LeetCode题解4
151. Reverse Words in a String
题目
Given an input string, reverse the string word by word.
Example 1:
Input: "the sky is blue"
Output: "blue is sky the"
Example 2:
Input: " hello world! "
Output: "world! hello"
Explanation: Your reversed string should not contain leading or trailing spaces.
Example 3:
Input: "a good example"
Output: "example good a"
Explanation: You need to reduce multiple spaces between two words to a single space in the reversed string.
Note:
- A word is defined as a sequence of non-space characters.
- Input string may contain leading or trailing spaces. However, your reversed string should not contain leading or trailing spaces.
- You need to reduce multiple spaces between two words to a single space in the reversed string.
Follow up:
For C programmers, try to solve it in-place in O(1) extra space.
题目大意
给定一个字符串,逐个翻转字符串中的每个单词。
说明:
- 无空格字符构成一个单词。
- 输入字符串可以在前面或者后面包含多余的空格,但是反转后的字符不能包括。
- 如果两个单词间有多余的空格,将反转后单词间的空格减少到只含一个。
进阶:
- 请选用 C 语言的用户尝试使用 O(1) 额外空间复杂度的原地解法。
解题思路
- 给出一个中间有空格分隔的字符串,要求把这个字符串按照单词的维度前后翻转。
- 依照题意,先把字符串按照空格分隔成每个小单词,然后把单词前后翻转,最后再把每个单词中间添加空格。
代码
package leetcode
import "strings"
func reverseWords151(s string) string {
ss := strings.Fields(s)
reverse151(&ss, 0, len(ss)-1)
return strings.Join(ss, " ")
}
func reverse151(m *[]string, i int, j int) {
for i <= j {
(*m)[i], (*m)[j] = (*m)[j], (*m)[i]
i++
j--
}
}
152. Maximum Product Subarray
题目
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the largest product.
Example 1:
Input: [2,3,-2,4]
Output: 6
Explanation: [2,3] has the largest product 6.
Example 2:
Input: [-2,0,-1]
Output: 0
Explanation: The result cannot be 2, because [-2,-1] is not a subarray.
题目大意
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找出一个序列中乘积最大的连续子序列(该序列至少包含一个数)。
解题思路
- 给出一个数组,要求找出这个数组中连续元素乘积最大的值。
- 这一题是 DP 的题,状态转移方程是:最大值是
Max(f(n)) = Max( Max(f(n-1)) * n, Min(f(n-1)) * n);最小值是Min(f(n)) = Min( Max(f(n-1)) * n, Min(f(n-1)) * n)。只要动态维护这两个值,如果最后一个数是负数,最大值就在负数 * 最小值中产生,如果最后一个数是正数,最大值就在正数 * 最大值中产生。
代码
package leetcode
func maxProduct(nums []int) int {
minimum, maximum, res := nums[0], nums[0], nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
if nums[i] < 0 {
maximum, minimum = minimum, maximum
}
maximum = max(nums[i], maximum*nums[i])
minimum = min(nums[i], minimum*nums[i])
res = max(res, maximum)
}
return res
}
153. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
题目
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
Find the minimum element.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Example 1:
Input: [3,4,5,1,2]
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]
Output: 0
题目大意
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。请找出其中最小的元素。
你可以假设数组中不存在重复元素。
解题思路
- 给出一个原本从小到大排序过的数组,但是在某一个分割点上,把数组切分后的两部分对调位置,数值偏大的放到了数组的前部。求这个数组中最小的元素。
- 求数组最小的元素其实就是找分割点,前一个数比当前数大,后一个数比当前数也要大。可以用二分搜索查找,需要查找的两个有序区间。时间复杂度 O(log n)。这一题也可以用暴力解法,从头开始遍历,动态维护一个最小值即可,时间复杂度 O(n)。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 二分
func findMin(nums []int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low < high {
if nums[low] < nums[high] {
return nums[low]
}
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if nums[mid] >= nums[low] {
low = mid + 1
} else {
high = mid
}
}
return nums[low]
}
// 解法二 二分
func findMin1(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
if len(nums) == 1 {
return nums[0]
}
if nums[len(nums)-1] > nums[0] {
return nums[0]
}
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if nums[low] < nums[high] {
return nums[low]
}
if (mid == len(nums)-1 && nums[mid-1] > nums[mid]) || (mid < len(nums)-1 && mid > 0 && nums[mid-1] > nums[mid] && nums[mid] < nums[mid+1]) {
return nums[mid]
}
if nums[mid] > nums[low] && nums[low] > nums[high] { // mid 在数值大的一部分区间里
low = mid + 1
} else if nums[mid] < nums[low] && nums[low] > nums[high] { // mid 在数值小的一部分区间里
high = mid - 1
} else {
if nums[low] == nums[mid] {
low++
}
if nums[high] == nums[mid] {
high--
}
}
}
return -1
}
// 解法三 暴力
func findMin2(nums []int) int {
min := nums[0]
for _, num := range nums[1:] {
if min > num {
min = num
}
}
return min
}
154. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
题目
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
Find the minimum element.
The array may contain duplicates.
Example 1:
Input: [1,3,5]
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: [2,2,2,0,1]
Output: 0
Note:
- This is a follow up problem to Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array.
