LeetCode题解2
51. N-Queens
题目
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens’ placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
Example:
Input: 4
Output: [
[".Q..", // Solution 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // Solution 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above.
题目大意
给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。每一种解法包含一个明确的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 ‘Q’ 和 ‘.’ 分别代表了皇后和空位。
解题思路
- 求解 n 皇后问题
- 利用 col 数组记录列信息,col 有
n列。用 dia1,dia2 记录从左下到右上的对角线,从左上到右下的对角线的信息,dia1 和 dia2 分别都有2*n-1个。 - dia1 对角线的规律是
i + j 是定值,例如[0,0],为 0;[1,0]、[0,1] 为 1;[2,0]、[1,1]、[0,2] 为 2; - dia2 对角线的规律是
i - j 是定值,例如[0,7],为 -7;[0,6]、[1,7] 为 -6;[0,5]、[1,6]、[2,7] 为 -5;为了使他们从 0 开始,i - j + n - 1 偏移到 0 开始,所以 dia2 的规律是i - j + n - 1 为定值。 - 还有一个位运算的方法,每行只能选一个位置放皇后,那么对每行遍历可能放皇后的位置。如何高效判断哪些点不能放皇后呢?这里的做法毕竟巧妙,把所有之前选过的点按照顺序存下来,然后根据之前选的点到当前行的距离,就可以快速判断是不是会有冲突。举个例子: 假如在 4 皇后问题中,如果第一二行已经选择了位置 [1, 3],那么在第三行选择时,首先不能再选 1, 3 列了,而对于第三行, 1 距离长度为2,所以它会影响到 -1, 3 两个列。同理,3 在第二行,距离第三行为 1,所以 3 会影响到列 2, 4。由上面的结果,我们知道 -1, 4 超出边界了不用去管,别的不能选的点是 1, 2, 3,所以第三行就只能选 0。在代码实现中,可以在每次遍历前根据之前选择的情况生成一个 occupied 用来记录当前这一行,已经被选了的和由于之前皇后攻击范围所以不能选的位置,然后只选择合法的位置进入到下一层递归。另外就是预处理了一个皇后放不同位置的字符串,这样这些字符串在返回结果的时候是可以在内存中复用的,省一点内存。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 DFS
func solveNQueens(n int) [][]string {
col, dia1, dia2, row, res := make([]bool, n), make([]bool, 2*n-1), make([]bool, 2*n-1), []int{}, [][]string{}
putQueen(n, 0, &col, &dia1, &dia2, &row, &res)
return res
}
// 尝试在一个n皇后问题中, 摆放第index行的皇后位置
func putQueen(n, index int, col, dia1, dia2 *[]bool, row *[]int, res *[][]string) {
if index == n {
*res = append(*res, generateBoard(n, row))
return
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
// 尝试将第index行的皇后摆放在第i列
if !(*col)[i] && !(*dia1)[index+i] && !(*dia2)[index-i+n-1] {
*row = append(*row, i)
(*col)[i] = true
(*dia1)[index+i] = true
(*dia2)[index-i+n-1] = true
putQueen(n, index+1, col, dia1, dia2, row, res)
(*col)[i] = false
(*dia1)[index+i] = false
(*dia2)[index-i+n-1] = false
*row = (*row)[:len(*row)-1]
}
}
return
}
func generateBoard(n int, row *[]int) []string {
board := []string{}
res := ""
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
res += "."
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
board = append(board, res)
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
tmp := []byte(board[i])
tmp[(*row)[i]] = 'Q'
board[i] = string(tmp)
}
return board
}
// 解法二 二进制操作法 Signed-off-by: Hanlin Shi [email protected]
func solveNQueens2(n int) (res [][]string) {
placements := make([]string, n)
for i := range placements {
buf := make([]byte, n)
for j := range placements {
if i == j {
buf[j] = 'Q'
} else {
buf[j] = '.'
