LeetCode题解3
101. Symmetric Tree
题目
Given a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (ie, symmetric around its center).
For example, this binary tree [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] is symmetric:
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
But the following [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] is not:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
Note:
Bonus points if you could solve it both recursively and iteratively.
题目大意
这一题要求判断 2 颗树是否是左右对称的。
解题思路
- 这道题是几道题的综合题。将根节点的左字数反转二叉树,然后再和根节点的右节点进行比较,是否完全相等。
- 反转二叉树是第 226 题。判断 2 颗树是否完全相等是第 100 题。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一 dfs
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
return isMirror(root.Left, root.Right)
}
func isMirror(left *TreeNode, right *TreeNode) bool {
if left == nil && right == nil {
return true
}
if left == nil || right == nil {
return false
}
return (left.Val == right.Val) && isMirror(left.Left, right.Right) && isMirror(left.Right, right.Left)
}
// 解法二
func isSymmetric1(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
return isSameTree(invertTree(root.Left), root.Right)
}
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
} else if p != nil && q != nil {
if p.Val != q.Val {
return false
}
return isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left) && isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
} else {
return false
}
}
func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
invertTree(root.Left)
invertTree(root.Right)
root.Left, root.Right = root.Right, root.Left
return root
}
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
题目
Given a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, level by level).
For Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its level order traversal as:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
题目大意
按层序从上到下遍历一颗树。
解题思路
用一个队列即可实现。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一 BFS
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return [][]int{}
}
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
res := make([][]int, 0)
for len(queue) > 0 {
l := len(queue)
tmp := make([]int, 0, l)
for i := 0; i < l; i++ {
if queue[i].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[i].Left)
}
if queue[i].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[i].Right)
}
tmp = append(tmp, queue[i].Val)
}
queue = queue[l:]
res = append(res, tmp)
}
return res
}
// 解法二 DFS
func levelOrder1(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
var res [][]int
var dfsLevel func(node *TreeNode, level int)
dfsLevel = func(node *TreeNode, level int) {
if node == nil {
return
}
if len(res) == level {
res = append(res, []int{node.Val})
} else {
res[level] = append(res[level], node.Val)
}
dfsLevel(node.Left, level+1)
dfsLevel(node.Right, level+1)
}
dfsLevel(root, 0)
return res
}
103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
题目
Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
For Example: Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its zigzag level order traversal as:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
题目大意
按照 Z 字型层序遍历一棵树。
解题思路
- 按层序从上到下遍历一颗树,但是每一层的顺序是相互反转的,即上一层是从左往右,下一层就是从右往左,以此类推。用一个队列即可实现。
- 第 102 题和第 107 题都是按层序遍历的。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一
func zigzagLevelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return [][]int{}
}
queue := []*TreeNode{}
queue = append(queue, root)
curNum, nextLevelNum, res, tmp, curDir := 1, 0, [][]int{}, []int{}, 0
for len(queue) != 0 {
if curNum > 0 {
node := queue[0]
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
nextLevelNum++
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
nextLevelNum++
}
curNum--
tmp = append(tmp, node.Val)
queue = queue[1:]
}
if curNum == 0 {
if curDir == 1 {
for i, j := 0, len(tmp)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
tmp[i], tmp[j] = tmp[j], tmp[i]
}
}
res = append(res, tmp)
curNum = nextLevelNum
nextLevelNum = 0
tmp = []int{}
if curDir == 0 {
curDir = 1
} else {
curDir = 0
}
}
}
return res
}
// 解法二 递归
func zigzagLevelOrder0(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
var res [][]int
search(root, 0, &res)
return res
}
func search(root *TreeNode, depth int, res *[][]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
for len(*res) < depth+1 {
*res = append(*res, []int{})
}
if depth%2 == 0 {
(*res)[depth] = append((*res)[depth], root.Val)
} else {
(*res)[depth] = append([]int{root.Val}, (*res)[depth]...)
}
search(root.Left, depth+1, res)
search(root.Right, depth+1, res)
}
// 解法三 BFS
func zigzagLevelOrder1(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
res := [][]int{}
if root == nil {
return res
}
q := []*TreeNode{root}
size, i, j, lay, tmp, flag := 0, 0, 0, []int{}, []*TreeNode{}, false
for len(q) > 0 {
size = len(q)
tmp = []*TreeNode{}
lay = make([]int, size)
j = size - 1
for i = 0; i < size; i++ {
root = q[0]
q = q[1:]
if !flag {
lay[i] = root.Val
} else {
lay[j] = root.Val
j--
}
if root.Left != nil {
tmp = append(tmp, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
tmp = append(tmp, root.Right)
}
}
res = append(res, lay)
flag = !flag
q = tmp
}
return res
}
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
题目
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its depth = 3.
题目大意
要求输出一棵树的最大高度。
解题思路
这一题递归遍历就可,遍历根节点的左孩子的高度和根节点右孩子的高度,取出两者的最大值再加一即为总高度。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return max(maxDepth(root.Left), maxDepth(root.Right)) + 1
}
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
题目
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note:You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
For example, given
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
题目大意
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
解题思路
- 给出 2 个数组,根据 preorder 和 inorder 数组构造一颗树。
- 利用递归思想,从 preorder 可以得到根节点,从 inorder 中得到左子树和右子树。只剩一个节点的时候即为根节点。不断的递归直到所有的树都生成完成。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一, 直接传入需要的 slice 范围作为输入, 可以避免申请对应 inorder 索引的内存, 内存使用(leetcode test case) 4.7MB -> 4.3MB.
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(preorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &TreeNode{Val: preorder[0]}
for pos, node := range inorder {
if node == root.Val {
root.Left = buildTree(preorder[1:pos+1], inorder[:pos])
root.Right = buildTree(preorder[pos+1:], inorder[pos+1:])
}
}
return root
}
// 解法二
func buildTree1(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
inPos := make(map[int]int)
for i := 0; i < len(inorder); i++ {
inPos[inorder[i]] = i
}
return buildPreIn2TreeDFS(preorder, 0, len(preorder)-1, 0, inPos)
}
func buildPreIn2TreeDFS(pre []int, preStart int, preEnd int, inStart int, inPos map[int]int) *TreeNode {
if preStart > preEnd {
return nil
}
root := &TreeNode{Val: pre[preStart]}
rootIdx := inPos[pre[preStart]]
leftLen := rootIdx - inStart
root.Left = buildPreIn2TreeDFS(pre, preStart+1, preStart+leftLen, inStart, inPos)
root.Right = buildPreIn2TreeDFS(pre, preStart+leftLen+1, preEnd, rootIdx+1, inPos)
return root
}
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
题目
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note: You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
For example, given
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
题目大意
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
解题思路
- 给出 2 个数组,根据 inorder 和 postorder 数组构造一颗树。
- 利用递归思想,从 postorder 可以得到根节点,从 inorder 中得到左子树和右子树。只剩一个节点的时候即为根节点。不断的递归直到所有的树都生成完成。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一, 直接传入需要的 slice 范围作为输入, 可以避免申请对应 inorder 索引的内存, 内存使用(leetcode test case) 4.7MB -> 4.3MB.
func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
postorderLen := len(postorder)
if len(inorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &TreeNode{Val: postorder[postorderLen-1]}
postorder = postorder[:postorderLen-1]
for pos, node := range inorder {
if node == root.Val {
root.Left = buildTree(inorder[:pos], postorder[:len(inorder[:pos])])
root.Right = buildTree(inorder[pos+1:], postorder[len(inorder[:pos]):])
}
}
return root
}
// 解法二
func buildTree1(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
inPos := make(map[int]int)
for i := 0; i < len(inorder); i++ {
inPos[inorder[i]] = i
}
return buildInPos2TreeDFS(postorder, 0, len(postorder)-1, 0, inPos)
}
func buildInPos2TreeDFS(post []int, postStart int, postEnd int, inStart int, inPos map[int]int) *TreeNode {
if postStart > postEnd {
return nil
}
root := &TreeNode{Val: post[postEnd]}
rootIdx := inPos[post[postEnd]]
leftLen := rootIdx - inStart
root.Left = buildInPos2TreeDFS(post, postStart, postStart+leftLen-1, inStart, inPos)
root.Right = buildInPos2TreeDFS(post, postStart+leftLen, postEnd-1, rootIdx+1, inPos)
return root
}
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
题目
Given a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
For Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its bottom-up level order traversal as:
[
[15,7],
[9,20],
[3]
]
题目大意
按层序从下到上遍历一颗树。
解题思路
用一个队列即可实现。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
tmp := levelOrder(root)
res := [][]int{}
for i := len(tmp) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
res = append(res, tmp[i])
}
return res
}
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
题目
Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted array: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
题目大意
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
解题思路
- 把一个有序数组转换成高度平衡的二叉搜索数,按照定义即可
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
return &TreeNode{Val: nums[len(nums)/2], Left: sortedArrayToBST(nums[:len(nums)/2]), Right: sortedArrayToBST(nums[len(nums)/2+1:])}
}
109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
题目
Given a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted linked list: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
题目大意
将链表转化为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。高度平衡的定义:每个结点的 2 个子结点的深度不能相差超过 1 。
解题思路
思路比较简单,依次把链表的中间点作为根结点,类似二分的思想,递归排列所有结点即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func sortedListToBST(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head != nil && head.Next == nil {
return &TreeNode{Val: head.Val, Left: nil, Right: nil}
}
middleNode, preNode := middleNodeAndPreNode(head)
if middleNode == nil {
return nil
}
if preNode != nil {
preNode.Next = nil
}
if middleNode == head {
head = nil
}
return &TreeNode{Val: middleNode.Val, Left: sortedListToBST(head), Right: sortedListToBST(middleNode.Next)}
}
func middleNodeAndPreNode(head *ListNode) (middle *ListNode, pre *ListNode) {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return nil, head
}
p1 := head
p2 := head
for p2.Next != nil && p2.Next.Next != nil {
pre = p1
p1 = p1.Next
p2 = p2.Next.Next
}
return p1, pre
}
110. Balanced Binary Tree
题目
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
Given the following tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Return true.