- Would allow duplicates affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
题目大意
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。请找出其中最小的元素。
注意数组中可能存在重复的元素。
解题思路
- 给出一个原本从小到大排序过的数组,注意数组中有重复的元素。但是在某一个分割点上,把数组切分后的两部分对调位置,数值偏大的放到了数组的前部。求这个数组中最小的元素。
- 这一题是第 153 题的加强版,增加了重复元素的条件。但是实际做法还是没有变,还是用二分搜索,只不过在相等元素上多增加一个判断即可。时间复杂度 O(log n)。
代码
package leetcode
func findMin154(nums []int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low < high {
if nums[low] < nums[high] {
return nums[low]
}
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if nums[mid] > nums[low] {
low = mid + 1
} else if nums[mid] == nums[low] {
low++
} else {
high = mid
}
}
return nums[low]
}
155. Min Stack
题目
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
push(x) – Push element x onto stack. pop() – Removes the element on top of the stack. top() – Get the top element. getMin() – Retrieve the minimum element in the stack.
Example:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> Returns -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> Returns 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> Returns -2.
题目大意
这道题是一个数据结构实现题。要求实现一个栈的类,实现 push()、pop()、top()、getMin()。
解题思路
按照题目要求实现即可。
代码
package leetcode
// MinStack define
type MinStack struct {
elements, min []int
l int
}
/** initialize your data structure here. */
// Constructor155 define
func Constructor155() MinStack {
return MinStack{make([]int, 0), make([]int, 0), 0}
}
// Push define
func (this *MinStack) Push(x int) {
this.elements = append(this.elements, x)
if this.l == 0 {
this.min = append(this.min, x)
} else {
min := this.GetMin()
if x < min {
this.min = append(this.min, x)
} else {
this.min = append(this.min, min)
}
}
this.l++
}
func (this *MinStack) Pop() {
this.l--
this.min = this.min[:this.l]
this.elements = this.elements[:this.l]
}
func (this *MinStack) Top() int {
return this.elements[this.l-1]
}
func (this *MinStack) GetMin() int {
return this.min[this.l-1]
}
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
题目
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
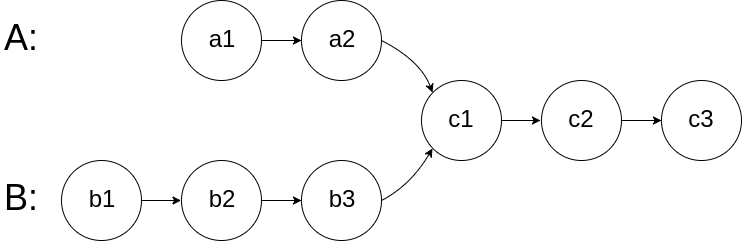
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
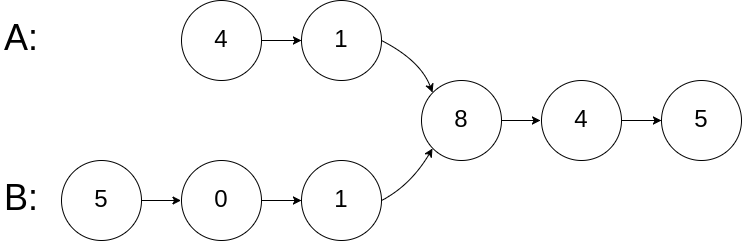
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
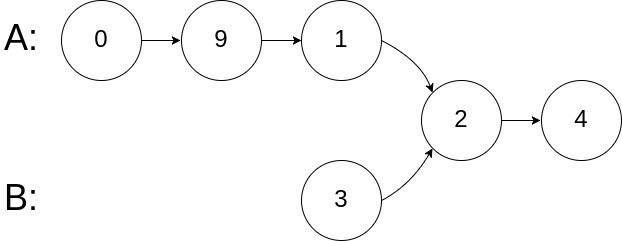
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
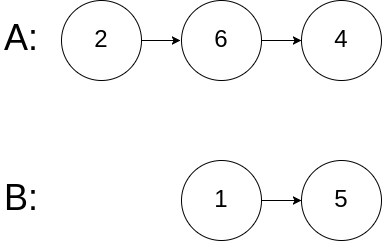
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
题目大意
找到 2 个链表的交叉点。
解题思路
这道题的思路其实类似链表找环。
给定的 2 个链表的长度如果一样长,都从头往后扫即可。如果不一样长,需要先“拼成”一样长。把 B 拼接到 A 后面,把 A 拼接到 B 后面。这样 2 个链表的长度都是 A + B。再依次扫描比较 2 个链表的结点是否相同。
代码
package leetcode
import "fmt"
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
//boundary check
if headA == nil || headB == nil {
return nil
}
a := headA
b := headB
//if a & b have different len, then we will stop the loop after second iteration
for a != b {
//for the end of first iteration, we just reset the pointer to the head of another linkedlist
if a == nil {
a = headB
} else {
a = a.Next
}
if b == nil {
b = headA
} else {
b = b.Next
}
fmt.Printf("a = %v b = %v\n", a, b)
}
return a
}
162. Find Peak Element
题目
A peak element is an element that is greater than its neighbors.
Given an input array nums, where nums[i] ≠ nums[i+1], find a peak element and return its index.
The array may contain multiple peaks, in that case return the index to any one of the peaks is fine.
You may imagine that nums[-1] = nums[n] = -∞.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: 3 is a peak element and your function should return the index number 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,1,3,5,6,4]
Output: 1 or 5
Explanation: Your function can return either index number 1 where the peak element is 2,
or index number 5 where the peak element is 6.