}
}
placements[i] = string(buf)
}
var construct func(prev []int)
construct = func(prev []int) {
if len(prev) == n {
plan := make([]string, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
plan[i] = placements[prev[i]]
}
res = append(res, plan)
return
}
occupied := 0
for i := range prev {
dist := len(prev) - i
bit := 1 << prev[i]
occupied |= bit | bit<<dist | bit>>dist
}
prev = append(prev, -1)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if (occupied>>i)&1 != 0 {
continue
}
prev[len(prev)-1] = i
construct(prev)
}
}
construct(make([]int, 0, n))
return
}
52. N-Queens II
题目
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return the number of distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Example:
Input: 4
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown below.
[
[".Q..", // Solution 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // Solution 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
题目大意
给定一个整数 n,返回 n 皇后不同的解决方案的数量。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 51 题的加强版,在第 51 题的基础上累加记录解的个数即可。
- 这一题也可以暴力打表法,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一,暴力打表法
func totalNQueens(n int) int {
res := []int{0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 10, 4, 40, 92, 352, 724}
return res[n]
}
// 解法二,DFS 回溯法
func totalNQueens1(n int) int {
col, dia1, dia2, row, res := make([]bool, n), make([]bool, 2*n-1), make([]bool, 2*n-1), []int{}, 0
putQueen52(n, 0, &col, &dia1, &dia2, &row, &res)
return res
}
// 尝试在一个n皇后问题中, 摆放第index行的皇后位置
func putQueen52(n, index int, col, dia1, dia2 *[]bool, row *[]int, res *int) {
if index == n {
*res++
return
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
// 尝试将第index行的皇后摆放在第i列
if !(*col)[i] && !(*dia1)[index+i] && !(*dia2)[index-i+n-1] {
*row = append(*row, i)
(*col)[i] = true
(*dia1)[index+i] = true
(*dia2)[index-i+n-1] = true
putQueen52(n, index+1, col, dia1, dia2, row, res)
(*col)[i] = false
(*dia1)[index+i] = false
(*dia2)[index-i+n-1] = false
*row = (*row)[:len(*row)-1]
}
}
return
}
// 解法三 二进制位操作法
// class Solution {
// public:
// int totalNQueens(int n) {
// int ans=0;
// int row=0,leftDiagonal=0,rightDiagonal=0;
// int bit=(1<<n)-1;//to clear high bits of the 32-bit int
// Queens(bit,row,leftDiagonal,rightDiagonal,ans);
// return ans;
// }
// void Queens(int bit,int row,int leftDiagonal,int rightDiagonal,int &ans){
// int cur=(~(row|leftDiagonal|rightDiagonal))&bit;//possible place for this queen
// if (!cur) return;//no pos for this queen
// while(cur){
// int curPos=(cur&(~cur + 1))&bit;//choose possible place in the right
// //update row,ld and rd
// row+=curPos;
// if (row==bit) ans++;//last row
// else Queens(bit,row,((leftDiagonal|curPos)<<1)&bit,((rightDiagonal|curPos)>>1)&bit,ans);
// cur-=curPos;//for next possible place
// row-=curPos;//reset row
// }
// }
// };
53. Maximum Subarray
题目
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Example:
Input: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
Output: 6
Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
Follow up:
If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
题目大意
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
解题思路
- 这一题可以用 DP 求解也可以不用 DP。
- 题目要求输出数组中某个区间内数字之和最大的那个值。
dp[i]表示[0,i]区间内各个子区间和的最大值,状态转移方程是dp[i] = nums[i] + dp[i-1] (dp[i-1] > 0),dp[i] = nums[i] (dp[i-1] ≤ 0)。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 DP
func maxSubArray(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
if len(nums) == 1 {
return nums[0]
}
dp, res := make([]int, len(nums)), nums[0]
dp[0] = nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
if dp[i-1] > 0 {
dp[i] = nums[i] + dp[i-1]
} else {
dp[i] = nums[i]
}
res = max(res, dp[i])
}
return res
}
// 解法二 模拟
func maxSubArray1(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 1 {
return nums[0]
}
maxSum, res, p := nums[0], 0, 0
for p < len(nums) {
res += nums[p]
if res > maxSum {
maxSum = res
}
if res < 0 {
res = 0
}
p++
}