Example 2:
Given the following tree [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]:
1
/ \
2 2
/ \
3 3
/ \
4 4
Return false.
题目大意
判断一棵树是不是平衡二叉树。平衡二叉树的定义是:树中每个节点都满足左右两个子树的高度差 \<= 1 的这个条件。
解题思路
根据定义判断即可,计算树的高度是第 104 题。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
leftHight := depth(root.Left)
rightHight := depth(root.Right)
return abs(leftHight-rightHight) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.Left) && isBalanced(root.Right)
}
func depth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return max(depth(root.Left), depth(root.Right)) + 1
}
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
题目
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
return its minimum depth = 2.
题目大意
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
解题思路
- 递归求出根节点到叶子节点的深度,输出最小值即可
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
if root.Left == nil {
return minDepth(root.Right) + 1
}
if root.Right == nil {
return minDepth(root.Left) + 1
}
return min(minDepth(root.Left), minDepth(root.Right)) + 1
}
112. Path Sum
题目
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
题目大意
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
解题思路
- 递归求解即可
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, sum int) bool {
if root == nil {
return false
}
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return sum == root.Val
}
return hasPathSum(root.Left, sum-root.Val) || hasPathSum(root.Right, sum-root.Val)
}
113. Path Sum II
题目
Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path’s sum equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
Return:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
题目大意
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 257 题和第 112 题的组合增强版
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, sum int) [][]int {
var slice [][]int
slice = findPath(root, sum, slice, []int(nil))
return slice
}
func findPath(n *TreeNode, sum int, slice [][]int, stack []int) [][]int {
if n == nil {
return slice
}
sum -= n.Val
stack = append(stack, n.Val)
if sum == 0 && n.Left == nil && n.Right == nil {
slice = append(slice, append([]int{}, stack...))
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
}
slice = findPath(n.Left, sum, slice, stack)
slice = findPath(n.Right, sum, slice, stack)
return slice
}
// 解法二
func pathSum1(root *TreeNode, sum int) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return [][]int{}
}
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
if sum == root.Val {
return [][]int{[]int{root.Val}}
}
}
path, res := []int{}, [][]int{}
tmpLeft := pathSum(root.Left, sum-root.Val)
path = append(path, root.Val)
if len(tmpLeft) > 0 {
for i := 0; i < len(tmpLeft); i++ {
tmpLeft[i] = append(path, tmpLeft[i]...)
}
res = append(res, tmpLeft...)
}
path = []int{}
tmpRight := pathSum(root.Right, sum-root.Val)
path = append(path, root.Val)
if len(tmpRight) > 0 {
for i := 0; i < len(tmpRight); i++ {
tmpRight[i] = append(path, tmpRight[i]...)
}
res = append(res, tmpRight...)
}
return res
}
114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
题目
Given a binary tree, flatten it to a linked list in-place.
For example, given the following tree:
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
The flattened tree should look like:
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
题目大意
给定一个二叉树,原地将它展开为链表。
解题思路
-
要求把二叉树“打平”,按照先根遍历的顺序,把树的结点都放在右结点中。
-
按照递归和非递归思路实现即可。
-
递归的思路可以这么想:倒序遍历一颗树,即是先遍历右孩子,然后遍历左孩子,最后再遍历根节点。
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
-----------
pre = 5
cur = 4
1
/
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
-----------
pre = 4
cur = 3
1
/
2
/
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
-----------
cur = 2
pre = 3
1
/
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
-----------
cur = 1
pre = 2
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6 -
可以先仿造先根遍历的代码,写出这个倒序遍历的逻辑:
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
} -
实现了倒序遍历的逻辑以后,再进行结点之间的拼接:
private TreeNode prev = null;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
root.right = prev;
root.left = null;
prev = root;
}
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一 非递归
func flatten(root *TreeNode) {
list, cur := []int{}, &TreeNode{}
preorder(root, &list)
cur = root
for i := 1; i < len(list); i++ {
cur.Left = nil
cur.Right = &TreeNode{Val: list[i], Left: nil, Right: nil}
cur = cur.Right
}
return
}
// 解法二 递归
func flatten1(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil || (root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil) {
return
}
flatten(root.Left)
flatten(root.Right)
currRight := root.Right
root.Right = root.Left
root.Left = nil
for root.Right != nil {
root = root.Right
}
root.Right = currRight
}
// 解法三 递归
func flatten2(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
flatten(root.Right)
if root.Left == nil {
return
}
flatten(root.Left)
p := root.Left
for p.Right != nil {
p = p.Right
}
p.Right = root.Right
root.Right = root.Left
root.Left = nil
}
115. Distinct Subsequences
题目
Given two strings s and t, return the number of distinct subsequences of s which equals t.
A string’s subsequence is a new string formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the remaining characters’ relative positions. (i.e., "ACE" is a subsequence of "ABCDE" while "AEC" is not).
It is guaranteed the answer fits on a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
Input: s = "rabbbit", t = "rabbit"
Output: 3
Explanation:
As shown below, there are 3 ways you can generate "rabbit" from S.
rabbbitrabbbitrabbbit
Example 2:
Input: s = "babgbag", t = "bag"
Output: 5
Explanation:
As shown below, there are 5 ways you can generate "bag" from S.
babgbagbabgbagbabgbagbabgbagbabgbag
Constraints:
0 <= s.length, t.length <= 1000sandtconsist of English letters.
题目大意
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串 t ,计算在 s 的子序列中 t 出现的个数。字符串的一个 子序列 是指,通过删除一些(也可以不删除)字符且不干扰剩余字符相对位置所组成的新字符串。(例如,“ACE” 是 “ABCDE” 的一个子序列,而 “AEC” 不是)题目数据保证答案符合 32 位带符号整数范围。
解题思路
-
在字符串
s中最多包含多少个字符串t。这里面包含很多重叠子问题,所以尝试用动态规划解决这个问题。定义dp[i][j]代表s[i:]的子序列中t[j:]出现的个数。初始化先判断边界条件。当i = len(s)且0≤ j < len(t)的时候,s[i:]为空字符串,t[j:]不为空,所以dp[len(s)][j] = 0。当j = len(t)且0 ≤ i < len(s)的时候,t[j:]不为空字符串,空字符串是任何字符串的子序列。所以dp[i][n] = 1。 -
当
i < len(s)且j < len(t)的时候,如果s[i] == t[j],有 2 种匹配方式,第一种将s[i]与t[j]匹配,那么t[j+1:]匹配s[i+1:]的子序列,子序列数为dp[i+1][j+1];第二种将s[i]不与t[j]匹配,t[j:]作为s[i+1:]的子序列,子序列数为dp[i+1][j]。综合 2 种情况,当s[i] == t[j]时,dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j+1] + dp[i+1][j]。 -
如果
s[i] != t[j],此时t[j:]只能作为s[i+1:]的子序列,子序列数为dp[i+1][j]。所以当s[i] != t[j]时,dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j]。综上分析得: -
最后是优化版本。写出上述代码以后,可以发现填表的过程是从右下角一直填到左上角。填表顺序是 从下往上一行一行的填。行内从右往左填。于是可以将这个二维数据压缩到一维。因为填充当前行只需要用到它的下一行信息即可,更进一步,用到的是下一行中右边元素的信息。于是可以每次更新该行时,先将旧的值存起来,计算更新该行的时候从右往左更新。这样做即可减少一维空间,将原来的二维数组压缩到一维数组。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 压缩版 DP
func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
dp := make([]int, len(s)+1)
for i, curT := range t {
pre := 0
for j, curS := range s {
if i == 0 {
pre = 1
}
newDP := dp[j+1]
if curT == curS {
dp[j+1] = dp[j] + pre
} else {
dp[j+1] = dp[j]
}
pre = newDP
}
}
return dp[len(s)]
}
// 解法二 普通 DP
func numDistinct1(s, t string) int {
m, n := len(s), len(t)
if m < n {
return 0
}
dp := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, n+1)
dp[i][n] = 1
}
for i := m - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for j := n - 1; j >= 0; j-- {
if s[i] == t[j] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j+1] + dp[i+1][j]
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j]
}
}
}
return dp[0][0]
}
116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
题目
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Follow up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, you may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation:Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is less than
4096. 1000 <= node.val <= 1000
题目大意
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
解题思路
- 本质上是二叉树的层序遍历,基于广度优先搜索,将每层的节点放入队列,并遍历队列进行连接。
代码
package leetcode
type Node struct {
Val int
Left *Node
Right *Node
Next *Node
}
//解法一:迭代
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return root
}
q := []*Node{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
var p []*Node
// 遍历这一层的所有节点
for i, node := range q {
if i+1 < len(q) {
node.Next = q[i+1]
}
if node.Left != nil {
p = append(p, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
p = append(p, node.Right)
}
}
q = p
}
return root
}
// 解法二 递归
func connect2(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
connectTwoNode(root.Left, root.Right)
return root
}
func connectTwoNode(node1, node2 *Node) {
if node1 == nil || node2 == nil {
return
}
node1.Next = node2
connectTwoNode(node1.Left, node1.Right)
connectTwoNode(node2.Left, node2.Right)
connectTwoNode(node1.Right, node2.Left)
}
118. Pascal’s Triangle
题目
Given a non-negative integer numRows, generate the first numRows of Pascal’s triangle.

Note: In Pascal’s triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it.