Note:
Your solution should be in logarithmic complexity.
题目大意
峰值元素是指其值大于左右相邻值的元素。给定一个输入数组 nums,其中 nums[i] ≠ nums[i+1],找到峰值元素并返回其索引。数组可能包含多个峰值,在这种情况下,返回任何一个峰值所在位置即可。你可以假设 nums[-1] = nums[n] = -∞。
说明:
- 你的解法应该是 O(logN) 时间复杂度的。
解题思路
- 给出一个数组,数组里面存在多个“山峰”,(山峰的定义是,下标
i比i-1、i+1位置上的元素都要大),找到这个“山峰”,并输出其中一个山峰的下标。 - 这一题是第 852 题的伪加强版,第 852 题中只存在一个山峰,这一题存在多个山峰。但是实际上搜索的代码是一样的,因为此题只要求随便输出一个山峰的下标即可。思路同第 852 题。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 二分
func findPeakElement(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 || len(nums) == 1 {
return 0
}
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if (mid == len(nums)-1 && nums[mid-1] < nums[mid]) || (mid > 0 && nums[mid-1] < nums[mid] && (mid <= len(nums)-2 && nums[mid+1] < nums[mid])) || (mid == 0 && nums[1] < nums[0]) {
return mid
}
if mid > 0 && nums[mid-1] < nums[mid] {
low = mid + 1
}
if mid > 0 && nums[mid-1] > nums[mid] {
high = mid - 1
}
if mid == low {
low++
}
if mid == high {
high--
}
}
return -1
}
// 解法二 二分
func findPeakElement1(nums []int) int {
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low < high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
// 如果 mid 较大,则左侧存在峰值,high = m,如果 mid + 1 较大,则右侧存在峰值,low = mid + 1
if nums[mid] > nums[mid+1] {
high = mid
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
}
return low
}
164. Maximum Gap
题目
Given an unsorted array, find the maximum difference between the successive elements in its sorted form.
Return 0 if the array contains less than 2 elements.
Example 1:
Input: [3,6,9,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: The sorted form of the array is [1,3,6,9], either
(3,6) or (6,9) has the maximum difference 3.
Example 2:
Input: [10]
Output: 0
Explanation: The array contains less than 2 elements, therefore return 0.
Note:
- You may assume all elements in the array are non-negative integers and fit in the 32-bit signed integer range.
- Try to solve it in linear time/space.
题目大意
在数组中找到 2 个数字之间最大的间隔。要求尽量用 O(1) 的时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
解题思路
虽然使用排序算法可以 AC 这道题。先排序,然后依次计算数组中两两数字之间的间隔,找到最大的一个间隔输出即可。
这道题满足要求的做法是基数排序。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 快排
func maximumGap(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) < 2 {
return 0
}
quickSort164(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
res := 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums)-1; i++ {
if (nums[i+1] - nums[i]) > res {
res = nums[i+1] - nums[i]
}
}
return res
}
func partition164(a []int, lo, hi int) int {
pivot := a[hi]
i := lo - 1
for j := lo; j < hi; j++ {
if a[j] < pivot {
i++
a[j], a[i] = a[i], a[j]
}
}
a[i+1], a[hi] = a[hi], a[i+1]
return i + 1
}
func quickSort164(a []int, lo, hi int) {
if lo >= hi {
return
}
p := partition164(a, lo, hi)
quickSort164(a, lo, p-1)
quickSort164(a, p+1, hi)
}
// 解法二 基数排序
func maximumGap1(nums []int) int {
if nums == nil || len(nums) < 2 {
return 0
}
// m is the maximal number in nums
m := nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
m = max(m, nums[i])
}
exp := 1 // 1, 10, 100, 1000 ...
R := 10 // 10 digits
aux := make([]int, len(nums))
for (m / exp) > 0 { // through all digits from LSB to MSB
count := make([]int, R)
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
count[(nums[i]/exp)%10]++
}
for i := 1; i < len(count); i++ {
count[i] += count[i-1]
}
for i := len(nums) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
tmp := count[(nums[i]/exp)%10]
tmp--
aux[tmp] = nums[i]
count[(nums[i]/exp)%10] = tmp
}
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
nums[i] = aux[i]
}
exp *= 10
}
maxValue := 0
for i := 1; i < len(aux); i++ {
maxValue = max(maxValue, aux[i]-aux[i-1])
}
return maxValue
}
func max(a int, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
题目
Given an array of integers that is already sorted in ascending order, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number.
The function twoSum should return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to the target, where index1 must be less than index2.
Note:
- Your returned answers (both index1 and index2) are not zero-based.
- You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Input: numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 2.
题目大意
找出两个数之和等于 target 的两个数字,要求输出它们的下标。注意一个数字不能使用 2 次。下标从小到大输出。假定题目一定有一个解。
解题思路
这一题比第 1 题 Two Sum 的问题还要简单,因为这里数组是有序的。可以直接用第一题的解法解决这道题。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 这一题可以利用数组有序的特性
func twoSum167(numbers []int, target int) []int {
i, j := 0, len(numbers)-1
for i < j {
if numbers[i]+numbers[j] == target {
return []int{i + 1, j + 1}
}
if numbers[i]+numbers[j] < target {
i++
} else {
j--
}
}
return nil
}
// 解法二 不管数组是否有序,空间复杂度比上一种解法要多 O(n)
func twoSum167_1(numbers []int, target int) []int {
m := make(map[int]int)
for i := 0; i < len(numbers); i++ {
another := target - numbers[i]
if idx, ok := m[another]; ok {
return []int{idx + 1, i + 1}
}
m[numbers[i]] = i
}
return nil
}
168. Excel Sheet Column Title
题目
Given a positive integer, return its corresponding column title as appear in an Excel sheet.