return maxSum
}
54. Spiral Matrix
题目
Given a matrix of m x n elements (m rows, n columns), return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
Example 2:
Input:
[
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9,10,11,12]
]
Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
题目大意
给定一个包含 m x n 个元素的矩阵(m 行, n 列),请按照顺时针螺旋顺序,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
解题思路
- 给出一个二维数组,按照螺旋的方式输出
- 解法一:需要注意的是特殊情况,比如二维数组退化成一维或者一列或者一个元素。注意了这些情况,基本就可以一次通过了。
- 解法二:提前算出一共多少个元素,一圈一圈地遍历矩阵,停止条件就是遍历了所有元素(count == sum)
代码
package leetcode
// 解法 1
func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) []int {
if len(matrix) == 0 {
return []int{}
}
res := []int{}
if len(matrix) == 1 {
for i := 0; i < len(matrix[0]); i++ {
res = append(res, matrix[0][i])
}
return res
}
if len(matrix[0]) == 1 {
for i := 0; i < len(matrix); i++ {
res = append(res, matrix[i][0])
}
return res
}
visit, m, n, round, x, y, spDir := make([][]int, len(matrix)), len(matrix), len(matrix[0]), 0, 0, 0, [][]int{
[]int{0, 1}, // 朝右
[]int{1, 0}, // 朝下
[]int{0, -1}, // 朝左
[]int{-1, 0}, // 朝上
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
visit[i] = make([]int, n)
}
visit[x][y] = 1
res = append(res, matrix[x][y])
for i := 0; i < m*n; i++ {
x += spDir[round%4][0]
y += spDir[round%4][1]
if (x == 0 && y == n-1) || (x == m-1 && y == n-1) || (y == 0 && x == m-1) {
round++
}
if x > m-1 || y > n-1 || x < 0 || y < 0 {
return res
}
if visit[x][y] == 0 {
visit[x][y] = 1
res = append(res, matrix[x][y])
}
switch round % 4 {
case 0:
if y+1 <= n-1 && visit[x][y+1] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
case 1:
if x+1 <= m-1 && visit[x+1][y] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
case 2:
if y-1 >= 0 && visit[x][y-1] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
case 3:
if x-1 >= 0 && visit[x-1][y] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
}
}
return res
}
// 解法 2
func spiralOrder2(matrix [][]int) []int {
m := len(matrix)
if m == 0 {
return nil
}
n := len(matrix[0])
if n == 0 {
return nil
}
// top、left、right、bottom 分别是剩余区域的上、左、右、下的下标
top, left, bottom, right := 0, 0, m-1, n-1
count, sum := 0, m*n
res := []int{}
// 外层循环每次遍历一圈
for count < sum {
i, j := top, left
for j <= right && count < sum {
res = append(res, matrix[i][j])
count++
j++
}
i, j = top + 1, right
for i <= bottom && count < sum {
res = append(res, matrix[i][j])
count++
i++
}
i, j = bottom, right - 1
for j >= left && count < sum {
res = append(res, matrix[i][j])
count++
j--
}
i, j = bottom - 1, left
for i > top && count < sum {
res = append(res, matrix[i][j])
count++
i--
}
// 进入到下一层
top, left, bottom, right = top+1, left+1, bottom-1, right-1
}
return res
}
55. Jump Game
题目
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
Example 1:
Input: [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: true
Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,1,0,4]
Output: false
Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum
jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
题目大意
给定一个非负整数数组,最初位于数组的第一个位置。数组中的每个元素代表在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。判断是否能够到达最后一个位置。
解题思路
- 给出一个非负数组,要求判断从数组 0 下标开始,能否到达数组最后一个位置。
- 这一题比较简单。如果某一个作为
起跳点的格子可以跳跃的距离是n,那么表示后面n个格子都可以作为起跳点。可以对每一个能作为起跳点的格子都尝试跳一次,把能跳到最远的距离maxJump不断更新。如果可以一直跳到最后,就成功了。如果中间有一个点比maxJump还要大,说明在这个点和 maxJump 中间连不上了,有些点不能到达最后一个位置。
代码
func canJump(nums []int) bool {
n := len(nums)
if n == 0 {
return false
}
if n == 1 {
return true
}
maxJump := 0
for i, v := range nums {
if i > maxJump {
return false
}
maxJump = max(maxJump, i+v)
}
return true
}
56. Merge Intervals
题目
Given a collection of intervals, merge all overlapping intervals.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
Example 2:
Input: [[1,4],[4,5]]
Output: [[1,5]]
Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
题目大意
合并给的多个区间,区间有重叠的要进行区间合并。
解题思路
先按照区间起点进行排序。然后从区间起点小的开始扫描,依次合并每个有重叠的区间。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for an interval.
