(nums []int, target int) int {
res, difference := 0, math.MaxInt16
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
for j := i + 1; j < len(nums); j++ {
for k := j + 1; k < len(nums); k++ {
if abs(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]-target) < difference {
difference = abs(nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] - target)
res = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]
}
}
}
}
return res
}
func abs(a int) int {
if a > 0 {
return a
}
return -a
}
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
题目
Given a string containing digits from 2-9 inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent.
A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.

Example:
Input: "23"
Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
Note:
Although the above answer is in lexicographical order, your answer could be in any order you want.
题目大意
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
解题思路
- DFS 递归深搜即可
代码
package leetcode
var (
letterMap = []string{
" ", //0
"", //1
"abc", //2
"def", //3
"ghi", //4
"jkl", //5
"mno", //6
"pqrs", //7
"tuv", //8
"wxyz", //9
}
res = []string{}
final = 0
)
// 解法一 DFS
func letterCombinations(digits string) []string {
if digits == "" {
return []string{}
}
res = []string{}
findCombination(&digits, 0, "")
return res
}
func findCombination(digits *string, index int, s string) {
if index == len(*digits) {
res = append(res, s)
return
}
num := (*digits)[index]
letter := letterMap[num-'0']
for i := 0; i < len(letter); i++ {
findCombination(digits, index+1, s+string(letter[i]))
}
return
}
// 解法二 非递归
func letterCombinations_(digits string) []string {
if digits == "" {
return []string{}
}
index := digits[0] - '0'
letter := letterMap[index]
tmp := []string{}
for i := 0; i < len(letter); i++ {
if len(res) == 0 {
res = append(res, "")
}
for j := 0; j < len(res); j++ {
tmp = append(tmp, res[j]+string(letter[i]))
}
}
res = tmp
final++
letterCombinations(digits[1:])
final--
if final == 0 {
tmp = res
res = []string{}
}
return tmp
}
// 解法三 回溯(参考回溯模板,类似DFS)
var result []string
var dict = map[string][]string{
"2" : []string{"a","b","c"},
"3" : []string{"d", "e", "f"},
"4" : []string{"g", "h", "i"},
"5" : []string{"j", "k", "l"},
"6" : []string{"m", "n", "o"},
"7" : []string{"p", "q", "r", "s"},
"8" : []string{"t", "u", "v"},
"9" : []string{"w", "x", "y", "z"},
}
func letterCombinationsBT(digits string) []string {
result = []string{}
if digits == "" {
return result
}
letterFunc("", digits)
return result
}
func letterFunc(res string, digits string) {
if digits == "" {
result = append(result, res)
return
}
k := digits[0:1]
digits = digits[1:]
for i := 0; i < len(dict[k]); i++ {
res += dict[k][i]
letterFunc(res, digits)
res = res[0 : len(res)-1]
}
}
18. 4Sum
题目
Given an array nums of n integers and an integer target, are there elements a, b, c, and d in nums such that a + b + c + d = target? Find all unique quadruplets in the array which gives the sum of target.
Note:
The solution set must not contain duplicate quadruplets.
Example:
Given array nums = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2], and target = 0.
A solution set is:
[
[-1, 0, 0, 1],
[-2, -1, 1, 2],
[-2, 0, 0, 2]
]
题目大意
给定一个数组,要求在这个数组中找出 4 个数之和为 0 的所有组合。
解题思路
用 map 提前计算好任意 3 个数字之和,保存起来,可以将时间复杂度降到 O(n^3)。这一题比较麻烦的一点在于,最后输出解的时候,要求输出不重复的解。数组中同一个数字可能出现多次,同一个数字也可能使用多次,但是最后输出解的时候,不能重复。例如 [-1,1,2, -2] 和 [2, -1, -2, 1]、[-2, 2, -1, 1] 这 3 个解是重复的,即使 -1, -2 可能出现 100 次,每次使用的 -1, -2 的数组下标都是不同的。
这一题是第 15 题的升级版,思路都是完全一致的。这里就需要去重和排序了。map 记录每个数字出现的次数,然后对 map 的 key 数组进行排序,最后在这个排序以后的数组里面扫,找到另外 3 个数字能和自己组成 0 的组合。
第 15 题和第 18 题的解法一致。
代码
package leetcode
import "sort"
// 解法一 双指针
func fourSum(nums []int, target int) (quadruplets [][]int) {
sort.Ints(nums)
n := len(nums)
for i := 0; i < n-3 && nums[i]+nums[i+1]+nums[i+2]+nums[i+3] <= target; i++ {
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] || nums[i]+nums[n-3]+nums[n-2]+nums[n-1] < target {
continue
}
for j := i + 1; j < n-2 && nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[j+1]+nums[j+2] <= target; j++ {
if j > i+1 && nums[j] == nums[j-1] || nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[n-2]+nums[n-1] < target {
continue
}
for left, right := j+1, n-1; left < right; {
if sum := nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]; sum == target {
quadruplets = append(quadruplets, []int{nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]})
for left++; left < right && nums[left] == nums[left-1]; left++ {
}
for right--; left < right && nums[right] == nums[right+1]; right-- {
}
} else if sum < target {
left++
} else {
right--
}
}
}
}
return
}
// 解法二 kSum
func fourSum1(nums []int, target int) [][]int {
res, cur := make([][]int, 0), make([]int, 0)
sort.Ints(nums)
kSum(nums, 0, len(nums)-1, target, 4, cur, &res)
return res
}
func kSum(nums []int, left, right int, target int, k int, cur []int, res *[][]int) {
if right-left+1 < k || k < 2 || target < nums[left]*k || target > nums[right]*k {
return
}
if k == 2 {
// 2 sum
twoSum(nums, left, right, target, cur, res)
} else {
for i := left; i < len(nums); i++ {
if i == left || (i > left && nums[i-1] != nums[i]) {
next := make([]int, len(cur))
copy(next, cur)
next = append(next, nums[i])
kSum(nums, i+1, len(nums)-1, target-nums[i], k-1, next, res)
}
}
}
}
func twoSum(nums []int, left, right int, target int, cur []int, res *[][]int) {
for left < right {
sum := nums[left] + nums[right]
if sum == target {
cur = append(cur, nums[left], nums[right])
temp := make([]int, len(cur))
copy(temp, cur)
*res = append(*res, temp)
// reset cur to previous state
cur = cur[:len(cur)-2]
left++
right--
for left < right && nums[left] == nums[left-1] {
left++
}
for left < right && nums[right] == nums[right+1] {
right--
}
} else if sum < target {
left++
} else {
right--
}
}
}
// 解法三
func fourSum2(nums []int, target int) [][]int {
res := [][]int{}
counter := map[int]int{}
for _, value := range nums {
counter[value]++
}
uniqNums := []int{}
for key := range counter {
uniqNums = append(uniqNums, key)
}
sort.Ints(uniqNums)
for i := 0; i < len(uniqNums); i++ {
if (uniqNums[i]*4 == target) && counter[uniqNums[i]] >= 4 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i]})
}
for j := i + 1; j < len(uniqNums); j++ {
if (uniqNums[i]*3+uniqNums[j] == target) && counter[uniqNums[i]] > 2 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j]})
}