For example:
1 -> A
2 -> B
3 -> C
...
26 -> Z
27 -> AA
28 -> AB
...
Example 1:
Input: 1
Output: "A"
Example 2:
Input: 28
Output: "AB"
Example 3:
Input: 701
Output: "ZY"
题目大意
给定一个正整数,返回它在 Excel 表中相对应的列名称。
例如,
1 -> A
2 -> B
3 -> C
...
26 -> Z
27 -> AA
28 -> AB
...
解题思路
- 给定一个正整数,返回它在 Excel 表中的对应的列名称
- 简单题。这一题就类似短除法的计算过程。以 26 进制的字母编码。按照短除法先除,然后余数逆序输出即可。
代码
package leetcode
func convertToTitle(n int) string {
result := []byte{}
for n > 0 {
result = append(result, 'A'+byte((n-1)%26))
n = (n - 1) / 26
}
for i, j := 0, len(result)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
result[i], result[j] = result[j], result[i]
}
return string(result)
}
169. Majority Element
题目
Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times.
You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always exist in the array.
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,3]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
Output: 2
题目大意
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的众数。众数是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在众数。
解题思路
- 题目要求找出数组中出现次数大于
⌊ n/2 ⌋次的数。要求空间复杂度为 O(1)。简单题。 - 这一题利用的算法是 Boyer-Moore Majority Vote Algorithm。 https://www.zhihu.com/question/49973163/answer/235921864
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 时间复杂度 O(n) 空间复杂度 O(1)
func majorityElement(nums []int) int {
res, count := nums[0], 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
if count == 0 {
res, count = nums[i], 1
} else {
if nums[i] == res {
count++
} else {
count--
}
}
}
return res
}
// 解法二 时间复杂度 O(n) 空间复杂度 O(n)
func majorityElement1(nums []int) int {
m := make(map[int]int)
for _, v := range nums {
m[v]++
if m[v] > len(nums)/2 {
return v
}
}
return 0
}
171. Excel Sheet Column Number
题目
Given a column title as appear in an Excel sheet, return its corresponding column number.
For example:
A -> 1
B -> 2
C -> 3
...
Z -> 26
AA -> 27
AB -> 28
...
Example 1:
Input: "A"
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: "AB"
Output: 28
Example 3:
Input: "ZY"
Output: 701
题目大意
给定一个 Excel 表格中的列名称,返回其相应的列序号。
解题思路
- 给出 Excel 中列的名称,输出其对应的列序号。
- 简单题。这一题是第 168 题的逆序题。按照 26 进制还原成十进制即可。
代码
package leetcode
func titleToNumber(s string) int {
val, res := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
val = int(s[i] - 'A' + 1)
res = res*26 + val
}
return res
}
172. Factorial Trailing Zeroes
题目
Given an integer n, return the number of trailing zeroes in n!.
Example 1:
Input: 3
Output: 0
Explanation: 3! = 6, no trailing zero.
Example 2:
Input: 5
Output: 1
Explanation: 5! = 120, one trailing zero.
Note: Your solution should be in logarithmic time complexity.
题目大意
给定一个整数 n,返回 n! 结果尾数中零的数量。说明: 你算法的时间复杂度应为 O(log n) 。
解题思路
- 给出一个数 n,要求 n!末尾 0 的个数。
- 这是一道数学题。计算 N 的阶乘有多少个后缀 0,即计算 N! 里有多少个 10,也是计算 N! 里有多少个 2 和 5(分解质因数),最后结果即 2 的个数和 5 的个数取较小值。每两个数字就会多一个质因数 2,而每五个数字才多一个质因数 5。每 5 个数字就会多一个质因数 5。0
4 的阶乘里没有质因数 5,59 的阶乘里有 1 个质因数 5,10~14 的阶乘里有 2 个质因数 5,依此类推。所以 0 的个数即为min(阶乘中 5 的个数和 2 的个数)。 - N! 有多少个后缀 0,即 N! 有多少个质因数 5。N! 有多少个质因数 5,即 N 可以划分成多少组 5个数字一组,加上划分成多少组 25 个数字一组,加上划分多少组成 125 个数字一组,等等。即
res = N/5 + N/(5^2) + N/(5^3) + ... = ((N / 5) / 5) / 5 /...。最终算法复杂度为 O(logN)。
代码
package leetcode
func trailingZeroes(n int) int {
if n/5 == 0 {
return 0
}
return n/5 + trailingZeroes(n/5)
}
173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
题目
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
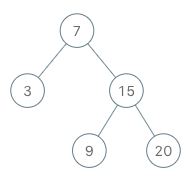
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // return 3
iterator.next(); // return 7
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 9
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 15
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 20
iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
题目大意
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器。调用 next() 将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数。
解题思路
- 用优先队列解决即可
代码