* type Interval struct {
* Start int
* End int
* }
*/
// Interval define
type Interval struct {
Start int
End int
}
func merge56(intervals []Interval) []Interval {
if len(intervals) == 0 {
return intervals
}
quickSort(intervals, 0, len(intervals)-1)
res := make([]Interval, 0)
res = append(res, intervals[0])
curIndex := 0
for i := 1; i < len(intervals); i++ {
if intervals[i].Start > res[curIndex].End {
curIndex++
res = append(res, intervals[i])
} else {
res[curIndex].End = max(intervals[i].End, res[curIndex].End)
}
}
return res
}
func max(a int, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func min(a int, b int) int {
if a > b {
return b
}
return a
}
func partitionSort(a []Interval, lo, hi int) int {
pivot := a[hi]
i := lo - 1
for j := lo; j < hi; j++ {
if (a[j].Start < pivot.Start) || (a[j].Start == pivot.Start && a[j].End < pivot.End) {
i++
a[j], a[i] = a[i], a[j]
}
}
a[i+1], a[hi] = a[hi], a[i+1]
return i + 1
}
func quickSort(a []Interval, lo, hi int) {
if lo >= hi {
return
}
p := partitionSort(a, lo, hi)
quickSort(a, lo, p-1)
quickSort(a, p+1, hi)
}
57. Insert Interval
题目
Given a set of non-overlapping intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals (merge if necessary).
You may assume that the intervals were initially sorted according to their start times.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]]
Explanation: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
题目大意
这一题是第 56 题的加强版。给出多个没有重叠的区间,然后再给一个区间,要求把如果有重叠的区间进行合并。
解题思路
可以分 3 段处理,先添加原来的区间,即在给的 newInterval 之前的区间。然后添加 newInterval ,注意这里可能需要合并多个区间。最后把原来剩下的部分添加到最终结果中即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for an interval.
* type Interval struct {
* Start int
* End int
* }
*/
func insert(intervals []Interval, newInterval Interval) []Interval {
res := make([]Interval, 0)
if len(intervals) == 0 {
res = append(res, newInterval)
return res
}
curIndex := 0
for curIndex < len(intervals) && intervals[curIndex].End < newInterval.Start {
res = append(res, intervals[curIndex])
curIndex++
}
for curIndex < len(intervals) && intervals[curIndex].Start <= newInterval.End {
newInterval = Interval{Start: min(newInterval.Start, intervals[curIndex].Start), End: max(newInterval.End, intervals[curIndex].End)}
curIndex++
}
res = append(res, newInterval)
for curIndex < len(intervals) {
res = append(res, intervals[curIndex])
curIndex++
}
return res
}
58. Length of Last Word
题目
Given a string s consisting of some words separated by some number of spaces, return the length of the last word in the string.
A word is a maximal substring consisting of non-space characters only.
Example 1:
Input: s = "Hello World"
Output: 5
Explanation: The last word is "World" with length 5.
Example 2:
Input: s = " fly me to the moon "
Output: 4
Explanation: The last word is "moon" with length 4.
Example 3:
Input: s = "luffy is still joyboy"
Output: 6
Explanation: The last word is "joyboy" with length 6.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 104sconsists of only English letters and spaces' '.- There will be at least one word in
s.