if (uniqNums[j]*3+uniqNums[i] == target) && counter[uniqNums[j]] > 2 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[j]})
}
if (uniqNums[j]*2+uniqNums[i]*2 == target) && counter[uniqNums[j]] > 1 && counter[uniqNums[i]] > 1 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[j]})
}
for k := j + 1; k < len(uniqNums); k++ {
if (uniqNums[i]*2+uniqNums[j]+uniqNums[k] == target) && counter[uniqNums[i]] > 1 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[k]})
}
if (uniqNums[j]*2+uniqNums[i]+uniqNums[k] == target) && counter[uniqNums[j]] > 1 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[k]})
}
if (uniqNums[k]*2+uniqNums[i]+uniqNums[j] == target) && counter[uniqNums[k]] > 1 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[k], uniqNums[k]})
}
c := target - uniqNums[i] - uniqNums[j] - uniqNums[k]
if c > uniqNums[k] && counter[c] > 0 {
res = append(res, []int{uniqNums[i], uniqNums[j], uniqNums[k], c})
}
}
}
}
return res
}
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
题目
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
Example 1:
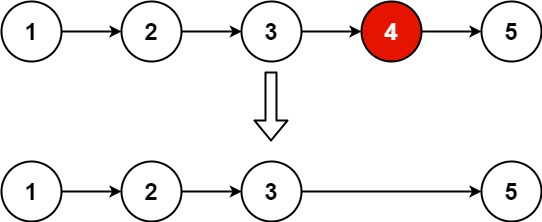
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
题目大意
删除链表中倒数第 n 个结点。
解题思路
这道题比较简单,先循环一次拿到链表的总长度,然后循环到要删除的结点的前一个结点开始删除操作。需要注意的一个特例是,有可能要删除头结点,要单独处理。
这道题有一种特别简单的解法。设置 2 个指针,一个指针距离前一个指针 n 个距离。同时移动 2 个指针,2 个指针都移动相同的距离。当一个指针移动到了终点,那么前一个指针就是倒数第 n 个节点了。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// ListNode define
type ListNode = structures.ListNode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
// 解法一
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummyHead := &ListNode{Next: head}
preSlow, slow, fast := dummyHead, head, head
for fast != nil {
if n <= 0 {
preSlow = slow
slow = slow.Next
}
n--
fast = fast.Next
}
preSlow.Next = slow.Next
return dummyHead.Next
}
// 解法二
func removeNthFromEnd1(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if n <= 0 {
return head
}
current := head
len := 0
for current != nil {
len++
current = current.Next
}
if n > len {
return head
}
if n == len {
current := head
head = head.Next
current.Next = nil
return head
}
current = head
i := 0
for current != nil {
if i == len-n-1 {
deleteNode := current.Next
current.Next = current.Next.Next
deleteNode.Next = nil
break
}
i++
current = current.Next
}
return head
}
20. Valid Parentheses
题目
Given a string containing just the characters ‘(’, ‘)’, ‘{’, ‘}’, ‘[’ and ‘]’, determine if the input string is valid.
An input string is valid if:
Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order. Note that an empty string is also considered valid.
Example 1:
Input: "()"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: "()[]{}"
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: "(]"
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: "([)]"
Output: false
Example 5:
Input: "{[]}"
Output: true
题目大意
括号匹配问题。
解题思路
遇到左括号就进栈push,遇到右括号并且栈顶为与之对应的左括号,就把栈顶元素出栈。最后看栈里面还有没有其他元素,如果为空,即匹配。
需要注意,空字符串是满足括号匹配的,即输出 true。
代码
package leetcode
func isValid(s string) bool {
// 空字符串直接返回 true
if len(s) == 0 {
return true
}
stack := make([]rune, 0)
for _, v := range s {
if (v == '[') || (v == '(') || (v == '{') {
stack = append(stack, v)
} else if ((v == ']') && len(stack) > 0 && stack[len(stack)-1] == '[') ||
((v == ')') && len(stack) > 0 && stack[len(stack)-1] == '(') ||
((v == '}') && len(stack) > 0 && stack[len(stack)-1] == '{') {
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
} else {
return false
}
}
return len(stack) == 0
}
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
题目
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Example:
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
题目大意
合并 2 个有序链表
解题思路
按照题意做即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func mergeTwoLists(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
if l1 == nil {
return l2
}
if l2 == nil {
return l1
}
if l1.Val < l2.Val {
l1.Next = mergeTwoLists(l1.Next, l2)
return l1
}
l2.Next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.Next)
return l2
}
22. Generate Parentheses
题目
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
For example, given n = 3, a solution set is:
[
"((()))",
"(()())",
"(())()",
"()(())",
"()()()"
]
题目大意
给出 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。
解题思路
- 这道题乍一看需要判断括号是否匹配的问题,如果真的判断了,那时间复杂度就到 O(n * 2^n)了,虽然也可以 AC,但是时间复杂度巨高。
- 这道题实际上不需要判断括号是否匹配的问题。因为在 DFS 回溯的过程中,会让
(和)成对的匹配上的。
代码
package leetcode
func generateParenthesis(n int) []string {
if n == 0 {
return []string{}
}
res := []string{}
findGenerateParenthesis(n, n, "", &res)
return res
}
func findGenerateParenthesis(lindex, rindex int, str string, res *[]string) {
if lindex == 0 && rindex == 0 {
*res = append(*res, str)
return
}
if lindex > 0 {
findGenerateParenthesis(lindex-1, rindex, str+"(", res)
}
if rindex > 0 && lindex < rindex {
findGenerateParenthesis(lindex, rindex-1, str+")", res)
}
}
23. Merge k Sorted Lists
题目
Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
Example:
Input:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
题目大意
合并 K 个有序链表
解题思路
借助分治的思想,把 K 个有序链表两两合并即可。相当于是第 21 题的加强版。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func mergeKLists(lists []*ListNode) *ListNode {
length := len(lists)
if length < 1 {
return nil
}
if length == 1 {
return lists[0]
}
num := length / 2
left := mergeKLists(lists[:num])
right := mergeKLists(lists[num:])
return mergeTwoLists1(left, right)
}
func mergeTwoLists1(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
if l1 == nil {
return l2
}
if l2 == nil {
return l1
}
if l1.Val < l2.Val {
l1.Next = mergeTwoLists1(l1.Next, l2)
return l1
}
l2.Next = mergeTwoLists1(l1, l2.Next)
return l2
}
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
题目
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
题目大意
两两相邻的元素,翻转链表
解题思路
按照题意做即可。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// ListNode define
type ListNode = structures.ListNode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{Next: head}
for pt := dummy; pt != nil && pt.Next != nil && pt.Next.Next != nil; {
pt, pt.Next, pt.Next.Next, pt.Next.Next.Next = pt.Next, pt.Next.Next, pt.Next.Next.Next, pt.Next
}
return dummy.Next
}
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
题目
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
Example:
Given this linked list: 1->2->3->4->5
For k = 2, you should return: 2->1->4->3->5
For k = 3, you should return: 3->2->1->4->5
Note:
- Only constant extra memory is allowed.