package leetcode
import (
"container/heap"
"github.com/halfrost/leetcode-go/structures"
)
// TreeNode define
type TreeNode = structures.TreeNode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// BSTIterator define
type BSTIterator struct {
pq PriorityQueueOfInt
count int
}
// Constructor173 define
func Constructor173(root *TreeNode) BSTIterator {
result, pq := []int{}, PriorityQueueOfInt{}
postorder(root, &result)
for _, v := range result {
heap.Push(&pq, v)
}
bs := BSTIterator{pq: pq, count: len(result)}
return bs
}
func postorder(root *TreeNode, output *[]int) {
if root != nil {
postorder(root.Left, output)
postorder(root.Right, output)
*output = append(*output, root.Val)
}
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
func (this *BSTIterator) Next() int {
this.count--
return heap.Pop(&this.pq).(int)
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
func (this *BSTIterator) HasNext() bool {
return this.count != 0
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(root);
* param_1 := obj.Next();
* param_2 := obj.HasNext();
*/
type PriorityQueueOfInt []int
func (pq PriorityQueueOfInt) Len() int {
return len(pq)
}
func (pq PriorityQueueOfInt) Less(i, j int) bool {
return pq[i] < pq[j]
}
func (pq PriorityQueueOfInt) Swap(i, j int) {
pq[i], pq[j] = pq[j], pq[i]
}
func (pq *PriorityQueueOfInt) Push(x interface{}) {
item := x.(int)
*pq = append(*pq, item)
}
func (pq *PriorityQueueOfInt) Pop() interface{} {
n := len(*pq)
item := (*pq)[n-1]
*pq = (*pq)[:n-1]
return item
}
174. Dungeon Game
题目
The demons had captured the princess (P) and imprisoned her in the bottom-right corner of a dungeon. The dungeon consists of M x N rooms laid out in a 2D grid. Our valiant knight (K) was initially positioned in the top-left room and must fight his way through the dungeon to rescue the princess.
The knight has an initial health point represented by a positive integer. If at any point his health point drops to 0 or below, he dies immediately.
Some of the rooms are guarded by demons, so the knight loses health (negative integers) upon entering these rooms; other rooms are either empty (0’s) or contain magic orbs that increase the knight’s health (positive integers).
In order to reach the princess as quickly as possible, the knight decides to move only rightward or downward in each step.
Write a function to determine the knight’s minimum initial health so that he is able to rescue the princess.
For example, given the dungeon below, the initial health of the knight must be at least 7 if he follows the optimal path RIGHT-> RIGHT -> DOWN -> DOWN.
Note:
- The knight’s health has no upper bound.
- Any room can contain threats or power-ups, even the first room the knight enters and the bottom-right room where the princess is imprisoned.
题目大意
一些恶魔抓住了公主(P)并将她关在了地下城的右下角。地下城是由 M x N 个房间组成的二维网格。我们英勇的骑士(K)最初被安置在左上角的房间里,他必须穿过地下城并通过对抗恶魔来拯救公主。
骑士的初始健康点数为一个正整数。如果他的健康点数在某一时刻降至 0 或以下,他会立即死亡。
有些房间由恶魔守卫,因此骑士在进入这些房间时会失去健康点数(若房间里的值为负整数,则表示骑士将损失健康点数);其他房间要么是空的(房间里的值为 0),要么包含增加骑士健康点数的魔法球(若房间里的值为正整数,则表示骑士将增加健康点数)。
为了尽快到达公主,骑士决定每次只向右或向下移动一步。编写一个函数来计算确保骑士能够拯救到公主所需的最低初始健康点数。
说明:
- 骑士的健康点数没有上限。
- 任何房间都可能对骑士的健康点数造成威胁,也可能增加骑士的健康点数,包括骑士进入的左上角房间以及公主被监禁的右下角房间。
解题思路
-
在二维地图上给出每个格子扣血数,负数代表扣血,正数代表补血。左上角第一个格子是起点,右下角最后一个格子是终点。问骑士初始最少多少血才能走完迷宫,顺利营救位于终点的公主。需要注意的是,起点和终点都会对血量进行影响。每到一个格子,骑士的血都不能少于 1,一旦少于 1 点血,骑士就会死去。
-
这一题首先想到的解题思路是动态规划。从终点逆推回起点。
dp[i][j]代表骑士进入坐标为(i,j)的格子之前最少的血量值。 那么dp[m-1][n-1]应该同时满足两个条件,dp[m-1][n-1] + dungeon[m-1][n-1] ≥ 1并且dp[m-1][n-1] ≥ 1,由于这两个不等式的方向是相同的,取交集以后,起决定作用的是数轴最右边的数,即max(1-dungeon[m-1][n-1] , 1)。算出dp[m-1][n-1]以后,接着可以推出dp[m-1][i]这一行和dp[i][n-1]这一列的值。因为骑士只能往右走和往下走。往回推,即只能往上走和往左走。到这里,DP 的初始条件都准备好了。那么状态转移方程是什么呢?分析一般的情况,dp[i][j]这个值应该是和dp[i+1][j]和dp[i][j+1]这两者有关系。即dp[i][j]经过自己本格子的扣血以后,要能至少满足下一行和右一列格子血量的最少要求。并且自己的血量也应该≥1。即需要满足下面这两组不等式。 上面不等式中第一组不等式是满足下一行格子的最低血量要求,第二组不等式是满足右一列格子的最低血量要求。第一个式子化简即