题目大意
给你一个字符串 s,由若干单词组成,单词前后用一些空格字符隔开。返回字符串中最后一个单词的长度。单词 是指仅由字母组成、不包含任何空格字符的最大子字符串。
解题思路
- 先从后过滤掉空格找到单词尾部,再从尾部向前遍历,找到单词头部,最后两者相减,即为单词的长度。
代码
package leetcode
func lengthOfLastWord(s string) int {
last := len(s) - 1
for last >= 0 && s[last] == ' ' {
last--
}
if last < 0 {
return 0
}
first := last
for first >= 0 && s[first] != ' ' {
first--
}
return last - first
}
59. Spiral Matrix II
题目
Given a positive integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to n2 in spiral order.
Example:
Input: 3
Output:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 8, 9, 4 ],
[ 7, 6, 5 ]
]
题目大意
给定一个正整数 n,生成一个包含 1 到 n^2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的正方形矩阵。
解题思路
- 给出一个数组 n,要求输出一个 n * n 的二维数组,里面元素是 1 - n*n,且数组排列顺序是螺旋排列的
- 这一题是第 54 题的加强版,没有需要注意的特殊情况,直接模拟即可。
代码
package leetcode
func generateMatrix(n int) [][]int {
if n == 0 {
return [][]int{}
}
if n == 1 {
return [][]int{[]int{1}}
}
res, visit, round, x, y, spDir := make([][]int, n), make([][]int, n), 0, 0, 0, [][]int{
[]int{0, 1}, // 朝右
[]int{1, 0}, // 朝下
[]int{0, -1}, // 朝左
[]int{-1, 0}, // 朝上
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
visit[i] = make([]int, n)
res[i] = make([]int, n)
}
visit[x][y] = 1
res[x][y] = 1
for i := 0; i < n*n; i++ {
x += spDir[round%4][0]
y += spDir[round%4][1]
if (x == 0 && y == n-1) || (x == n-1 && y == n-1) || (y == 0 && x == n-1) {
round++
}
if x > n-1 || y > n-1 || x < 0 || y < 0 {
return res
}
if visit[x][y] == 0 {
visit[x][y] = 1
res[x][y] = i + 2
}
switch round % 4 {
case 0:
if y+1 <= n-1 && visit[x][y+1] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
case 1:
if x+1 <= n-1 && visit[x+1][y] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
case 2:
if y-1 >= 0 && visit[x][y-1] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
case 3:
if x-1 >= 0 && visit[x-1][y] == 1 {
round++
continue
}
}
}
return res
}
60. Permutation Sequence
题目
The set [1,2,3,...,*n*] contains a total of n! unique permutations.
By listing and labeling all of the permutations in order, we get the following sequence for n = 3:
"123""132""213""231""312""321"
Given n and k, return the kth permutation sequence.
Note:
- Given n will be between 1 and 9 inclusive.
- Given k will be between 1 and n! inclusive.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, k = 3
Output: "213"
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, k = 9
Output: "2314"
题目大意
给出集合 [1,2,3,…,n],其所有元素共有 n! 种排列。
按大小顺序列出所有排列情况,并一一标记,当 n = 3 时, 所有排列如下:“123”,“132”,“213”,“231”,“312”,“321”,给定 n 和 k,返回第 k 个排列。
解题思路
- 用 DFS 暴力枚举,这种做法时间复杂度特别高,想想更优的解法。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func getPermutation(n int, k int) string {
if k == 0 {
return ""
}
used, p, res := make([]bool, n), []int{}, ""
findPermutation(n, 0, &k, p, &res, &used)
return res
}
func findPermutation(n, index int, k *int, p []int, res *string, used *[]bool) {
fmt.Printf("n = %v index = %v k = %v p = %v res = %v user = %v\n", n, index, *k, p, *res, *used)
if index == n {
*k--
if *k == 0 {
for _, v := range p {
*res += strconv.Itoa(v + 1)
}
}
return
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if !(*used)[i] {
(*used)[i] = true
p = append(p, i)
findPermutation(n, index+1, k, p, res, used)
p = p[:len(p)-1]
(*used)[i] = false
}
}
return
}
61. Rotate List
题目
Given a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Example 2:
Input: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
Output: 2->0->1->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 1->2->0->NULL
rotate 3 steps to the right: 0->1->2->NULL
rotate 4 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