- You may not alter the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
题目大意
按照每 K 个元素翻转的方式翻转链表。如果不满足 K 个元素的就不翻转。
解题思路
这一题是 problem 24 的加强版,problem 24 是两两相邻的元素,翻转链表。而 problem 25 要求的是 k 个相邻的元素,翻转链表,problem 相当于是 k = 2 的特殊情况。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {
node := head
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
if node == nil {
return head
}
node = node.Next
}
newHead := reverse(head, node)
head.Next = reverseKGroup(node, k)
return newHead
}
func reverse(first *ListNode, last *ListNode) *ListNode {
prev := last
for first != last {
tmp := first.Next
first.Next = prev
prev = first
first = tmp
}
return prev
}
26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
题目
Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appear only once and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1,1,2],
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
Example 2:
Given nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums being modified to 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
Clarification:
Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
Note that the input array is passed in by reference, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
Internally you can think of this:
// nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
// any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
// using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
题目大意
给定一个有序数组 nums,对数组中的元素进行去重,使得原数组中的每个元素只有一个。最后返回去重以后数组的长度值。
解题思路
这道题和第 27 题很像。这道题和第 283 题,第 27 题基本一致,283 题是删除 0,27 题是删除指定元素,这一题是删除重复元素,实质是一样的。
这里数组的删除并不是真的删除,只是将删除的元素移动到数组后面的空间内,然后返回数组实际剩余的元素个数,OJ 最终判断题目的时候会读取数组剩余个数的元素进行输出。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一
func removeDuplicates(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
last, finder := 0, 0
for last < len(nums)-1 {
for nums[finder] == nums[last] {
finder++
if finder == len(nums) {
return last + 1
}
}
nums[last+1] = nums[finder]
last++
}
return last + 1
}
// 解法二
func removeDuplicates1(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
length := len(nums)
lastNum := nums[length-1]
i := 0
for i = 0; i < length-1; i++ {
if nums[i] == lastNum {
break
}
if nums[i+1] == nums[i] {
removeElement1(nums, i+1, nums[i])
// fmt.Printf("此时 num = %v length = %v\n", nums, length)
}
}
return i + 1
}
func removeElement1(nums []int, start, val int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
j := start
for i := start; i < len(nums); i++ {
if nums[i] != val {
if i != j {
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
j++
} else {
j++
}
}
}
return j
}
27. Remove Element
题目
Given an array nums and a value val, remove all instances of that value in-place and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn’t matter what you leave beyond the new length.
Example 1:
Given nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
Example 2:
Given nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 1, 3, 0, and 4.
Note that the order of those five elements can be arbitrary.
It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
Clarification:
Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
Note that the input array is passed in by reference, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
Internally you can think of this:
// nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
// any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
// using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
题目大意
给定一个数组 nums 和一个数值 val,将数组中所有等于 val 的元素删除,并返回剩余的元素个数。
解题思路
这道题和第 283 题很像。这道题和第 283 题基本一致,283 题是删除 0,这一题是给定的一个 val,实质是一样的。
这里数组的删除并不是真的删除,只是将删除的元素移动到数组后面的空间内,然后返回数组实际剩余的元素个数,OJ 最终判断题目的时候会读取数组剩余个数的元素进行输出。
代码
package leetcode
func removeElement(nums []int, val int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
j := 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
if nums[i] != val {
if i != j {
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
}
j++
}
}
return j
}
28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String
题目
Implement strStr().
Return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
Output: -1
Clarification:
What should we return when needle is an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 when needle is an empty string. This is consistent to C’s strstr() and Java’s indexOf().
题目大意
实现一个查找 substring 的函数。如果在母串中找到了子串,返回子串在母串中出现的下标,如果没有找到,返回 -1,如果子串是空串,则返回 0 。
解题思路
这一题比较简单,直接写即可。
代码
package leetcode
import "strings"
// 解法一
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
for i := 0; ; i++ {
for j := 0; ; j++ {
if j == len(needle) {
return i
}
if i+j == len(haystack) {
return -1
}
if needle[j] != haystack[i+j] {
break
}
}
}
}
// 解法二
func strStr1(haystack string, needle string) int {
return strings.Index(haystack, needle)
}
29. Divide Two Integers
题目
Given two integers dividend and divisor, divide two integers without using multiplication, division and mod operator.
Return the quotient after dividing dividend by divisor.
The integer division should truncate toward zero.
Example 1:
Input: dividend = 10, divisor = 3
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: dividend = 7, divisor = -3
Output: -2
Note:
- Both dividend and divisor will be 32-bit signed integers.
- The divisor will never be 0.
- Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 2^31 − 1 when the division result overflows.
题目大意
给定两个整数,被除数 dividend 和除数 divisor。将两数相除,要求不使用乘法、除法和 mod 运算符。返回被除数 dividend 除以除数 divisor 得到的商。
说明:
- 被除数和除数均为 32 位有符号整数。
- 除数不为 0。
- 假设我们的环境只能存储 32 位有符号整数,其数值范围是 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]。本题中,如果除法结果溢出,则返回 2^31 − 1。
解题思路
- 给出除数和被除数,要求计算除法运算以后的商。注意值的取值范围在 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1] 之中。超过范围的都按边界计算。
- 这一题可以用二分搜索来做。要求除法运算之后的商,把商作为要搜索的目标。商的取值范围是 [0, dividend],所以从 0 到被除数之间搜索。利用二分,找到(商 + 1 ) * 除数 > 被除数并且 商 * 除数 ≤ 被除数 或者 (商+1)* 除数 ≥ 被除数并且商 * 除数 < 被除数的时候,就算找到了商,其余情况继续二分即可。最后还要注意符号和题目规定的 Int32 取值范围。
- 二分的写法常写错的 3 点:
- low ≤ high (注意二分循环退出的条件是小于等于)
- mid = low + (high-low)»1 (防止溢出)
- low = mid + 1 ; high = mid - 1 (注意更新 low 和 high 的值,如果更新不对就会死循环)
代码
package leetcode
import (
"math"
)
// 解法一 递归版的二分搜索
func divide(dividend int, divisor int) int {
sign, res := -1, 0
// low, high := 0, abs(dividend)
if dividend == 0 {
return 0
}
if divisor == 1 {
return dividend
}
if dividend == math.MinInt32 && divisor == -1 {
return math.MaxInt32
}
if dividend > 0 && divisor > 0 || dividend < 0 && divisor < 0 {
sign = 1
}
if dividend > math.MaxInt32 {
dividend = math.MaxInt32
}
// 如果把递归改成非递归,可以改成下面这段代码
// for low <= high {
// quotient := low + (high-low)>>1
// if ((quotient+1)*abs(divisor) > abs(dividend) && quotient*abs(divisor) <= abs(dividend)) || ((quotient+1)*abs(divisor) >= abs(dividend) && quotient*abs(divisor) < abs(dividend)) {
// if (quotient+1)*abs(divisor) == abs(dividend) {
// res = quotient + 1
// break
// }
// res = quotient
// break
// }
// if (quotient+1)*abs(divisor) > abs(dividend) && quotient*abs(divisor) > abs(dividend) {
// high = quotient - 1
// }
// if (quotient+1)*abs(divisor) < abs(dividend) && quotient*abs(divisor) < abs(dividend) {
// low = quotient + 1
// }
// }
res = binarySearchQuotient(0, abs(dividend), abs(divisor), abs(dividend))
if res > math.MaxInt32 {
return sign * math.MaxInt32
}
if res < math.MinInt32 {
return sign * math.MinInt32
}
return sign * res
}
func binarySearchQuotient(low, high, val, dividend int) int {
quotient := low + (high-low)>>1
if ((quotient+1)*val > dividend && quotient*val <= dividend) || ((quotient+1)*val >= dividend && quotient*val < dividend) {
if (quotient+1)*val == dividend {
return quotient + 1
}
return quotient
}
if (quotient+1)*val > dividend && quotient*val > dividend {
return binarySearchQuotient(low, quotient-1, val, dividend)
}
if (quotient+1)*val < dividend && quotient*val < dividend {
return binarySearchQuotient(quotient+1, high, val, dividend)
}
return 0
}
// 解法二 非递归版的二分搜索
func divide1(divided int, divisor int) int {
if divided == math.MinInt32 && divisor == -1 {
return math.MaxInt32
}
result := 0
sign := -1
if divided > 0 && divisor > 0 || divided < 0 && divisor < 0 {
sign = 1
}
dvd, dvs := abs(divided), abs(divisor)
for dvd >= dvs {
temp := dvs
m := 1
for temp<<1 <= dvd {
temp <<= 1
m <<= 1
}
dvd -= temp
result += m
}
return sign * result
}
30. Substring with Concatenation of All Words
题目
You are given a string, s, and a list of words, words, that are all of the same length. Find all starting indices of substring(s) in s that is a concatenation of each word in words exactly once and without any intervening characters.