上面不等式中第一组不等式是满足下一行格子的最低血量要求,第二组不等式是满足右一列格子的最低血量要求。第一个式子化简即 dp[i][j] = max(1, dp[i+1][j]-dungeon[i][j]),第二个式子化简即dp[i][j] = max(1, dp[i][j+1]-dungeon[i][j])。求得了这两种走法的最低血量值,从这两个值里面取最小,即是当前格子所需的最低血量,所以状态转移方程为dp[i][j] = min(max(1, dp[i][j+1]-dungeon[i][j]), max(1, dp[i+1][j]-dungeon[i][j]))。DP 完成以后,dp[0][0]中记录的就是骑士初始最低血量值。时间复杂度 O(mn),空间复杂度 O(mn)。 -
这一题还可以用二分搜索来求解。骑士的血量取值范围一定是在
[1,+∞)这个区间内。那么二分这个区间,每次二分的中间值,再用 dp 在地图中去判断是否能到达终点,如果能,就缩小搜索空间至[1,mid],否则搜索空间为[mid + 1,+∞)。时间复杂度 O(mn log math.MaxInt64),空间复杂度 O(m*n)。
代码
package leetcode
import "math"
// 解法一 动态规划
func calculateMinimumHP(dungeon [][]int) int {
if len(dungeon) == 0 {
return 0
}
m, n := len(dungeon), len(dungeon[0])
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, n)
}
dp[m-1][n-1] = max(1-dungeon[m-1][n-1], 1)
for i := n - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
dp[m-1][i] = max(1, dp[m-1][i+1]-dungeon[m-1][i])
}
for i := m - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
dp[i][n-1] = max(1, dp[i+1][n-1]-dungeon[i][n-1])
}
for i := m - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
for j := n - 2; j >= 0; j-- {
dp[i][j] = min(max(1, dp[i][j+1]-dungeon[i][j]), max(1, dp[i+1][j]-dungeon[i][j]))
}
}
return dp[0][0]
}
// 解法二 二分搜索
func calculateMinimumHP1(dungeon [][]int) int {
low, high := 1, math.MaxInt64
for low < high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if canCross(dungeon, mid) {
high = mid
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
}
return low
}
func canCross(dungeon [][]int, start int) bool {
m, n := len(dungeon), len(dungeon[0])
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, n)
}
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(dp[i]); j++ {
if i == 0 && j == 0 {
dp[i][j] = start + dungeon[0][0]
} else {
a, b := math.MinInt64, math.MinInt64
if i > 0 && dp[i-1][j] > 0 {
a = dp[i-1][j] + dungeon[i][j]
}
if j > 0 && dp[i][j-1] > 0 {
b = dp[i][j-1] + dungeon[i][j]
}
dp[i][j] = max(a, b)
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1] > 0
}
179. Largest Number
题目
Given a list of non negative integers, arrange them such that they form the largest number.
Example 1:
Input: [10,2]
Output: "210"
Example 2:
Input: [3,30,34,5,9]
Output: "9534330"
Note:
The result may be very large, so you need to return a string instead of an integer.
题目大意
给出一个数组,要求排列这些数组里的元素,使得最终排列出来的数字是最大的。
解题思路
这一题很容易想到把数字都转化为字符串,利用字符串比较,来排序,这样 9 开头的一定排在最前面。不过这样做有一个地方是错误的,比如:“3” 和 “30” 比较,“30” 比 “3” 的字符序要大,这样排序以后就出错了。实际上就这道题而言, “3” 应该排在 “30” 前面。
在比较 2 个字符串大小的时候,不单纯的只用字符串顺序进行比较,还加入一个顺序。
aStr := a + b
bStr := b + a
通过比较 aStr 和 bStr 的大小来得出是 a 大还是 b 大。
举个例子,还是 “3” 和 “30” 的例子,比较这 2 个字符串的大小。
aStr := "3" + "30" = "330"
bStr := "30" + "3" = "303"
通过互相补齐位数之后再进行比较,就没有问题了。很显然这里 “3” 比 “30” 要大。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"strconv"
)
func largestNumber(nums []int) string {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return ""
}
numStrs := toStringArray(nums)
quickSortString(numStrs, 0, len(numStrs)-1)
res := ""
for _, str := range numStrs {
if res == "0" && str == "0" {
continue
}
res = res + str
}
return res
}
func toStringArray(nums []int) []string {
strs := make([]string, 0)
for _, num := range nums {
strs = append(strs, strconv.Itoa(num))
}
return strs
}
func partitionString(a []string, lo, hi int) int {
pivot := a[hi]
i := lo - 1
for j := lo; j < hi; j++ {
ajStr := a[j] + pivot
pivotStr := pivot + a[j]
if ajStr > pivotStr { // 这里的判断条件是关键
i++
a[j], a[i] = a[i], a[j]
}
}
a[i+1], a[hi] = a[hi], a[i+1]
return i + 1
}
func quickSortString(a []string, lo, hi int) {
if lo >= hi {
return
}
p := partitionString(a, lo, hi)
quickSortString(a, lo, p-1)
quickSortString(a, p+1, hi)
}
187. Repeated DNA Sequences
题目
All DNA is composed of a series of nucleotides abbreviated as A, C, G, and T, for Example: “ACGAATTCCG”. When studying DNA, it is sometimes useful to identify repeated sequences within the DNA.