Example:
Input: 5
Output:
[
[1],
[1,1],
[1,2,1],
[1,3,3,1],
[1,4,6,4,1]
]
题目大意
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成杨辉三角的前 numRows 行。在杨辉三角中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
解题思路
- 给定一个 n,要求打印杨辉三角的前 n 行。
- 简单题。按照杨辉三角的生成规则循环打印即可。
代码
package leetcode
func generate(numRows int) [][]int {
result := [][]int{}
for i := 0; i < numRows; i++ {
row := []int{}
for j := 0; j < i+1; j++ {
if j == 0 || j == i {
row = append(row, 1)
} else if i > 1 {
row = append(row, result[i-1][j-1]+result[i-1][j])
}
}
result = append(result, row)
}
return result
}
119. Pascal’s Triangle II
题目
Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth row of the Pascal’s triangle.
Notice that the row index starts from 0.

In Pascal’s triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it.
Follow up:
Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(k) extra space?
Example 1:
Input: rowIndex = 3
Output: [1,3,3,1]
Example 2:
Input: rowIndex = 0
Output: [1]
Example 3:
Input: rowIndex = 1
Output: [1,1]
Constraints:
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
题目大意
给定一个非负索引 k,其中 k ≤ 33,返回杨辉三角的第 k 行。
解题思路
-
题目中的三角是杨辉三角,每个数字是
(a+b)^n二项式展开的系数。题目要求我们只能使用 O(k) 的空间。那么需要找到两两项直接的递推关系。由组合知识得知:���=�!�!(�−�)!���−1=�!(�−1)!(�−�+1)!CnmCn**m−1=m!(n−m)!n!=(m−1)!(n−m+1)!n!
于是得到递推公式:
���=���−1×�−�+1�Cnm=Cnm−1×m**n−m+1
利用这个递推公式即可以把空间复杂度优化到 O(k)
代码
package leetcode
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
row := make([]int, rowIndex+1)
row[0] = 1
for i := 1; i <= rowIndex; i++ {
row[i] = row[i-1] * (rowIndex - i + 1) / i
}
return row
}
120. Triangle
题目
Given a triangle, find the minimum path sum from top to bottom. Each step you may move to adjacent numbers on the row below.
For example, given the following triangle
[
[2],
[3,4],
[6,5,7],
[4,1,8,3]
]
The minimum path sum from top to bottom is 11 (i.e., 2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11).
Note:
Bonus point if you are able to do this using only O(n) extra space, where n is the total number of rows in the triangle.
题目大意
给定一个三角形,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。
解题思路
- 求出从三角形顶端到底端的最小和。要求最好用 O(n) 的时间复杂度。
- 这一题最优解是不用辅助空间,直接从下层往上层推。普通解法是用二维数组 DP,稍微优化的解法是一维数组 DP。解法如下:
代码
package leetcode
import (
"math"
)
// 解法一 倒序 DP,无辅助空间
func minimumTotal(triangle [][]int) int {
if triangle == nil {
return 0
}
for row := len(triangle) - 2; row >= 0; row-- {
for col := 0; col < len(triangle[row]); col++ {
triangle[row][col] += min(triangle[row+1][col], triangle[row+1][col+1])
}
}
return triangle[0][0]
}
// 解法二 正常 DP,空间复杂度 O(n)
func minimumTotal1(triangle [][]int) int {
if len(triangle) == 0 {
return 0
}
dp, minNum, index := make([]int, len(triangle[len(triangle)-1])), math.MaxInt64, 0
for ; index < len(triangle[0]); index++ {
dp[index] = triangle[0][index]
}
for i := 1; i < len(triangle); i++ {
for j := len(triangle[i]) - 1; j >= 0; j-- {
if j == 0 {
// 最左边
dp[j] += triangle[i][0]
} else if j == len(triangle[i])-1 {
// 最右边
dp[j] += dp[j-1] + triangle[i][j]
} else {
// 中间
dp[j] = min(dp[j-1]+triangle[i][j], dp[j]+triangle[i][j])
}
}
}
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
if dp[i] < minNum {
minNum = dp[i]
}
}
return minNum
}
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
题目
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
Note that you cannot sell a stock before you buy one.
Example 1:
Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 5
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
Not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price.
Example 2:
Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
题目大意
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。如果你最多只允许完成一笔交易(即买入和卖出一支股票),设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。注意你不能在买入股票前卖出股票。
解题思路
- 题目要求找出股票中能赚的钱最多的差价
- 这一题也有多个解法,可以用 DP,也可以用单调栈
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 模拟 DP
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
if len(prices) < 1 {
return 0
}
min, maxProfit := prices[0], 0
for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
if prices[i]-min > maxProfit {
maxProfit = prices[i] - min
}
if prices[i] < min {
min = prices[i]
}
}
return maxProfit
}
// 解法二 单调栈
func maxProfit1(prices []int) int {
if len(prices) == 0 {
return 0
}
stack, res := []int{prices[0]}, 0
for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
if prices[i] > stack[len(stack)-1] {
stack = append(stack, prices[i])
} else {
index := len(stack) - 1
for ; index >= 0; index-- {
if stack[index] < prices[i] {
break
}
}
stack = stack[:index+1]
stack = append(stack, prices[i])
}
res = max(res, stack[len(stack)-1]-stack[0])
}
return res
}
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
题目
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times).
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Example 1:
Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 7
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Note that you cannot buy on day 1, buy on day 2 and sell them later, as you are
engaging multiple transactions at the same time. You must sell before buying again.
Example 3:
Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
题目大意
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 121 题的加强版。要求输出最大收益,这一题不止买卖一次,可以买卖多次,买卖不能在同一天内操作。
- 最大收益来源,必然是每次跌了就买入,涨到顶峰的时候就抛出。只要有涨峰就开始计算赚的钱,连续涨可以用两两相减累加来计算,两两相减累加,相当于涨到波峰的最大值减去谷底的值。这一点看通以后,题目非常简单。
代码
package leetcode
func maxProfit122(prices []int) int {
profit := 0
for i := 0; i < len(prices)-1; i++ {
if prices[i+1] > prices[i] {
profit += prices[i+1] - prices[i]
}
}
return profit
}
124. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
题目
Given a non-empty binary tree, find the maximum path sum.
For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along the parent-child connections. The path must contain at least one node and does not need to go through the root.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
Output: 6
Example 2:
Input: [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
-10
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Output: 42
题目大意
给定一个非空二叉树,返回其最大路径和。本题中,路径被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,达到任意节点的序列。该路径至少包含一个节点,且不一定经过根节点。
解题思路
- 给出一个二叉树,要求找一条路径使得路径的和是最大的。
- 这一题思路比较简单,递归维护最大值即可。不过需要比较的对象比较多。
maxPathSum(root) = max(maxPathSum(root.Left), maxPathSum(root.Right), maxPathSumFrom(root.Left) (if>0) + maxPathSumFrom(root.Right) (if>0) + root.Val),其中,maxPathSumFrom(root) = max(maxPathSumFrom(root.Left), maxPathSumFrom(root.Right)) + root.Val
代码
package leetcode
import "math"
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
max := math.MinInt32
getPathSum(root, &max)
return max
}
func getPathSum(root *TreeNode, maxSum *int) int {
if root == nil {
return math.MinInt32
}
left := getPathSum(root.Left, maxSum)
right := getPathSum(root.Right, maxSum)
currMax := max(max(left+root.Val, right+root.Val), root.Val)
*maxSum = max(*maxSum, max(currMax, left+right+root.Val))
return currMax
}
125. Valid Palindrome
题目
Given a string, determine if it is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters and ignoring cases.
For example,
"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama" is a palindrome.
"race a car" is not a palindrome.
Note:
Have you consider that the string might be empty? This is a good question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we define empty string as valid palindrome.
题目大意
判断所给的字符串是否是有效的回文串。
解题思路
简单题,按照题意做即可。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"strings"
)
func isPalindrome(s string) bool {
s = strings.ToLower(s)
i, j := 0, len(s)-1
for i < j {
for i < j && !isChar(s[i]) {
i++
}
for i < j && !isChar(s[j]) {
j--
}
if s[i] != s[j] {
return false
}
i++
j--
}
return true
}
// 判断 c 是否是字符或者数字
func isChar(c byte) bool {
if ('a' <= c && c <= 'z') || ('0' <= c && c <= '9') {
return true
}
return false
}
126. Word Ladder II
题目
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary’s word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord, such that:
- Only one letter can be changed at a time
- Each transformed word must exist in the word list. Note that beginWord is not a transformed word.
Note:
- Return an empty list if there is no such transformation sequence.
- All words have the same length.
- All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
- You may assume no duplicates in the word list.
- You may assume beginWord and endWord are non-empty and are not the same.
Example 1:
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output:
[
["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],
["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]
]
Example 2:
Input:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: []
Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
题目大意
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典 wordList,找出所有从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列。转换需遵循如下规则:
- 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
- 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典中的单词。
说明:
- 如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回一个空列表。
- 所有单词具有相同的长度。
- 所有单词只由小写字母组成。
- 字典中不存在重复的单词。
- 你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 127 题的加强版,除了找到路径的长度,还进一步要求输出所有路径。解题思路同第 127 题一样,也是用 BFS 遍历。
- 当前做法不是最优解,是否可以考虑双端 BFS 优化,或者迪杰斯塔拉算法?
代码
package leetcode
func findLadders(beginWord string, endWord string, wordList []string) [][]string {
result, wordMap := make([][]string, 0), make(map[string]bool)
for _, w := range wordList {
wordMap[w] = true
}
if !wordMap[endWord] {
return result
}
// create a queue, track the path
queue := make([][]string, 0)
queue = append(queue, []string{beginWord})
// queueLen is used to track how many slices in queue are in the same level
// if found a result, I still need to finish checking current level cause I need to return all possible paths
queueLen := 1
// use to track strings that this level has visited
// when queueLen == 0, remove levelMap keys in wordMap
levelMap := make(map[string]bool)
for len(queue) > 0 {
path := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
lastWord := path[len(path)-1]
for i := 0; i < len(lastWord); i++ {
for c := 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++ {
nextWord := lastWord[:i] + string(c) + lastWord[i+1:]
if nextWord == endWord {
path = append(path, endWord)
result = append(result, path)
continue
}
if wordMap[nextWord] {
// different from word ladder, don't remove the word from wordMap immediately
// same level could reuse the key.