Example 1:
Input:
s = "barfoothefoobarman",
words = ["foo","bar"]
Output: [0,9]
Explanation: Substrings starting at index 0 and 9 are "barfoor" and "foobar" respectively.
The output order does not matter, returning [9,0] is fine too.
Example 2:
Input:
s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword",
words = ["word","good","best","word"]
Output: []
题目大意
给定一个源字符串 s,再给一个字符串数组,要求在源字符串中找到由字符串数组各种组合组成的连续串的起始下标,如果存在多个,在结果中都需要输出。
解题思路
这一题看似很难,但是有 2 个限定条件也导致这题不是特别难。1. 字符串数组里面的字符串长度都是一样的。2. 要求字符串数组中的字符串都要连续连在一起的,前后顺序可以是任意排列组合。
解题思路,先将字符串数组里面的所有字符串都存到 map 中,并累计出现的次数。然后从源字符串从头开始扫,每次判断字符串数组里面的字符串时候全部都用完了(计数是否为 0),如果全部都用完了,并且长度正好是字符串数组任意排列组合的总长度,就记录下这个组合的起始下标。如果不符合,就继续考察源字符串的下一个字符,直到扫完整个源字符串。
代码
package leetcode
func findSubstring(s string, words []string) []int {
if len(words) == 0 {
return []int{}
}
res := []int{}
counter := map[string]int{}
for _, w := range words {
counter[w]++
}
length, totalLen, tmpCounter := len(words[0]), len(words[0])*len(words), copyMap(counter)
for i, start := 0, 0; i < len(s)-length+1 && start < len(s)-length+1; i++ {
//fmt.Printf("sub = %v i = %v lenght = %v start = %v tmpCounter = %v totalLen = %v\n", s[i:i+length], i, length, start, tmpCounter, totalLen)
if tmpCounter[s[i:i+length]] > 0 {
tmpCounter[s[i:i+length]]--
//fmt.Printf("******sub = %v i = %v lenght = %v start = %v tmpCounter = %v totalLen = %v\n", s[i:i+length], i, length, start, tmpCounter, totalLen)
if checkWords(tmpCounter) && (i+length-start == totalLen) {
res = append(res, start)
continue
}
i = i + length - 1
} else {
start++
i = start - 1
tmpCounter = copyMap(counter)
}
}
return res
}
func checkWords(s map[string]int) bool {
flag := true
for _, v := range s {
if v > 0 {
flag = false
break
}
}
return flag
}
func copyMap(s map[string]int) map[string]int {
c := map[string]int{}
for k, v := range s {
c[k] = v
}
return c
}
31. Next Permutation
题目
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such an arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in place and use only constant extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
Output: [1,2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,5]
Output: [1,5,1]
Example 4:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 100
题目大意
实现获取 下一个排列 的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列。如果不存在下一个更大的排列,则将数字重新排列成最小的排列(即升序排列)。必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
解题思路
- 题目有 3 个问题需要解决。如何找到下一个排列。不存在下一个排列的时候如何生成最小的排列。如何原地修改。先解决第一个问题,如何找到下一个排列。下一个排列是找到一个大于当前排序的字典序,且变大的幅度最小。那么只能将较小的数与较大数做一次原地交换。并且较小数的下标要尽量靠右,较大数也要尽可能小。原地交换以后,还需要将较大数右边的数按照升序重新排列。这样交换以后,才能生成下一个排列。以排列 [8,9,6,10,7,2] 为例:能找到的符合条件的一对「较小数」与「较大数」的组合为 6 与 7,满足「较小数」尽量靠右,而「较大数」尽可能小。当完成交换后排列变为 [8,9,7,10,6,2],此时我们可以重排「较小数」右边的序列,序列变为 [8,9,7,2,6,10]。
- 第一步:在
nums[i]中找到i使得nums[i] < nums[i+1],此时较小数为nums[i],并且[i+1, n)一定为下降区间。第二步:如果找到了这样的i,则在下降区间[i+1, n)中从后往前找到第一个j,使得nums[i] < nums[j],此时较大数为nums[j]。第三步,交换nums[i]和nums[j],此时区间[i+1, n)一定为降序区间。最后原地交换[i+1, n)区间内的元素,使其变为升序,无需对该区间进行排序。 - 如果第一步找不到符合条件的下标
i,说明当前序列已经是一个最大的排列。那么应该直接执行第三步,生成最小的排列。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一
func nextPermutation(nums []int) {
i, j := 0, 0
for i = len(nums) - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
if nums[i] < nums[i+1] {
break
}
}
if i >= 0 {
for j = len(nums) - 1; j > i; j-- {
if nums[j] > nums[i] {
break
}
}
swap(&nums, i, j)
}
reverse(&nums, i+1, len(nums)-1)
}
func reverse(nums *[]int, i, j int) {
for i < j {
swap(nums, i, j)
i++
j--
}
}
func swap(nums *[]int, i, j int) {
(*nums)[i], (*nums)[j] = (*nums)[j], (*nums)[i]
}
// 解法二
// [2,(3),6,5,4,1] -> 2,(4),6,5,(3),1 -> 2,4, 1,3,5,6
func nextPermutation1(nums []int) {
var n = len(nums)
var pIdx = checkPermutationPossibility(nums)
if pIdx == -1 {
reverse(&nums, 0, n-1)
return
}
var rp = len(nums) - 1
// start from right most to leftward,find the first number which is larger than PIVOT
for rp > 0 {
if nums[rp] > nums[pIdx] {
swap(&nums, pIdx, rp)
break
} else {
rp--
}
}
// Finally, Reverse all elements which are right from pivot
reverse(&nums, pIdx+1, n-1)
}
// checkPermutationPossibility returns 1st occurrence Index where
// value is in decreasing order(from right to left)
// returns -1 if not found(it's already in its last permutation)
func checkPermutationPossibility(nums []int) (idx int) {
// search right to left for 1st number(from right) that is not in increasing order
var rp = len(nums) - 1
for rp > 0 {
if nums[rp-1] < nums[rp] {
idx = rp - 1
return idx
}
rp--
}
return -1
}
32. Longest Valid Parentheses
题目
Given a string containing just the characters '(' and ')', find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
Example 1:
Input: s = "(()"
Output: 2
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()".
Example 2:
Input: s = ")()())"
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()()".
Example 3:
Input: s = ""
Output: 0
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 3 * 104s[i]is'(', or')'.