Write a function to find all the 10-letter-long sequences (substrings) that occur more than once in a DNA molecule.
Example:
Input: s = "AAAAACCCCCAAAAACCCCCCAAAAAGGGTTT"
Output: ["AAAAACCCCC", "CCCCCAAAAA"]
题目大意
所有 DNA 由一系列缩写为 A,C,G 和 T 的核苷酸组成,例如:“ACGAATTCCG”。在研究 DNA 时,识别 DNA 中的重复序列有时会对研究非常有帮助。编写一个函数来查找 DNA 分子中所有出现超多一次的10个字母长的序列(子串)。
解题思路
- 这一题不用位运算比较好做,维护一个长度为 10 的字符串,在 map 中出现次数 > 1 就输出。
- 用位运算想做这一题,需要动态的维护长度为 10 的 hashkey,先计算开头长度为 9 的 hash,在往后面扫描的过程中,如果长度超过了 10 ,就移除 hash 开头的一个字符,加入后面一个字符。具体做法是先将 ATCG 变成 00,01,10,11 的编码,那么长度为 10 ,hashkey 就需要维护在 20 位。mask = 0xFFFFF 就是 20 位的。维护了 hashkey 以后,根据这个 hashkey 进行去重和统计频次。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一
func findRepeatedDnaSequences(s string) []string {
if len(s) < 10 {
return nil
}
charMap, mp, result := map[uint8]uint32{'A': 0, 'C': 1, 'G': 2, 'T': 3}, make(map[uint32]int, 0), []string{}
var cur uint32
for i := 0; i < 9; i++ { // 前9位,忽略
cur = cur<<2 | charMap[s[i]]
}
for i := 9; i < len(s); i++ {
cur = ((cur << 2) & 0xFFFFF) | charMap[s[i]]
if mp[cur] == 0 {
mp[cur] = 1
} else if mp[cur] == 1 { // >2,重复
mp[cur] = 2
result = append(result, s[i-9:i+1])
}
}
return result
}
// 解法二
func findRepeatedDnaSequences1(s string) []string {
if len(s) < 10 {
return []string{}
}
ans, cache := make([]string, 0), make(map[string]int)
for i := 0; i <= len(s)-10; i++ {
curr := string(s[i : i+10])
if cache[curr] == 1 {
ans = append(ans, curr)
}
cache[curr]++
}
return ans
}
189. Rotate Array
题目
Given an array, rotate the array to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.
Follow up:
- Try to come up as many solutions as you can, there are at least 3 different ways to solve this problem.
- Could you do it in-place with O(1) extra space?
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
Output: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2
Output: [3,99,-1,-100]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [99,-1,-100,3]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [3,99,-1,-100]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 10^4-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 10 <= k <= 10^5
题目大意
给定一个数组,将数组中的元素向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
解题思路
- 解法二,使用一个额外的数组,先将原数组下标为 i 的元素移动到
(i+k) mod n的位置,再将剩下的元素拷贝回来即可。 - 解法一,由于题目要求不能使用额外的空间,所以本题最佳解法不是解法二。翻转最终态是,末尾
k mod n个元素移动至了数组头部,剩下的元素右移k mod n个位置至最尾部。确定了最终态以后再变换就很容易。先将数组中所有元素从头到尾翻转一次,尾部的所有元素都到了头部,然后再将[0,(k mod n) − 1]区间内的元素翻转一次,最后再将[k mod n, n − 1]区间内的元素翻转一次,即可满足题目要求。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)
func rotate(nums []int, k int) {
k %= len(nums)
reverse(nums)
reverse(nums[:k])
reverse(nums[k:])
}
func reverse(a []int) {
for i, n := 0, len(a); i < n/2; i++ {
a[i], a[n-1-i] = a[n-1-i], a[i]
}
}
// 解法二 时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)
func rotate1(nums []int, k int) {
newNums := make([]int, len(nums))
for i, v := range nums {
newNums[(i+k)%len(nums)] = v
}
copy(nums, newNums)
}
190. Reverse Bits
题目
Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
Example 1:
Input: 00000010100101000001111010011100
Output: 00111001011110000010100101000000
Explanation: The input binary string 00000010100101000001111010011100 represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is 00111001011110000010100101000000.
Example 2:
Input: 11111111111111111111111111111101
Output: 10111111111111111111111111111111
Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 represents the unsigned integer 4294967293, so return 3221225471 which its binary representation is 10101111110010110010011101101001.
Note:
- Note that in some languages such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, both input and output will be given as signed integer type and should not affect your implementation, as the internal binary representation of the integer is the same whether it is signed or unsigned.
- In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2’s complement notation. Therefore, in Example 2 above the input represents the signed integer
-3and the output represents the signed integer-1073741825.
题目大意
颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。提示:
- 请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型。在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不应影响您的实现,因为无论整数是有符号的还是无符号的,其内部的二进制表示形式都是相同的。
- 在 Java 中,编译器使用二进制补码记法来表示有符号整数。因此,在上面的 示例 2 中,输入表示有符号整数 -3,输出表示有符号整数 -1073741825。
解题思路
- 简单题,要求反转 32 位的二进制位。
- 把 num 往右移动,不断的消灭右边最低位的 1,将这个 1 给 res,res 不断的左移即可实现反转二进制位的目的。
代码
package leetcode
func reverseBits(num uint32) uint32 {
var res uint32
for i := 0; i < 32; i++ {
res = res<<1 | num&1
num >>= 1
}
return res
}
191. Number of 1 Bits
题目
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and return the number of ‘1’ bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight).