// delete from wordMap only when currently level is done.
levelMap[nextWord] = true
newPath := make([]string, len(path))
copy(newPath, path)
newPath = append(newPath, nextWord)
queue = append(queue, newPath)
}
}
}
queueLen--
// if queueLen is 0, means finish traversing current level. if result is not empty, return result
if queueLen == 0 {
if len(result) > 0 {
return result
}
for k := range levelMap {
delete(wordMap, k)
}
// clear levelMap
levelMap = make(map[string]bool)
queueLen = len(queue)
}
}
return result
}
127. Word Ladder
题目
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary’s word list, find the length of shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, such that:
- Only one letter can be changed at a time.
- Each transformed word must exist in the word list. Note that beginWord is not a transformed word.
Note:
- Return 0 if there is no such transformation sequence.
- All words have the same length.
- All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
- You may assume no duplicates in the word list.
- You may assume beginWord and endWord are non-empty and are not the same.
Example 1:
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Output: 5
Explanation: As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
Example 2:
Input:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Output: 0
Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore no possible transformation.
题目大意
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列的长度。转换需遵循如下规则:
- 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
- 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典中的单词。
说明:
- 如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
- 所有单词具有相同的长度。
- 所有单词只由小写字母组成。
- 字典中不存在重复的单词。
- 你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
解题思路
- 这一题要求输出从
beginWord变换到endWord最短变换次数。可以用 BFS,从beginWord开始变换,把该单词的每个字母都用'a'~'z'变换一次,生成的数组到wordList中查找,这里用 Map 来记录查找。找得到就入队列,找不到就输出 0 。入队以后按照 BFS 的算法依次遍历完,当所有单词都len(queue)<=0出队以后,整个程序结束。 - 这一题题目中虽然说了要求找到一条最短的路径,但是实际上最短的路径的寻找方法已经告诉你了:
- 每次只变换一个字母
- 每次变换都必须在
wordList中 所以不需要单独考虑何种方式是最短的。
代码
package leetcode
func ladderLength(beginWord string, endWord string, wordList []string) int {
wordMap, que, depth := getWordMap(wordList, beginWord), []string{beginWord}, 0
for len(que) > 0 {
depth++
qlen := len(que)
for i := 0; i < qlen; i++ {
word := que[0]
que = que[1:]
candidates := getCandidates(word)
for _, candidate := range candidates {
if _, ok := wordMap[candidate]; ok {
if candidate == endWord {
return depth + 1
}
delete(wordMap, candidate)
que = append(que, candidate)
}
}
}
}
return 0
}
func getWordMap(wordList []string, beginWord string) map[string]int {
wordMap := make(map[string]int)
for i, word := range wordList {
if _, ok := wordMap[word]; !ok {
if word != beginWord {
wordMap[word] = i
}
}
}
return wordMap
}
func getCandidates(word string) []string {
var res []string
for i := 0; i < 26; i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(word); j++ {
if word[j] != byte(int('a')+i) {
res = append(res, word[:j]+string(int('a')+i)+word[j+1:])
}
}
}
return res
}
128. Longest Consecutive Sequence
题目
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
Your algorithm should run in O(n) complexity.
Example:
Input: [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4.
题目大意
给定一个未排序的整数数组,找出最长连续序列的长度。要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n)。
解题思路
- 给出一个数组,要求找出最长连续序列,输出这个最长的长度。要求时间复杂度为
O(n)。 - 这一题可以先用暴力解决解决,代码见解法三。思路是把每个数都存在
map中,先删去map中没有前一个数nums[i]-1也没有后一个数nums[i]+1的数nums[i],这种数前后都不连续。然后在map中找到前一个数nums[i]-1不存在,但是后一个数nums[i]+1存在的数,这种数是连续序列的起点,那么不断的往后搜,直到序列“断”了。最后输出最长序列的长度。 - 这一题最优的解法是解法一,针对每一个
map中不存在的数n,插入进去都做 2 件事情。第一件事,先查看n - 1和n + 1是否都存在于map中,如果都存在,代表存在连续的序列,那么就更新left,right边界。那么n对应的这个小的子连续序列长度为sum = left + right + 1。第二件事就是更新left和right左右边界对应的length = sum。 - 这一题还可以用并查集解决,见解法二。利用每个数在
nums中的下标,把下标和下标进行union(),具体做法是看前一个数nums[i]-1和后一个数nums[i]+1在map中是否存在,如果存在就union(),最终输出整个并查集中包含最多元素的那个集合的元素总数。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/template"
)
// 解法一 map,时间复杂度 O(n)
func longestConsecutive(nums []int) int {
res, numMap := 0, map[int]int{}
for _, num := range nums {
if numMap[num] == 0 {
left, right, sum := 0, 0, 0
if numMap[num-1] > 0 {
left = numMap[num-1]
} else {
left = 0
}
if numMap[num+1] > 0 {
right = numMap[num+1]
} else {
right = 0
}
// sum: length of the sequence n is in
sum = left + right + 1
numMap[num] = sum
// keep track of the max length
res = max(res, sum)
// extend the length to the boundary(s) of the sequence
// will do nothing if n has no neighbors
numMap[num-left] = sum
numMap[num+right] = sum
} else {
continue
}
}
return res
}
// 解法二 并查集
func longestConsecutive1(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
numMap, countMap, lcs, uf := map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}, 0, template.UnionFind{}
uf.Init(len(nums))
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
countMap[i] = 1
}
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
if _, ok := numMap[nums[i]]; ok {
continue
}
numMap[nums[i]] = i
if _, ok := numMap[nums[i]+1]; ok {
uf.Union(i, numMap[nums[i]+1])
}
if _, ok := numMap[nums[i]-1]; ok {
uf.Union(i, numMap[nums[i]-1])
}
}
for key := range countMap {
parent := uf.Find(key)
if parent != key {
countMap[parent]++
}
if countMap[parent] > lcs {
lcs = countMap[parent]
}
}
return lcs
}
// 解法三 暴力解法,时间复杂度 O(n^2)
func longestConsecutive2(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
numMap, length, tmp, lcs := map[int]bool{}, 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
numMap[nums[i]] = true
}
for key := range numMap {
if !numMap[key-1] && !numMap[key+1] {
delete(numMap, key)
}
}
if len(numMap) == 0 {
return 1
}
for key := range numMap {
if !numMap[key-1] && numMap[key+1] {
length, tmp = 1, key+1
for numMap[tmp] {
length++
tmp++
}
lcs = max(lcs, length)
}
}
return max(lcs, length)
}
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
题目
Given a binary tree containing digits from 0-9 only, each root-to-leaf path could represent a number.
An example is the root-to-leaf path 1->2->3 which represents the number 123.
Find the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
Example 2:
Input: [4,9,0,5,1]
4
/ \
9 0
/ \
5 1
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
题目大意
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放一个 0-9 的数字,每条从根到叶子节点的路径都代表一个数字。例如,从根到叶子节点路径 1->2->3 代表数字 123。计算从根到叶子节点生成的所有数字之和。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 257 题的变形题,第 257 题要求输出每条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,这一题变成了把每一个从根节点到叶子节点的数字都串联起来,再累加每条路径,求出最后的总和。实际做题思路基本没变。运用前序遍历的思想,当从根节点出发一直加到叶子节点,每个叶子节点汇总一次。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
res := 0
dfs(root,0,&res)
return res
}
func dfs(root *TreeNode,sum int,res *int) {
if root == nil{
return
}
sum = sum*10 + root.Val
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil{
*res += sum
return
}
dfs(root.Left,sum,res)
dfs(root.Right,sum,res)
}
130. Surrounded Regions
题目
Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O' (the letter O), capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Example:
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
After running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
Explanation:
Surrounded regions shouldn’t be on the border, which means that any 'O' on the border of the board are not flipped to 'X'. Any 'O' that is not on the border and it is not connected to an 'O' on the border will be flipped to 'X'. Two cells are connected if they are adjacent cells connected horizontally or vertically.