题目大意
给你一个只包含 ‘(’ 和 ‘)’ 的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号子串的长度。
解题思路
- 提到括号匹配,第一时间能让人想到的就是利用栈。这里需要计算嵌套括号的总长度,所以栈里面不能单纯的存左括号,而应该存左括号在原字符串的下标,这样通过下标相减可以获取长度。那么栈如果是非空,栈底永远存的是当前遍历过的字符串中上一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标。上一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标可以理解为每段括号匹配之间的“隔板”。例如,
())((())),第三个右括号,即为左右 2 段正确的括号匹配中间的“隔板”。“隔板”的存在影响计算最长括号长度。如果不存在“隔板”,前后 2 段正确的括号匹配应该“融合”在一起,最长长度为2 + 6 = 8,但是这里存在了“隔板”,所以最长长度仅为6。 - 具体算法实现,遇到每个
'(',将它的下标压入栈中。对于遇到的每个')',先弹出栈顶元素表示匹配了当前右括号。如果栈为空,说明当前的右括号为没有被匹配的右括号,于是将其下标放入栈中来更新上一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标。如果栈不为空,当前右括号的下标减去栈顶元素即为以该右括号为结尾的最长有效括号的长度。需要注意初始化时,不存在上一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标,那么将-1放入栈中,充当下标为0的“隔板”。时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)。 - 在栈的方法中,实际用到的元素仅仅是栈底的上一个没有被匹配的右括号的下标。那么考虑能否把这个值存在一个变量中,这样可以省去栈 O(n) 的时间复杂度。利用两个计数器 left 和 right 。首先,从左到右遍历字符串,每当遇到
'(',增加 left 计数器,每当遇到')',增加 right 计数器。每当 left 计数器与 right 计数器相等时,计算当前有效字符串的长度,并且记录目前为止找到的最长子字符串。当 right 计数器比 left 计数器大时,说明括号不匹配,于是将 left 和 right 计数器同时变回 0。这样的做法利用了贪心的思想,考虑了以当前字符下标结尾的有效括号长度,每次当右括号数量多于左括号数量的时候之前的字符就扔掉不再考虑,重新从下一个字符开始计算。 - 但上面的做法会漏掉一种情况,就是遍历的时候左括号的数量始终大于右括号的数量,即
((),这种时候最长有效括号是求不出来的。解决办法是反向再计算一遍,如果从右往左计算,(()先计算匹配的括号,最后只剩下'(',这样依旧可以算出最长匹配的括号长度。反过来计算的方法和上述从左往右计算的方法一致:当 left 计数器比 right 计数器大时,将 left 和 right 计数器同时变回 0;当 left 计数器与 right 计数器相等时,计算当前有效字符串的长度,并且记录目前为止找到的最长子字符串。这种方法的时间复杂度是 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 栈
func longestValidParentheses(s string) int {
stack, res := []int{}, 0
stack = append(stack, -1)
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
if s[i] == '(' {
stack = append(stack, i)
} else {
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
if len(stack) == 0 {
stack = append(stack, i)
} else {
res = max(res, i-stack[len(stack)-1])
}
}
}
return res
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
// 解法二 双指针
func longestValidParentheses1(s string) int {
left, right, maxLength := 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
if s[i] == '(' {
left++
} else {
right++
}
if left == right {
maxLength = max(maxLength, 2*right)
} else if right > left {
left, right = 0, 0
}
}
left, right = 0, 0
for i := len(s) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
if s[i] == '(' {
left++
} else {
right++
}
if left == right {
maxLength = max(maxLength, 2*left)
} else if left > right {
left, right = 0, 0
}
}
return maxLength
}
33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
题目
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return its index, otherwise return -1.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Your algorithm’s runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: -1
题目大意
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。
你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别。
解题思路
- 给出一个数组,数组中本来是从小到大排列的,并且数组中没有重复数字。但是现在把后面随机一段有序的放到数组前面,这样形成了前后两端有序的子序列。在这样的一个数组里面查找一个数,设计一个 O(log n) 的算法。如果找到就输出数组的小标,如果没有找到,就输出 -1 。
- 由于数组基本有序,虽然中间有一个“断开点”,还是可以使用二分搜索的算法来实现。现在数组前面一段是数值比较大的数,后面一段是数值偏小的数。如果 mid 落在了前一段数值比较大的区间内了,那么一定有
nums[mid] > nums[low],如果是落在后面一段数值比较小的区间内,nums[mid] ≤ nums[low]。如果 mid 落在了后一段数值比较小的区间内了,那么一定有nums[mid] < nums[high],如果是落在前面一段数值比较大的区间内,nums[mid] ≤ nums[high]。还有nums[low] == nums[mid]和nums[high] == nums[mid]的情况,单独处理即可。最后找到则输出 mid,没有找到则输出 -1 。
代码
package leetcode
func search33(nums []int, target int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return -1
}
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if nums[mid] == target {
return mid
} else if nums[mid] > nums[low] { // 在数值大的一部分区间里
if nums[low] <= target && target < nums[mid] {
high = mid - 1
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
} else if nums[mid] < nums[high] { // 在数值小的一部分区间里
if nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[high] {
low = mid + 1
} else {
high = mid - 1
}
} else {
if nums[low] == nums[mid] {
low++
}
if nums[high] == nums[mid] {
high--
}
}
}
return -1
}
34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array
题目
Given an array of integers nums sorted in ascending order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
Your algorithm’s runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
If the target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
Output: [3,4]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
Output: [-1,-1]
题目大意
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别。如果数组中不存在目标值,返回 [-1, -1]。
解题思路
-
给出一个有序数组
nums和一个数target,要求在数组中找到第一个和这个元素相等的元素下标,最后一个和这个元素相等的元素下标。 -
这一题是经典的二分搜索变种题。二分搜索有 4 大基础变种题:
- 查找第一个值等于给定值的元素
- 查找最后一个值等于给定值的元素
- 查找第一个大于等于给定值的元素
- 查找最后一个小于等于给定值的元素
这一题的解题思路可以分别利用变种 1 和变种 2 的解法就可以做出此题。或者用一次变种 1 的方法,然后循环往后找到最后一个与给定值相等的元素。不过后者这种方法可能会使时间复杂度下降到 O(n),因为有可能数组中 n 个元素都和给定元素相同。(4 大基础变种的实现见代码)
代码
package leetcode
func searchRange(nums []int, target int) []int {
return []int{searchFirstEqualElement(nums, target), searchLastEqualElement(nums, target)}
}
// 二分查找第一个与 target 相等的元素,时间复杂度 O(logn)
func searchFirstEqualElement(nums []int, target int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + ((high - low) >> 1)
if nums[mid] > target {
high = mid - 1
} else if nums[mid] < target {
low = mid + 1
} else {
if (mid == 0) || (nums[mid-1] != target) { // 找到第一个与 target 相等的元素
return mid
}
high = mid - 1
}
}
return -1
}
// 二分查找最后一个与 target 相等的元素,时间复杂度 O(logn)
func searchLastEqualElement(nums []int, target int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + ((high - low) >> 1)
if nums[mid] > target {
high = mid - 1
} else if nums[mid] < target {
low = mid + 1
} else {
if (mid == len(nums)-1) || (nums[mid+1] != target) { // 找到最后一个与 target 相等的元素
return mid
}
low = mid + 1
}
}
return -1
}
// 二分查找第一个大于等于 target 的元素,时间复杂度 O(logn)
func searchFirstGreaterElement(nums []int, target int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + ((high - low) >> 1)
if nums[mid] >= target {
if (mid == 0) || (nums[mid-1] < target) { // 找到第一个大于等于 target 的元素
return mid
}
high = mid - 1
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
}
return -1
}
// 二分查找最后一个小于等于 target 的元素,时间复杂度 O(logn)
func searchLastLessElement(nums []int, target int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + ((high - low) >> 1)
if nums[mid] <= target {
if (mid == len(nums)-1) || (nums[mid+1] > target) { // 找到最后一个小于等于 target 的元素
return mid
}
low = mid + 1
} else {
high = mid - 1
}
}
return -1
}
35. Search Insert Position
题目
Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
You may assume no duplicates in the array.