Example 1:
Input: 00000000000000000000000000001011
Output: 3
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
Example 2:
Input: 00000000000000000000000010000000
Output: 1
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000010000000 has a total of one '1' bit.
Example 3:
Input: 11111111111111111111111111111101
Output: 31
Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 has a total of thirty one '1' bits.
Note:
- Note that in some languages such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as signed integer type and should not affect your implementation, as the internal binary representation of the integer is the same whether it is signed or unsigned.
- In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2’s complement notation. Therefore, in Example 3 above the input represents the signed integer
-3.
题目大意
编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数,返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为汉明重量)。
解题思路
- 求 uint32 数的二进制位中 1 的个数。
- 这一题的解题思路就是利用二进制位操作。
X = X & ( X -1 )这个操作可以清除最低位的二进制位 1,利用这个操作,直至把数清零。操作了几次即为有几个二进制位 1 。 - 最简单的方法即是直接调用库函数
bits.OnesCount(uint(num))。
代码
package leetcode
import "math/bits"
// 解法一
func hammingWeight(num uint32) int {
return bits.OnesCount(uint(num))
}
// 解法二
func hammingWeight1(num uint32) int {
count := 0
for num != 0 {
num = num & (num - 1)
count++
}
return count
}
198. House Robber
题目
You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security system connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night.
Given a list of non-negative integers representing the amount of money of each house, determine the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3).
Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4.
Example 2:
Input: [2,7,9,3,1]
Output: 12
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) and rob house 5 (money = 1).
Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.
题目大意
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你在不触动警报装置的情况下,能够偷窃到的最高金额。
解题思路
- 你是一个专业的小偷,打算洗劫一条街的所有房子。每个房子里面有不同价值的宝物,但是如果你选择偷窃连续的 2 栋房子,就会触发警报系统,编程求出你最多可以偷窃价值多少的宝物?
- 这一题可以用 DP 来解答,也可以用找规律的方法来解答。
- DP 的状态定义是:
dp[i]代表抢nums[0,i]这个区间内房子的最大值,状态转移方程是dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], nums[i]+dp[i-2])。可以优化迭代的过程,用两个临时变量来存储中间结果,以节约辅助空间。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 DP
func rob198(nums []int) int {
n := len(nums)
if n == 0 {
return 0
}
if n == 1 {
return nums[0]
}
// dp[i] 代表抢 nums[0...i] 房子的最大价值
dp := make([]int, n)
dp[0], dp[1] = nums[0], max(nums[1], nums[0])
for i := 2; i < n; i++ {
dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], nums[i]+dp[i-2])
}
return dp[n-1]
}
// 解法二 DP 优化辅助空间,把迭代的值保存在 2 个变量中
func rob198_1(nums []int) int {
n := len(nums)
if n == 0 {
return 0
}
curMax, preMax := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
tmp := curMax
curMax = max(curMax, nums[i]+preMax)
preMax = tmp
}
return curMax
}
// 解法三 模拟
func rob(nums []int) int {
// a 对于偶数位上的最大值的记录
// b 对于奇数位上的最大值的记录
a, b := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
if i%2 == 0 {
a = max(a+nums[i], b)
} else {
b = max(a, b+nums[i])
}
}
return max(a, b)
}
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
题目
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1, 3, 4]
Explanation:
1 <---
/ \
2 3 <---
\ \
5 4 <---
题目大意
从右边看一个树,输出看到的数字。注意有遮挡。
解题思路
- 这一题是按层序遍历的变种题。按照层序把每层的元素都遍历出来,然后依次取每一层的最右边的元素即可。用一个队列即可实现。
- 第 102 题和第 107 题都是按层序遍历的。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
res := []int{}
if root == nil {
return res
}
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(queue) > 0 {
n := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if queue[i].Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[i].Left)
}
if queue[i].Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, queue[i].Right)
}
}
res = append(res, queue[n-1].Val)
queue = queue[n:]
}
return res
}
200. Number of Islands
题目
Given a 2d grid map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), count the number of islands. An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1:
Input:
11110
11010
11000
00000
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input:
11000
11000
00100
00011
Output: 3
题目大意
给定一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
解题思路
- 要求找出地图中的孤岛。孤岛的含义是四周被海水包围的岛。
- 这一题可以按照第 79 题的思路进行搜索,只要找到为 “1” 的岛以后,从这里开始搜索这周连通的陆地,也都标识上访问过。每次遇到新的 “1” 且没有访问过,就相当于遇到了新的岛屿了。
代码
package leetcode
func numIslands(grid [][]byte) int {
m := len(grid)
if m == 0 {
return 0
}
n := len(grid[0])
if n == 0 {
return 0
}
res, visited := 0, make([][]bool, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j] {
searchIslands(grid, &visited, i, j)
res++
}
}
}
return res
}
func searchIslands(grid [][]byte, visited *[][]bool, x, y int) {
(*visited)[x][y] = true
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
nx := x + dir[i][0]
ny := y + dir[i][1]
if isInBoard(grid, nx, ny) && !(*visited)[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == '1' {
searchIslands(grid, visited, nx, ny)
}
}
}