题目大意
给定一个二维的矩阵,包含 ‘X’ 和 ‘O’(字母 O)。找到所有被 ‘X’ 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 ‘O’ 用 ‘X’ 填充。被围绕的区间不会存在于边界上,换句话说,任何边界上的 ‘O’ 都不会被填充为 ‘X’。 任何不在边界上,或不与边界上的 ‘O’ 相连的 ‘O’ 最终都会被填充为 ‘X’。如果两个元素在水平或垂直方向相邻,则称它们是“相连”的。
解题思路
- 给出一张二维地图,要求把地图上非边缘上的 ‘O’ 都用 ‘X’ 覆盖掉。
- 这一题有多种解法。第一种解法是并查集。先将边缘上的 ‘O’ 全部都和一个特殊的点进行
union()。然后再把地图中间的 ‘O’ 都进行union(),最后把和特殊点不是同一个集合的点都标记成 ‘X’。第二种解法是 DFS 或者 BFS,可以先将边缘上的 ‘O’ 先标记成另外一个字符,然后在递归遍历过程中,把剩下的 ‘O’ 都标记成 ‘X’。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/template"
)
// 解法一 并查集
func solve(board [][]byte) {
if len(board) == 0 {
return
}
m, n := len(board[0]), len(board)
uf := template.UnionFind{}
uf.Init(n*m + 1) // 特意多一个特殊点用来标记
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if (i == 0 || i == n-1 || j == 0 || j == m-1) && board[i][j] == 'O' { //棋盘边缘上的 'O' 点
uf.Union(i*m+j, n*m)
} else if board[i][j] == 'O' { //棋盘非边缘上的内部的 'O' 点
if board[i-1][j] == 'O' {
uf.Union(i*m+j, (i-1)*m+j)
}
if board[i+1][j] == 'O' {
uf.Union(i*m+j, (i+1)*m+j)
}
if board[i][j-1] == 'O' {
uf.Union(i*m+j, i*m+j-1)
}
if board[i][j+1] == 'O' {
uf.Union(i*m+j, i*m+j+1)
}
}
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if uf.Find(i*m+j) != uf.Find(n*m) {
board[i][j] = 'X'
}
}
}
}
// 解法二 DFS
func solve1(board [][]byte) {
for i := range board {
for j := range board[i] {
if i == 0 || i == len(board)-1 || j == 0 || j == len(board[i])-1 {
if board[i][j] == 'O' {
dfs130(i, j, board)
}
}
}
}
for i := range board {
for j := range board[i] {
if board[i][j] == '*' {
board[i][j] = 'O'
} else if board[i][j] == 'O' {
board[i][j] = 'X'
}
}
}
}
func dfs130(i, j int, board [][]byte) {
if i < 0 || i > len(board)-1 || j < 0 || j > len(board[i])-1 {
return
}
if board[i][j] == 'O' {
board[i][j] = '*'
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
dfs130(i+dir[k][0], j+dir[k][1], board)
}
}
}
131. Palindrome Partitioning
题目
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.
Example:
Input: "aab"
Output:
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]
题目大意
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
解题思路
- 要求输出一个字符串可以被拆成回文串的所有解,DFS 递归求解即可。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一
func partition131(s string) [][]string {
if s == "" {
return [][]string{}
}
res, pal := [][]string{}, []string{}
findPalindrome(s, 0, "", true, pal, &res)
return res
}
func findPalindrome(str string, index int, s string, isPal bool, pal []string, res *[][]string) {
if index == len(str) {
if isPal {
tmp := make([]string, len(pal))
copy(tmp, pal)
*res = append(*res, tmp)
}
return
}
if index == 0 {
s = string(str[index])
pal = append(pal, s)
findPalindrome(str, index+1, s, isPal && isPalindrome131(s), pal, res)
} else {
temp := pal[len(pal)-1]
s = pal[len(pal)-1] + string(str[index])
pal[len(pal)-1] = s
findPalindrome(str, index+1, s, isPalindrome131(s), pal, res)
pal[len(pal)-1] = temp
if isPalindrome131(temp) {
pal = append(pal, string(str[index]))
findPalindrome(str, index+1, temp, isPal && isPalindrome131(temp), pal, res)
pal = pal[:len(pal)-1]
}
}
return
}
func isPalindrome131(s string) bool {
slen := len(s)
for i, j := 0, slen-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
if s[i] != s[j] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// 解法二
func partition131_1(s string) [][]string {
result := [][]string{}
size := len(s)
if size == 0 {
return result
}
current := make([]string, 0, size)
dfs131(s, 0, current, &result)
return result
}
func dfs131(s string, idx int, cur []string, result *[][]string) {
start, end := idx, len(s)
if start == end {
temp := make([]string, len(cur))
copy(temp, cur)
*result = append(*result, temp)
return
}
for i := start; i < end; i++ {
if isPal(s, start, i) {
dfs131(s, i+1, append(cur, s[start:i+1]), result)
}
}
}
func isPal(str string, s, e int) bool {
for s < e {
if str[s] != str[e] {
return false
}
s++
e--
}
return true
}
135. Candy
题目
There are n children standing in a line. Each child is assigned a rating value given in the integer array ratings.
You are giving candies to these children subjected to the following requirements:
- Each child must have at least one candy.
- Children with a higher rating get more candies than their neighbors.
Return the minimum number of candies you need to have to distribute the candies to the children.
Example 1:
Input: ratings = [1,0,2]
Output: 5
Explanation: You can allocate to the first, second and third child with 2, 1, 2 candies respectively.
Example 2:
Input: ratings = [1,2,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: You can allocate to the first, second and third child with 1, 2, 1 candies respectively.
The third child gets 1 candy because it satisfies the above two conditions.
Constraints:
n == ratings.length1 <= n <= 2 * 10^40 <= ratings[i] <= 2 * 10^4
题目大意
老师想给孩子们分发糖果,有 N 个孩子站成了一条直线,老师会根据每个孩子的表现,预先给他们评分。你需要按照以下要求,帮助老师给这些孩子分发糖果:
- 每个孩子至少分配到 1 个糖果。
- 评分更高的孩子必须比他两侧的邻位孩子获得更多的糖果。
那么这样下来,老师至少需要准备多少颗糖果呢?
解题思路
- 本题的突破口在于,评分更高的孩子必须比他两侧的邻位孩子获得更多的糖果,这句话。这个规则可以理解为 2 条规则,想象成按身高排队,站在下标为 0 的地方往后“看”,评分高即为个子高的,应该比前面个子矮(评分低)的分到糖果多;站在下标为 n - 1 的地方往后“看”,评分高即为个子高的,同样应该比前面个子矮(评分低)的分到糖果多。你可能会有疑问,规则都是一样的,为什么会出现至少需要多少糖果呢?因为可能出现评分一样高的同学。扫描数组两次,处理出每一个学生分别满足左规则或右规则时,最少需要被分得的糖果数量。每个人最终分得的糖果数量即为这两个数量的最大值。两次遍历结束,将所有糖果累加起来即为至少需要准备的糖果数。由于每个人至少分配到 1 个糖果,所以每个人糖果数再加一。
代码
package leetcode
func candy(ratings []int) int {
candies := make([]int, len(ratings))
for i := 1; i < len(ratings); i++ {
if ratings[i] > ratings[i-1] {
candies[i] += candies[i-1] + 1
}
}
for i := len(ratings) - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
if ratings[i] > ratings[i+1] && candies[i] <= candies[i+1] {
candies[i] = candies[i+1] + 1
}
}
total := 0
for _, candy := range candies {
total += candy + 1
}
return total
}
136. Single Number
题目
Given a non-empty array of integers, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
Note:
Your algorithm should have a linear runtime complexity. Could you implement it without using extra memory?
Example 1:
Input: [2,2,1]
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4
题目大意
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。要求算法时间复杂度是线性的,并且不使用额外的辅助空间。
解题思路
- 题目要求不能使用辅助空间,并且时间复杂度只能是线性的。
- 题目为什么要强调有一个数字出现一次,其他的出现两次?我们想到了异或运算的性质:任何一个数字异或它自己都等于0。也就是说,如果我们从头到尾依次异或数组中的每一个数字,那么最终的结果刚好是那个只出现一次的数字,因为那些出现两次的数字全部在异或中抵消掉了。于是最终做法是从头到尾依次异或数组中的每一个数字,那么最终得到的结果就是两个只出现一次的数字的异或结果。因为其他数字都出现了两次,在异或中全部抵消掉了。利用的性质是 x^x = 0。
代码
package leetcode
func singleNumber(nums []int) int {
result := 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
result ^= nums[i]
}
return result
}
137. Single Number II
题目
Given a non-empty array of integers, every element appears three times except for one, which appears exactly once. Find that single one.
Note:
Your algorithm should have a linear runtime complexity. Could you implement it without using extra memory?