Example 1:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 5
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 2
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 7
Output: 4
Example 4:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 0
Output: 0
题目大意
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
解题思路
- 给出一个已经从小到大排序后的数组,要求在数组中找到插入 target 元素的位置。
- 这一题是经典的二分搜索的变种题,在有序数组中找到最后一个比 target 小的元素。
代码
package leetcode
func searchInsert(nums []int, target int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if nums[mid] >= target {
high = mid - 1
} else {
if (mid == len(nums)-1) || (nums[mid+1] >= target) {
return mid + 1
}
low = mid + 1
}
}
return 0
}
36. Valid Sudoku
题目
Determine if a 9x9 Sudoku board is valid. Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the following rules:
- Each row must contain the digits
1-9without repetition. - Each column must contain the digits
1-9without repetition. - Each of the 9
3x3sub-boxes of the grid must contain the digits1-9without repetition.
A partially filled sudoku which is valid.
The Sudoku board could be partially filled, where empty cells are filled with the character '.'.
Example 1:
Input:
[
["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: true
Example 2:
Input:
[
["8","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: false
Explanation: Same as Example 1, except with the 5 in the top left corner being
modified to 8. Since there are two 8's in the top left 3x3 sub-box, it is invalid.
Note:
- A Sudoku board (partially filled) could be valid but is not necessarily solvable.
- Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the mentioned rules.
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'. - The given board size is always
9x9.
题目大意
判断一个 9x9 的数独是否有效。只需要根据以下规则,验证已经填入的数字是否有效即可。
- 数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
- 数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
- 数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
解题思路
- 给出一个数独的棋盘,要求判断这个棋盘当前是否满足数独的要求:即行列是否都只包含 1-9,每个九宫格里面是否也只包含 1-9 。
- 注意这题和第 37 题是不同的,这一题是判断当前棋盘状态是否满足数独的要求,而第 37 题是要求求解数独。本题中的棋盘有些是无解的,但是棋盘状态是满足题意的。
代码
package leetcode
import "strconv"
// 解法一 暴力遍历,时间复杂度 O(n^3)
func isValidSudoku(board [][]byte) bool {
// 判断行 row
for i := 0; i < 9; i++ {
tmp := [10]int{}
for j := 0; j < 9; j++ {
cellVal := board[i][j : j+1]
if string(cellVal) != "." {
index, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(cellVal))
if index > 9 || index < 1 {
return false
}
if tmp[index] == 1 {
return false
}
tmp[index] = 1
}
}
}
// 判断列 column
for i := 0; i < 9; i++ {
tmp := [10]int{}
for j := 0; j < 9; j++ {
cellVal := board[j][i]
if string(cellVal) != "." {
index, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(cellVal))
if index > 9 || index < 1 {
return false
}
if tmp[index] == 1 {
return false
}
tmp[index] = 1
}
}
}
// 判断 9宫格 3X3 cell
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
for j := 0; j < 3; j++ {
tmp := [10]int{}
for ii := i * 3; ii < i*3+3; ii++ {
for jj := j * 3; jj < j*3+3; jj++ {
cellVal := board[ii][jj]
if string(cellVal) != "." {
index, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(cellVal))
if tmp[index] == 1 {
return false
}
tmp[index] = 1
}
}
}
}
}
return true
}
// 解法二 添加缓存,时间复杂度 O(n^2)
func isValidSudoku1(board [][]byte) bool {
rowbuf, colbuf, boxbuf := make([][]bool, 9), make([][]bool, 9), make([][]bool, 9)
for i := 0; i < 9; i++ {
rowbuf[i] = make([]bool, 9)
colbuf[i] = make([]bool, 9)
boxbuf[i] = make([]bool, 9)
}
// 遍历一次,添加缓存
for r := 0; r < 9; r++ {
for c := 0; c < 9; c++ {
if board[r][c] != '.' {
num := board[r][c] - '0' - byte(1)
if rowbuf[r][num] || colbuf[c][num] || boxbuf[r/3*3+c/3][num] {
return false
}
rowbuf[r][num] = true
colbuf[c][num] = true
boxbuf[r/3*3+c/3][num] = true // r,c 转换到box方格中
}
}
}
return true
}
37. Sudoku Solver
题目
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
- Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each row. - Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each column. - Each of the the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each of the 93x3sub-boxes of the grid.
Empty cells are indicated by the character '.'.
A sudoku puzzle…
…and its solution numbers marked in red.
Note:
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'. - You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
- The given board size is always
9x9.
题目大意
编写一个程序,通过已填充的空格来解决数独问题。一个数独的解法需遵循如下规则:
- 数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
- 数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
- 数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
空白格用 ‘.’ 表示。
解题思路
- 给出一个数独谜题,要求解出这个数独
- 解题思路 DFS 暴力回溯枚举。数独要求每横行,每竖行,每九宫格内,
1-9的数字不能重复,每次放下一个数字的时候,在这 3 个地方都需要判断一次。 - 另外找到一组解以后就不需要再继续回溯了,直接返回即可。
代码
package leetcode
type position struct {
x int
y int
}
func solveSudoku(board [][]byte) {
pos, find := []position{}, false
for i := 0; i < len(board); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(board[0]); j++ {
if board[i][j] == '.' {
pos = append(pos, position{x: i, y: j})
}
}
}
putSudoku(&board, pos, 0, &find)
}
func putSudoku(board *[][]byte, pos []position, index int, succ *bool) {
if *succ == true {
return
}
if index == len(pos) {
*succ = true
return
}
for i := 1; i < 10; i++ {
if checkSudoku(board, pos[index], i) && !*succ {
(*board)[pos[index].x][pos[index].y] = byte(i) + '0'
putSudoku(board, pos, index+1, succ)
if *succ == true {
return
}
(*board)[pos[index].x][pos[index].y] = '.'
}
}
}
func checkSudoku(board *[][]byte, pos position, val int) bool {
// 判断横行是否有重复数字
for i := 0; i < len((*board)[0]); i++ {
if (*board)[pos.x][i] != '.' && int((*board)[pos.x][i]-'0') == val {
return false
}
}
// 判断竖行是否有重复数字
for i := 0; i < len((*board)); i++ {
if (*board)[i][pos.y] != '.' && int((*board)[i][pos.y]-'0') == val {
return false
}
}
// 判断九宫格是否有重复数字
posx, posy := pos.x-pos.x%3, pos.y-pos.y%3
for i := posx; i < posx+3; i++ {
for j := posy; j < posy+3; j++ {
if (*board)[i][j] != '.' && int((*board)[i][j]-'0') == val {
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
39. Combination Sum
题目
Given a set of candidate numbers (candidates) (without duplicates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
The same repeated number may be chosen from candidates unlimited number of times.
Note:
- All numbers (including
target) will be positive integers. - The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
A solution set is:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
题目大意
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
解题思路
- 题目要求出总和为 sum 的所有组合,组合需要去重。
- 这一题和第 47 题类似,只不过元素可以反复使用。
代码
package leetcode
import "sort"
func combinationSum(candidates []int, target int) [][]int {
if len(candidates) == 0 {
return [][]int{}
}
c, res := []int{}, [][]int{}
sort.Ints(candidates)
findcombinationSum(candidates, target, 0, c, &res)
return res
}
func findcombinationSum(nums []int, target, index int, c []int, res *[][]int) {
if target <= 0 {
if target == 0 {
b := make([]int, len(c))
copy(b, c)
*res = append(*res, b)
}
return
}
for i := index; i < len(nums); i++ {
if nums[i] > target { // 这里可以剪枝优化
break
}
c = append(c, nums[i])
findcombinationSum(nums, target-nums[i], i, c, res) // 注意这里迭代的时候 index 依旧不变,因为一个元素可以取多次
c = c[:len(c)-1]
}
}
40. Combination Sum II
题目
Given a collection of candidate numbers (candidates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
Each number in candidates may only be used once in the combination.
Note:
- All numbers (including
target) will be positive integers. - The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
A solution set is:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
题目大意
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
解题思路
- 题目要求出总和为 sum 的所有组合,组合需要去重。这一题是第 39 题的加强版,第 39 题中元素可以重复利用(重复元素可无限次使用),这一题中元素只能有限次数的利用,因为存在重复元素,并且每个元素只能用一次(重复元素只能使用有限次)
- 这一题和第 47 题类似。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"sort"
)
func combinationSum2(candidates []int, target int) [][]int {
if len(candidates) == 0 {
return [][]int{}
}
c, res := []int{}, [][]int{}
sort.Ints(candidates) // 这里是去重的关键逻辑
findcombinationSum2(candidates, target, 0, c, &res)
return res
}
func findcombinationSum2(nums []int, target, index int, c []int, res *[][]int) {
if target == 0 {
b := make([]int, len(c))
copy(b, c)
*res = append(*res, b)
return
}
for i := index; i < len(nums); i++ {
if i > index && nums[i] == nums[i-1] { // 这里是去重的关键逻辑,本次不取重复数字,下次循环可能会取重复数字
continue
}
if target >= nums[i] {
c = append(c, nums[i])
findcombinationSum2(nums, target-nums[i], i+1, c, res)
c = c[:len(c)-1]
}
}
}
41. First Missing Positive
题目
Given an unsorted integer array, find the smallest missing positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,0]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: [3,4,-1,1]
Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: [7,8,9,11,12]
Output: 1
Note:
Your algorithm should run in O(n) time and uses constant extra space.
题目大意
找到缺失的第一个正整数。
解题思路
为了减少时间复杂度,可以把 input 数组都装到 map 中,然后 i 循环从 1 开始,依次比对 map 中是否存在 i,只要不存在 i 就立即返回结果,即所求。
代码
package leetcode
func firstMissingPositive(nums []int) int {
numMap := make(map[int]int, len(nums))
for _, v := range nums {
numMap[v] = v
}
for index := 1; index < len(nums)+1; index++ {
if _, ok := numMap[index]; !ok {
return index
}
}
return len(nums) + 1
}
42. Trapping Rain Water
题目
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped. Thanks Marcos for contributing this image!
Example:
Input: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
题目大意
从 x 轴开始,给出一个数组,数组里面的数字代表从 (0,0) 点开始,宽度为 1 个单位,高度为数组元素的值。如果下雨了,问这样一个容器能装多少单位的水?
解题思路
- 每个数组里面的元素值可以想象成一个左右都有壁的圆柱筒。例如下图中左边的第二个元素 1,当前左边最大的元素是 2 ,所以 2 高度的水会装到 1 的上面(因为想象成了左右都有筒壁)。这道题的思路就是左指针从 0 开始往右扫,右指针从最右边开始往左扫。额外还需要 2 个变量分别记住左边最大的高度和右边最大高度。遍历扫数组元素的过程中,如果左指针的高度比右指针的高度小,就不断的移动左指针,否则移动右指针。循环的终止条件就是左右指针碰上以后就结束。只要数组中元素的高度比保存的局部最大高度小,就累加 res 的值,否则更新局部最大高度。最终解就是 res 的值。

- 抽象一下,本题是想求针对每个 i,找到它左边最大值 leftMax,右边的最大值 rightMax,然后 min(leftMax,rightMax) 为能够接到水的高度。left 和 right 指针是两边往中间移动的游标指针。最傻的解题思路是针对每个下标 i,往左循环找到第一个最大值,往右循环找到第一个最大值,然后把这两个最大值取出最小者,即为当前雨水的高度。这样做时间复杂度高,浪费了很多循环。i 在从左往右的过程中,是可以动态维护最大值的。右边的最大值用右边的游标指针来维护。从左往右扫一遍下标,和,从两边往中间遍历一遍下标,是相同的结果,每个下标都遍历了一次。
- 每个 i 的宽度固定为 1,所以每个“坑”只需要求出高度,即当前这个“坑”能积攒的雨水。最后依次将每个“坑”中的雨水相加即是能接到的雨水数。
代码
package leetcode
func trap(height []int) int {
res, left, right, maxLeft, maxRight := 0, 0, len(height)-1, 0, 0
for left <= right {
if height[left] <= height[right] {
if height[left] > maxLeft {
maxLeft = height[left]
} else {
res += maxLeft - height[left]
}
left++
} else {
if height[right] >= maxRight {
maxRight = height[right]
} else {
res += maxRight - height[right]
}
right--
}
}
return res
}
43. Multiply Strings
题目
Given two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as strings, return the product of num1 and num2, also represented as a string.
Note: You must not use any built-in BigInteger library or convert the inputs to integer directly.
Example 1:
Input: num1 = "2", num2 = "3"
Output: "6"
Example 2:
Input: num1 = "123", num2 = "456"
Output: "56088"
Constraints:
1 <= num1.length, num2.length <= 200num1andnum2consist of digits only.- Both
num1andnum2do not contain any leading zero, except the number0itself.
题目大意
给定两个以字符串形式表示的非负整数 num1 和 num2,返回 num1 和 num2 的乘积,它们的乘积也表示为字符串形式。
解题思路
- 用数组模拟乘法。创建一个数组长度为
len(num1) + len(num2)的数组用于存储乘积。对于任意0 ≤ i < len(num1),0 ≤ j < len(num2),num1[i] * num2[j]的结果位于tmp[i+j+1],如果tmp[i+j+1]≥10,则将进位部分加到tmp[i+j]。最后,将数组tmp转成字符串,如果最高位是 0 则舍弃最高位。
代码
package leetcode
func multiply(num1 string, num2 string) string {
if num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" {
return "0"
}
b1, b2, tmp := []byte(num1), []byte(num2), make([]int, len(num1)+len(num2))
for i := 0; i < len(b1); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(b2); j++ {
tmp[i+j+1] += int(b1[i]-'0') * int(b2[j]-'0')
}
}
for i := len(tmp) - 1; i > 0; i-- {
tmp[i-1] += tmp[i] / 10
tmp[i] = tmp[i] % 10
}
if tmp[0] == 0 {
tmp = tmp[1:]
}
res := make([]byte, len(tmp))
for i := 0; i < len(tmp); i++ {
res[i] = '0' + byte(tmp[i])
}
return string(res)
}
45. Jump Game II
题目
Given an array of non-negative integers nums, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Your goal is to reach the last index in the minimum number of jumps.