Example 1:
Input: [2,2,3,2]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: [0,1,0,1,0,1,99]
Output: 99
题目大意
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。要求算法时间复杂度是线性的,并且不使用额外的辅助空间。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 136 题的加强版。这类题也可以扩展,在数组中每个元素都出现 5 次,找出只出现 1 次的数。
- 本题中要求找出只出现 1 次的数,出现 3 次的数都要被消除。第 136 题是消除出现 2 次的数。这一题也会相当相同的解法,出现 3 次的数也要被消除。定义状态,00、10、01,这 3 个状态。当一个数出现 3 次,那么它每个位置上的 1 出现的次数肯定是 3 的倍数,所以当 1 出现 3 次以后,就归零清除。如何能做到这点呢?仿造
三进制(00,01,10)就可以做到。 - 变量 ones 中记录遍历中每个位上出现 1 的个数。将它与 A[i] 进行异或,目的是:
- 每位上两者都是 1 的,表示历史统计结果 ones 出现1次、A[i]中又出现 1 次,则是出现 2 次,需要进位到 twos 变量中。
- 每位上两者分别为 0、1 的,加入到 ones 统计结果中。
- 最后还要 & ^twos ,是为了能做到三进制,出现 3 次就清零。例如 ones = x,那么 twos = 0,当 twos = x,那么 ones = 0;
- 变量 twos 中记录遍历中每个位上出现 1 ,2次 的个数。与 A[i] 进行异或的目的和上述描述相同,不再赘述。
在 golang 中,&^ 表示 AND NOT 的意思。这里的 ^ 作为一元操作符,表示按位取反 (^0001 0100 = 1110 1011),X &^ Y 的意思是将 X 中与 Y 相异的位保留,相同的位清零。
在 golang 中没有 Java 中的 ~ 位操作运算符,Java 中的 ~ 运算符代表按位取反。这个操作就想当于 golang 中的 ^ 运算符当做一元运算符使用的效果。
| (twos,ones) | xi | (twos’',ones’) | ones’ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 0 | 00 | 0 |
| 00 | 1 | 01 | 1 |
| 01 | 0 | 01 | 1 |
| 01 | 1 | 10 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| 10 | 1 | 00 | 0 |
- 第一步,先将 ones -> ones’。通过观察可以看出 ones = (ones ^ nums[i]) & ^twos
| (twos,ones’) | xi | twos’ |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | 0 | 0 |
| 01 | 1 | 0 |
| 01 | 0 | 0 |
| 00 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 |
- 第二步,再将 twos -> twos’。这一步需要用到前一步的 ones。通过观察可以看出 twos = (twos ^ nums[i]) & ^ones。
这一题还可以继续扩展,在数组中每个元素都出现 5 次,找出只出现 1 次的数。那该怎么做呢?思路还是一样的,模拟一个五进制,5 次就会消除。代码如下:
// 解法一
func singleNumberIII(nums []int) int {
na, nb, nc := 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
nb = nb ^ (nums[i] & na)
na = (na ^ nums[i]) & ^nc
nc = nc ^ (nums[i] & ^na & ^nb)
}
return na & ^nb & ^nc
}
// 解法二
func singleNumberIIII(nums []int) int {
twos, threes, ones := 0xffffffff, 0xffffffff, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
threes = threes ^ (nums[i] & twos)
twos = (twos ^ nums[i]) & ^ones
ones = ones ^ (nums[i] & ^twos & ^threes)
}
return ones
}
代码
package leetcode
func singleNumberII(nums []int) int {
ones, twos := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
ones = (ones ^ nums[i]) & ^twos
twos = (twos ^ nums[i]) & ^ones
}
return ones
}
// 以下是拓展题
// 在数组中每个元素都出现 5 次,找出只出现 1 次的数。
// 解法一
func singleNumberIIIII(nums []int) int {
na, nb, nc := 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
nb = nb ^ (nums[i] & na)
na = (na ^ nums[i]) & ^nc
nc = nc ^ (nums[i] & ^na & ^nb)
}
return na & ^nb & ^nc
}
// 解法二
func singleNumberIIIII1(nums []int) int {
twos, threes, ones := 0xffffffff, 0xffffffff, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
threes = threes ^ (nums[i] & twos)
twos = (twos ^ nums[i]) & ^ones
ones = ones ^ (nums[i] & ^twos & ^threes)
}
return ones
}
138. Copy List with Random Pointer
题目
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Example 1:
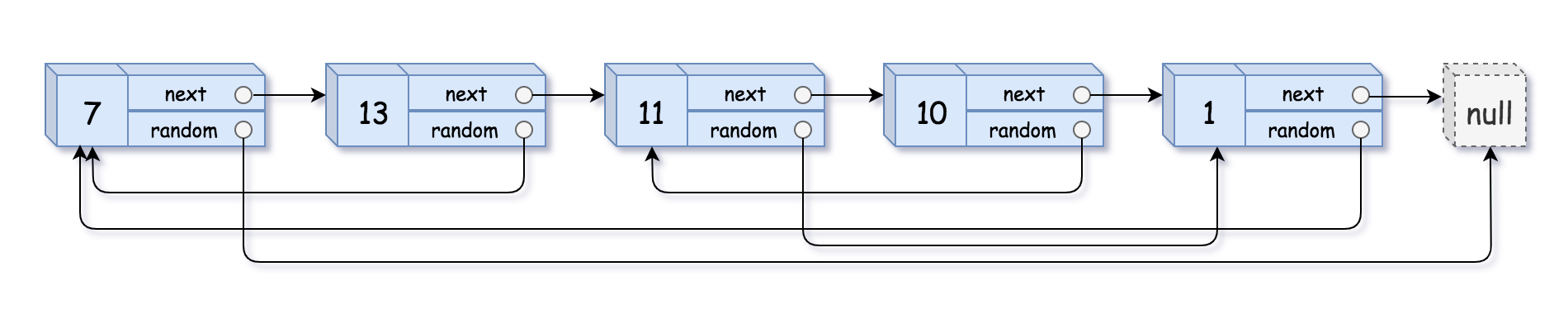
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
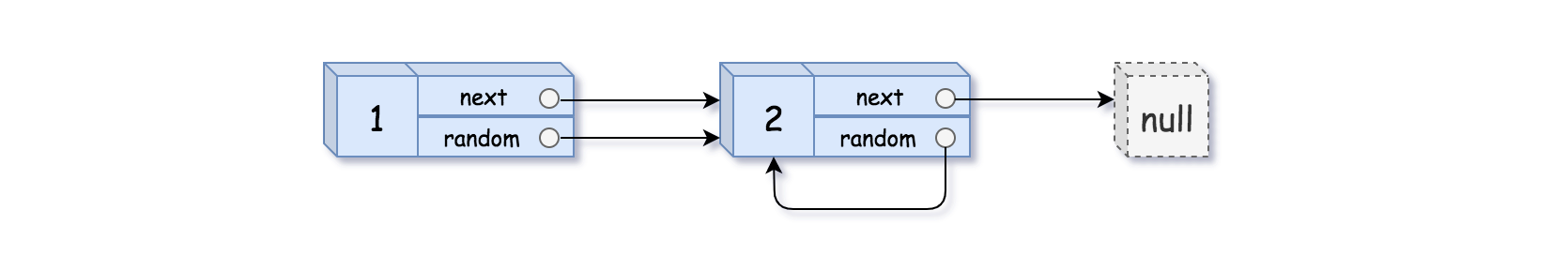
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
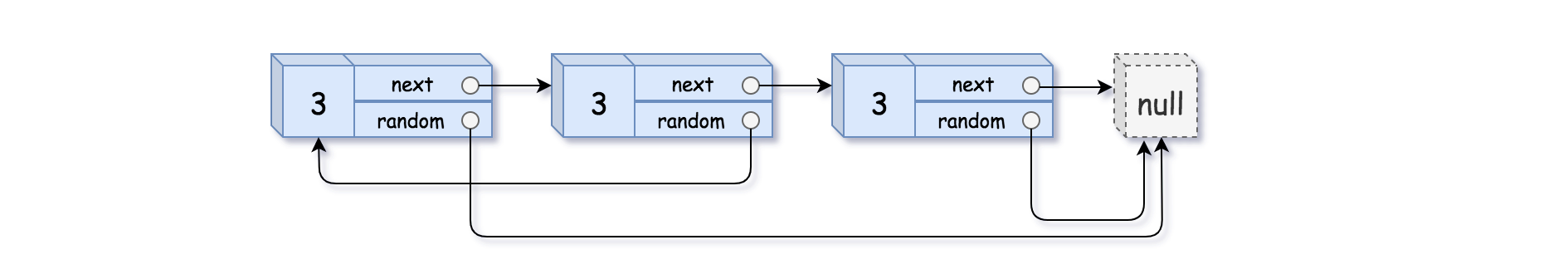
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: Given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomis null or pointing to a node in the linked list.- The number of nodes will not exceed 1000.
题目大意
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
我们用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
- val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
- random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
解题思路
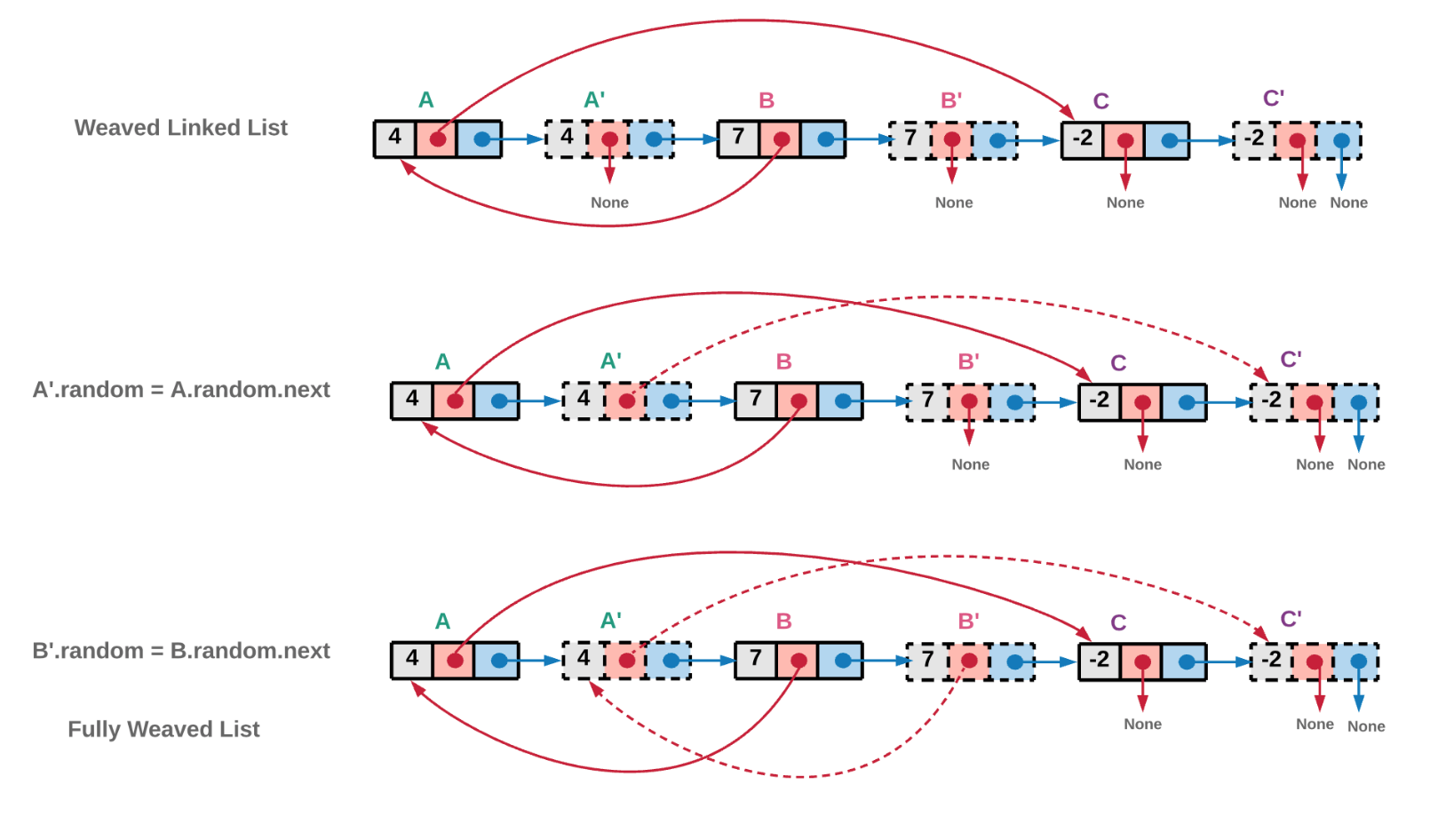
-
这道题严格意义上是数据结构题,根据给定的数据结构,对它进行深拷贝。
-
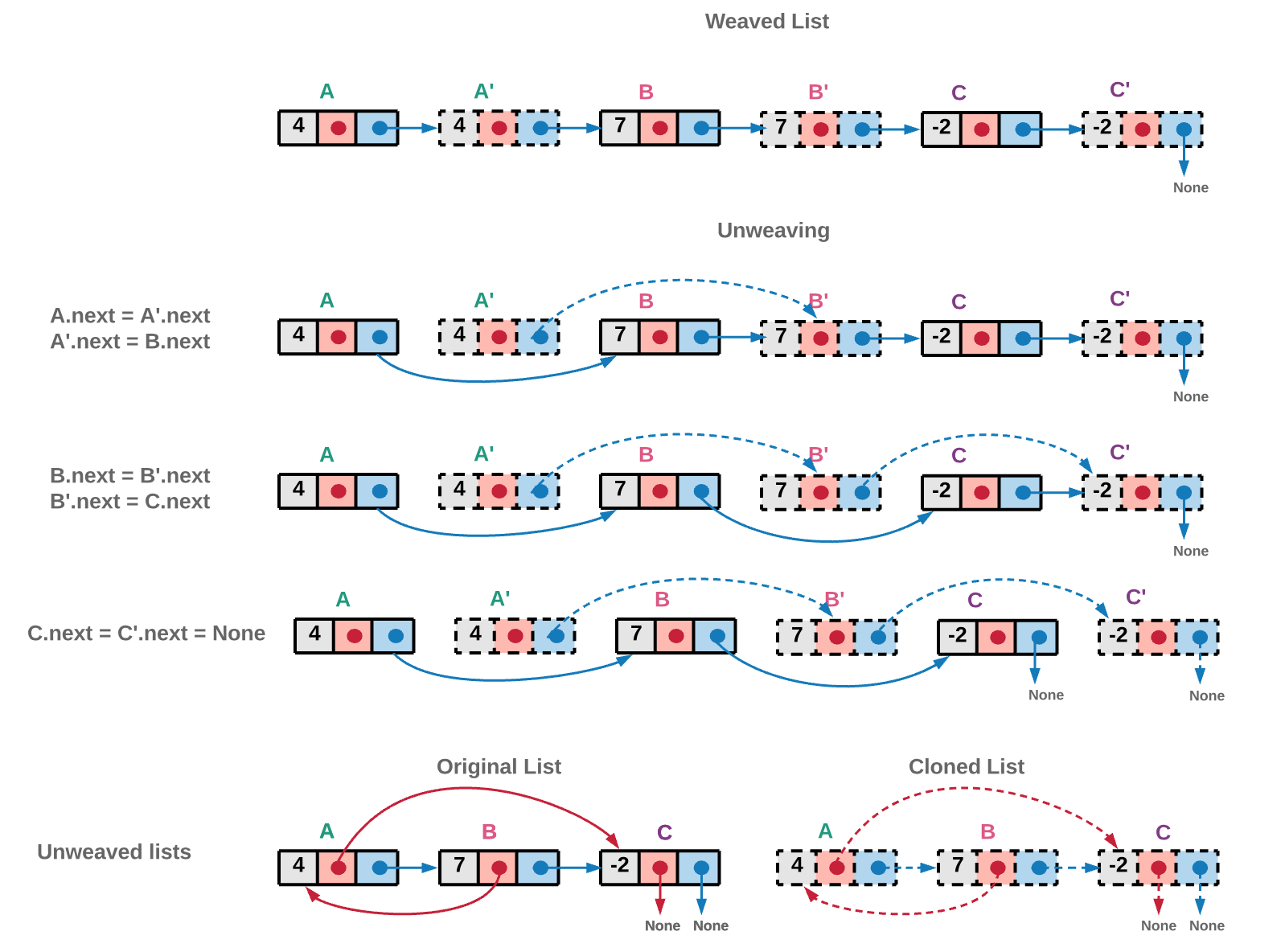
先将每个节点都复制一份,放在它的 next 节点中。如此穿插的复制一份链表。
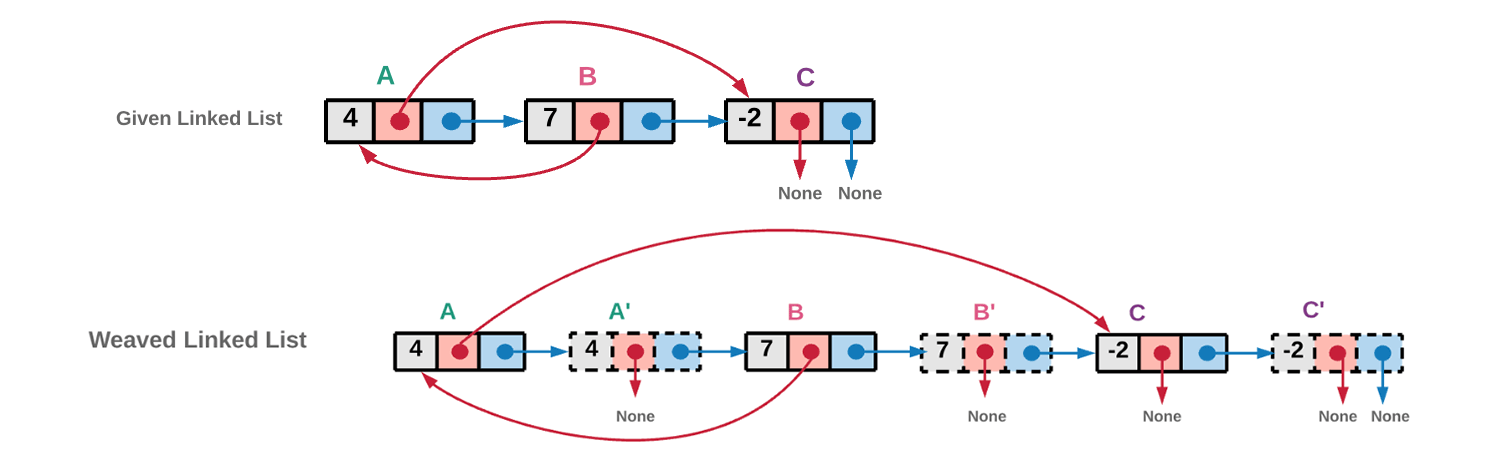
再将穿插版的链表的 random 指针指向正确的位置。
再将穿插版的链表的 next 指针指向正确的位置。最后分开这交织在一起的两个链表的头节点,即可分开 2 个链表。
代码
package leetcode
// Node define
type Node struct {
Val int
Next *Node
Random *Node
}
func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
tempHead := copyNodeToLinkedList(head)
return splitLinkedList(tempHead)
}
func splitLinkedList(head *Node) *Node {
cur := head
head = head.Next
for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil {
cur.Next, cur = cur.Next.Next, cur.Next
}
return head
}
func copyNodeToLinkedList(head *Node) *Node {
cur := head
for cur != nil {
node := &Node{
Val: cur.Val,
Next: cur.Next,
}
cur.Next, cur = node, cur.Next
}
cur = head
for cur != nil {
if cur.Random != nil {
cur.Next.Random = cur.Random.Next
}
cur = cur.Next.Next
}
return head
}
141. Linked List Cycle
题目
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
Follow up: Can you solve it without using extra space?
题目大意
判断链表是否有环,不能使用额外的空间。
解题思路
给 2 个指针,一个指针是另外一个指针的下一个指针。快指针一次走 2 格,慢指针一次走 1 格。如果存在环,那么前一个指针一定会经过若干圈之后追上慢的指针。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// ListNode define
type ListNode = structures.ListNode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func hasCycle(head *ListNode) bool {
fast := head
slow := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
fast = fast.Next.Next
slow = slow.Next
if fast == slow {
return true
}
}
return false
}
142. Linked List Cycle II
题目
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
题目大意
判断链表是否有环,不能使用额外的空间。如果有环,输出环的起点指针,如果没有环,则输出空。
解题思路
这道题是第 141 题的加强版。在判断是否有环的基础上,还需要输出环的第一个点。
分析一下判断环的原理。fast 指针一次都 2 步,slow 指针一次走 1 步。令链表 head 到环的一个点需要 x1 步,从环的第一个点到相遇点需要 x2 步,从环中相遇点回到环的第一个点需要 x3 步。那么环的总长度是 x2 + x3 步。
fast 和 slow 会相遇,说明他们走的时间是相同的,可以知道他们走的路程有以下的关系:
fast 的 t = (x1 + x2 + x3 + x2) / 2
slow 的 t = (x1 + x2) / 1
x1 + x2 + x3 + x2 = 2 * (x1 + x2)
所以 x1 = x3
所以 2 个指针相遇以后,如果 slow 继续往前走,fast 指针回到起点 head,两者都每次走一步,那么必定会在环的起点相遇,相遇以后输出这个点即是结果。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return nil
}
isCycle, slow := hasCycle142(head)
if !isCycle {
return nil
}
fast := head
for fast != slow {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return fast
}
func hasCycle142(head *ListNode) (bool, *ListNode) {
fast := head
slow := head
for slow != nil && fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
fast = fast.Next.Next
slow = slow.Next
if fast == slow {
return true, slow
}
}
return false, nil
}
143. Reorder List
题目
Given a singly linked list L: L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln, reorder it to: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example 1:
Given 1->2->3->4, reorder it to 1->4->2->3.