You can assume that you can always reach the last index.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2. Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,3,0,1,4]
Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 10^5
题目大意
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
解题思路
- 要求找到最少跳跃次数,顺理成章的会想到用贪心算法解题。扫描步数数组,维护当前能够到达最大下标的位置,记为能到达的最远边界,如果扫描过程中到达了最远边界,更新边界并将跳跃次数 + 1。
- 扫描数组的时候,其实不需要扫描最后一个元素,因为在跳到最后一个元素之前,能到达的最远边界一定大于等于最后一个元素的位置,不然就跳不到最后一个元素,到达不了终点了;如果遍历到最后一个元素,说明边界正好为最后一个位置,最终跳跃次数直接 + 1 即可,也不需要访问最后一个元素。
代码
package leetcode
func jump(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 1 {
return 0
}
needChoose, canReach, step := 0, 0, 0
for i, x := range nums {
if i+x > canReach {
canReach = i + x
if canReach >= len(nums)-1 {
return step + 1
}
}
if i == needChoose {
needChoose = canReach
step++
}
}
return step
}
46. Permutations
题目
Given a collection of distinct integers, return all possible permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
题目大意
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
解题思路
- 求出一个数组的排列组合中的所有排列,用 DFS 深搜即可。
代码
package leetcode
func permute(nums []int) [][]int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return [][]int{}
}
used, p, res := make([]bool, len(nums)), []int{}, [][]int{}
generatePermutation(nums, 0, p, &res, &used)
return res
}
func generatePermutation(nums []int, index int, p []int, res *[][]int, used *[]bool) {
if index == len(nums) {
temp := make([]int, len(p))
copy(temp, p)
*res = append(*res, temp)
return
}
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
if !(*used)[i] {
(*used)[i] = true
p = append(p, nums[i])
generatePermutation(nums, index+1, p, res, used)
p = p[:len(p)-1]
(*used)[i] = false
}
}
return
}
47. Permutations II
题目
Given a collection of numbers that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,1,2]
Output:
[
[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]
]
题目大意
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 46 题的加强版,第 46 题中求数组的排列,数组中元素不重复,但是这一题中,数组元素会重复,所以需要最终排列出来的结果需要去重。
- 去重的方法是经典逻辑,将数组排序以后,判断重复元素再做逻辑判断。
- 其他思路和第 46 题完全一致,DFS 深搜即可。
代码
package leetcode
import "sort"
func permuteUnique(nums []int) [][]int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return [][]int{}
}
used, p, res := make([]bool, len(nums)), []int{}, [][]int{}
sort.Ints(nums) // 这里是去重的关键逻辑
generatePermutation47(nums, 0, p, &res, &used)
return res
}
func generatePermutation47(nums []int, index int, p []int, res *[][]int, used *[]bool) {
if index == len(nums) {
temp := make([]int, len(p))
copy(temp, p)
*res = append(*res, temp)
return
}
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
if !(*used)[i] {
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && !(*used)[i-1] { // 这里是去重的关键逻辑
continue
}
(*used)[i] = true
p = append(p, nums[i])
generatePermutation47(nums, index+1, p, res, used)
p = p[:len(p)-1]
(*used)[i] = false
}
}
return
}
48. Rotate Image
题目
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image.
Rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
Note:
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
Example 1:
Given input matrix =
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
],
rotate the input matrix in-place such that it becomes:
[
[7,4,1],
[8,5,2],
[9,6,3]
]
Example 2:
Given input matrix =
[
[ 5, 1, 9,11],
[ 2, 4, 8,10],
[13, 3, 6, 7],
[15,14,12,16]
],
rotate the input matrix in-place such that it becomes:
[
[15,13, 2, 5],
[14, 3, 4, 1],
[12, 6, 8, 9],
[16, 7,10,11]
]
题目大意
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像。将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。说明:你必须在原地旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
解题思路
- 给出一个二维数组,要求顺时针旋转 90 度。
- 这一题比较简单,按照题意做就可以。这里给出 2 种旋转方法的实现,顺时针旋转和逆时针旋转。
/*
* clockwise rotate 顺时针旋转
* first reverse up to down, then swap the symmetry
* 1 2 3 7 8 9 7 4 1
* 4 5 6 => 4 5 6 => 8 5 2
* 7 8 9 1 2 3 9 6 3
*/
void rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
reverse(matrix.begin(), matrix.end());
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
/*
* anticlockwise rotate 逆时针旋转
* first reverse left to right, then swap the symmetry
* 1 2 3 3 2 1 3 6 9
* 4 5 6 => 6 5 4 => 2 5 8
* 7 8 9 9 8 7 1 4 7
*/
void anti_rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
for (auto vi : matrix) reverse(vi.begin(), vi.end());
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一
func rotate(matrix [][]int) {
length := len(matrix)
// rotate by diagonal 对角线变换
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
for j := i + 1; j < length; j++ {
matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i] = matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]
}
}
// rotate by vertical centerline 竖直轴对称翻转
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
for j := 0; j < length/2; j++ {
matrix[i][j], matrix[i][length-j-1] = matrix[i][length-j-1], matrix[i][j]
}
}
}
// 解法二
func rotate1(matrix [][]int) {
n := len(matrix)
if n == 1 {
return
}
/* rotate clock-wise = 1. transpose matrix => 2. reverse(matrix[i])
1 2 3 4 1 5 9 13 13 9 5 1
5 6 7 8 => 2 6 10 14 => 14 10 6 2
9 10 11 12 3 7 11 15 15 11 7 3
13 14 15 16 4 8 12 16 16 12 8 4
*/
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
// transpose, i=rows, j=columns
// j = i+1, coz diagonal elements didn't change in a square matrix
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
swap(matrix, i, j)
}
// reverse each row of the image
matrix[i] = reverse(matrix[i])
}
}
// swap changes original slice's i,j position
func swap(nums [][]int, i, j int) {
nums[i][j], nums[j][i] = nums[j][i], nums[i][j]
}
// reverses a row of image, matrix[i]
func reverse(nums []int) []int {
var lp, rp = 0, len(nums) - 1
for lp < rp {
nums[lp], nums[rp] = nums[rp], nums[lp]
lp++
rp--
}
return nums
}
49. Group Anagrams
题目
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
Example:
Input: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Output:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
Note:
- All inputs will be in lowercase.
- The order of your output does not matter.
题目大意
给出一个字符串数组,要求对字符串数组里面有 Anagrams 关系的字符串进行分组。Anagrams 关系是指两个字符串的字符完全相同,顺序不同,两者是由排列组合组成。
解题思路
这道题可以将每个字符串都排序,排序完成以后,相同 Anagrams 的字符串必然排序结果一样。把排序以后的字符串当做 key 存入到 map 中。遍历数组以后,就能得到一个 map,key 是排序以后的字符串,value 对应的是这个排序字符串以后的 Anagrams 字符串集合。最后再将这些 value 对应的字符串数组输出即可。
代码
package leetcode
import "sort"
type sortRunes []rune
func (s sortRunes) Less(i, j int) bool {
return s[i] < s[j]
}
func (s sortRunes) Swap(i, j int) {
s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i]
}
func (s sortRunes) Len() int {
return len(s)
}
func groupAnagrams(strs []string) [][]string {
record, res := map[string][]string{}, [][]string{}
for _, str := range strs {
sByte := []rune(str)
sort.Sort(sortRunes(sByte))
sstrs := record[string(sByte)]
sstrs = append(sstrs, str)
record[string(sByte)] = sstrs
}
for _, v := range record {
res = append(res, v)
}
return res
}
50. Pow(x, n)
题目
Implement pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n (xn).
Example 1:
Input: 2.00000, 10
Output: 1024.00000
Example 2:
Input: 2.10000, 3
Output: 9.26100
Example 3:
Input: 2.00000, -2
Output: 0.25000
Explanation: 2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
Note:
- -100.0 < x < 100.0
- n is a 32-bit signed integer, within the range [−2^31, 2^31− 1]
题目大意
实现 pow(x, n) ,即计算 x 的 n 次幂函数。
解题思路
- 要求计算 Pow(x, n)
- 这一题用递归的方式,不断的将 n 2 分下去。注意 n 的正负数,n 的奇偶性。
代码
package leetcode
// 时间复杂度 O(log n),空间复杂度 O(1)
func myPow(x float64, n int) float64 {
if n == 0 {
return 1
}
if n == 1 {
return x
}
if n < 0 {
n = -n
x = 1 / x
}
tmp := myPow(x, n/2)
if n%2 == 0 {
return tmp * tmp
}
return tmp * tmp * x
}