Example 2:
Given 1->2->3->4->5, reorder it to 1->5->2->4->3.
题目大意
按照指定规则重新排序链表:第一个元素和最后一个元素排列在一起,接着第二个元素和倒数第二个元素排在一起,接着第三个元素和倒数第三个元素排在一起。
解题思路
最近简单的方法是先把链表存储到数组里,然后找到链表中间的结点,按照规则拼接即可。这样时间复杂度是 O(n),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
更好的做法是结合之前几道题的操作:链表逆序,找中间结点。
先找到链表的中间结点,然后利用逆序区间的操作,如 [第 92 题里的 reverseBetween() 操作,只不过这里的反转区间是从中点一直到末尾。最后利用 2 个指针,一个指向头结点,一个指向中间结点,开始拼接最终的结果。这种做法的时间复杂度是 O(n),空间复杂度是 O(1)。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
// 解法一 单链表
func reorderList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
// 寻找中间结点
p1 := head
p2 := head
for p2.Next != nil && p2.Next.Next != nil {
p1 = p1.Next
p2 = p2.Next.Next
}
// 反转链表后半部分 1->2->3->4->5->6 to 1->2->3->6->5->4
preMiddle := p1
preCurrent := p1.Next
for preCurrent.Next != nil {
current := preCurrent.Next
preCurrent.Next = current.Next
current.Next = preMiddle.Next
preMiddle.Next = current
}
// 重新拼接链表 1->2->3->6->5->4 to 1->6->2->5->3->4
p1 = head
p2 = preMiddle.Next
for p1 != preMiddle {
preMiddle.Next = p2.Next
p2.Next = p1.Next
p1.Next = p2
p1 = p2.Next
p2 = preMiddle.Next
}
return head
}
// 解法二 数组
func reorderList1(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
array := listToArray(head)
length := len(array)
if length == 0 {
return head
}
cur := head
last := head
for i := 0; i < len(array)/2; i++ {
tmp := &ListNode{Val: array[length-1-i], Next: cur.Next}
cur.Next = tmp
cur = tmp.Next
last = tmp
}
if length%2 == 0 {
last.Next = nil
} else {
cur.Next = nil
}
return head
}
func listToArray(head *ListNode) []int {
array := []int{}
if head == nil {
return array
}
cur := head
for cur != nil {
array = append(array, cur.Val)
cur = cur.Next
}
return array
}
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
题目
Given a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example:
Input: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
Output: [1,2,3]
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
题目大意
先根遍历一颗树。
解题思路
两种递归的实现方法,见代码。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一 递归
func preorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
res := []int{}
if root != nil {
res = append(res, root.Val)
tmp := preorderTraversal(root.Left)
for _, t := range tmp {
res = append(res, t)
}
tmp = preorderTraversal(root.Right)
for _, t := range tmp {
res = append(res, t)
}
}
return res
}
// 解法二 递归
func preorderTraversal1(root *TreeNode) []int {
var result []int
preorder(root, &result)
return result
}
func preorder(root *TreeNode, output *[]int) {
if root != nil {
*output = append(*output, root.Val)
preorder(root.Left, output)
preorder(root.Right, output)
}
}
// 解法三 非递归,用栈模拟递归过程
func preorderTraversal2(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
stack, res := []*TreeNode{}, []int{}
stack = append(stack, root)
for len(stack) != 0 {
node := stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
if node != nil {
res = append(res, node.Val)
}
if node.Right != nil {
stack = append(stack, node.Right)
}
if node.Left != nil {
stack = append(stack, node.Left)
}
}
return res
}
145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
题目
Given a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example:
Input: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
Output: [3,2,1]
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
题目大意
后根遍历一颗树。
解题思路
递归的实现方法,见代码。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func postorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
var result []int
postorder(root, &result)
return result
}
func postorder(root *TreeNode, output *[]int) {
if root != nil {
postorder(root.Left, output)
postorder(root.Right, output)
*output = append(*output, root.Val)
}
}
146. LRU Cache
题目
Design a data structure that follows the constraints of a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache.
Implement the LRUCache class:
LRUCache(int capacity)Initialize the LRU cache with positive sizecapacity.int get(int key)Return the value of thekeyif the key exists, otherwise return1.void put(int key, int value)Update the value of thekeyif thekeyexists. Otherwise, add thekey-valuepair to the cache. If the number of keys exceeds thecapacityfrom this operation, evict the least recently used key.
Follow up:Could you do get and put in O(1) time complexity?
Example 1:
Input
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
Output
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
Explanation
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // cache is {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // cache is {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // return 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // LRU key was 2, evicts key 2, cache is {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // LRU key was 1, evicts key 1, cache is {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // return -1 (not found)
lRUCache.get(3); // return 3
lRUCache.get(4); // return 4
Constraints:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 30000 <= value <= 104- At most
3 * 104calls will be made togetandput.
题目大意
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。 实现 LRUCache 类:
- LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
- int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
- void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
解题思路
- 这一题是 LRU 经典面试题,详细解释见第三章模板。
代码
package leetcode
type LRUCache struct {
head, tail *Node
Keys map[int]*Node
Cap int
}
type Node struct {
Key, Val int
Prev, Next *Node
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LRUCache {
return LRUCache{Keys: make(map[int]*Node), Cap: capacity}
}
func (this *LRUCache) Get(key int) int {
if node, ok := this.Keys[key]; ok {
this.Remove(node)
this.Add(node)
return node.Val
}
return -1
}
func (this *LRUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
if node, ok := this.Keys[key]; ok {
node.Val = value
this.Remove(node)
this.Add(node)
return
} else {
node = &Node{Key: key, Val: value}
this.Keys[key] = node
this.Add(node)
}
if len(this.Keys) > this.Cap {
delete(this.Keys, this.tail.Key)
this.Remove(this.tail)
}
}
func (this *LRUCache) Add(node *Node) {
node.Prev = nil
node.Next = this.head
if this.head != nil {
this.head.Prev = node
}
this.head = node
if this.tail == nil {
this.tail = node
this.tail.Next = nil
}
}
func (this *LRUCache) Remove(node *Node) {
if node == this.head {
this.head = node.Next
node.Next = nil
return
}
if node == this.tail {
this.tail = node.Prev
node.Prev.Next = nil
node.Prev = nil
return
}
node.Prev.Next = node.Next
node.Next.Prev = node.Prev
}
147. Insertion Sort List
题目
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.

A graphical example of insertion sort. The partial sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list. With each iteration one element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list
Algorithm of Insertion Sort:
Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and growing a sorted output list. At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list, and inserts it there. It repeats until no input elements remain.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5
题目大意
链表的插入排序
解题思路
按照题意做即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func insertionSortList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return head
}
newHead := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: nil} // 这里初始化不要直接指向 head,为了下面循环可以统一处理
cur, pre := head, newHead
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
for pre.Next != nil && pre.Next.Val < cur.Val {
pre = pre.Next
}
cur.Next = pre.Next
pre.Next = cur
pre = newHead // 归位,重头开始
cur = next
}
return newHead.Next
}
148. Sort List
题目
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5
题目大意
链表的排序,要求时间复杂度必须是 O(n log n),空间复杂度是 O(1)
解题思路
这道题只能用归并排序才能符合要求。归并排序需要的 2 个操作在其他题目已经出现过了,取中间点是第 876 题,合并 2 个有序链表是第 21 题。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func sortList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
length := 0
cur := head
for cur != nil {
length++
cur = cur.Next
}
if length <= 1 {
return head
}
middleNode := middleNode(head)
cur = middleNode.Next
middleNode.Next = nil
middleNode = cur
left := sortList(head)
right := sortList(middleNode)
return mergeTwoLists(left, right)
}
func middleNode(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
p1 := head
p2 := head
for p2.Next != nil && p2.Next.Next != nil {
p1 = p1.Next
p2 = p2.Next.Next
}
return p1
}
func mergeTwoLists(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
if l1 == nil {
return l2
}
if l2 == nil {
return l1
}
if l1.Val < l2.Val {
l1.Next = mergeTwoLists(l1.Next, l2)
return l1
}
l2.Next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.Next)
return l2
}
150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
题目
Evaluate the value of an arithmetic expression in Reverse Polish Notation.
Valid operators are +, -, *, /. Each operand may be an integer or another expression.
Note:
- Division between two integers should truncate toward zero.
- The given RPN expression is always valid. That means the expression would always evaluate to a result and there won’t be any divide by zero operation.
Example 1:
Input: ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
Output: 9
Explanation: ((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
Example 2:
Input: ["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"]
Output: 6
Explanation: (4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
Example 3:
Input: ["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"]
Output: 22
Explanation:
((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / (12 * -11))) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5
= ((10 * 0) + 17) + 5
= (0 + 17) + 5
= 17 + 5
= 22
题目大意
计算逆波兰表达式。
解题思路
这道题就是经典的考察栈的知识的题目。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"strconv"
)
func evalRPN(tokens []string) int {
stack := make([]int, 0, len(tokens))
for _, token := range tokens {
v, err := strconv.Atoi(token)
if err == nil {
stack = append(stack, v)
} else {
num1, num2 := stack[len(stack)-2], stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-2]
switch token {
case "+":
stack = append(stack, num1+num2)
case "-":
stack = append(stack, num1-num2)
case "*":
stack = append(stack, num1*num2)
case "/":
stack = append(stack, num1/num2)
}
}
}
return stack[0]
}