题目大意
旋转链表 K 次。
解题思路
这道题需要注意的点是,K 可能很大,K = 2000000000 ,如果是循环肯定会超时。应该找出 O(n) 的复杂度的算法才行。由于是循环旋转,最终状态其实是确定的,利用链表的长度取余可以得到链表的最终旋转结果。
这道题也不能用递归,递归解法会超时。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func rotateRight(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil || k == 0 {
return head
}
newHead := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: head}
len := 0
cur := newHead
for cur.Next != nil {
len++
cur = cur.Next
}
if (k % len) == 0 {
return head
}
cur.Next = head
cur = newHead
for i := len - k%len; i > 0; i-- {
cur = cur.Next
}
res := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: cur.Next}
cur.Next = nil
return res.Next
}
62. Unique Paths
题目
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
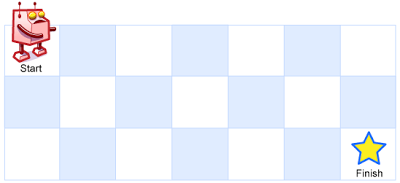
Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: m = 7, n = 3
Output: 28
题目大意
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。问总共有多少条不同的路径?
解题思路
- 这是一道简单的 DP 题。输出地图上从左上角走到右下角的走法数。
- 由于机器人只能向右走和向下走,所以地图的第一行和第一列的走法数都是 1,地图中任意一点的走法数是
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
代码
package leetcode
func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
dp := make([][]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, m)
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if i == 0 || j == 0 {
dp[i][j] = 1
continue
}
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
}
}
return dp[n-1][m-1]
}
63. Unique Paths II
题目
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?

An obstacle and empty space is marked as 1 and 0 respectively in the grid.
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
题目大意
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
解题思路
- 这一题是第 62 题的加强版。也是一道考察 DP 的简单题。
- 这一题比第 62 题增加的条件是地图中会出现障碍物,障碍物的处理方法是
dp[i][j]=0。 - 需要注意的一种情况是,起点就是障碍物,那么这种情况直接输出 0 。
代码
package leetcode
func uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) int {
if len(obstacleGrid) == 0 || obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1 {
return 0
}
m, n := len(obstacleGrid), len(obstacleGrid[0])
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, n)
}
dp[0][0] = 1
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
if dp[0][i-1] != 0 && obstacleGrid[0][i] != 1 {
dp[0][i] = 1
}
}
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
if dp[i-1][0] != 0 && obstacleGrid[i][0] != 1 {
dp[i][0] = 1
}
}
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
for j := 1; j < n; j++ {
if obstacleGrid[i][j] != 1 {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1]
}
64. Minimum Path Sum
题目
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example:
Input:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.
题目大意
给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
解题思路
- 在地图上求出从左上角到右下角的路径中,数字之和最小的一个,输出数字和。
- 这一题最简单的想法就是用一个二维数组来 DP,当然这是最原始的做法。由于只能往下和往右走,只需要维护 2 列信息就可以了,从左边推到最右边即可得到最小的解。更近一步,可以直接在原来的数组中做原地 DP,空间复杂度为 0 。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 原地 DP,无辅助空间
func minPathSum(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
grid[i][0] += grid[i-1][0]
}
for j := 1; j < n; j++ {
grid[0][j] += grid[0][j-1]
}
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
for j := 1; j < n; j++ {
grid[i][j] += min(grid[i-1][j], grid[i][j-1])
}
}
return grid[m-1][n-1]
}
// 解法二 最原始的方法,辅助空间 O(n^2)
func minPathSum1(grid [][]int) int {
if len(grid) == 0 {
return 0
}
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
if m == 0 || n == 0 {
return 0
}
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, n)
}
// initFirstCol
for i := 0; i < len(dp); i++ {
if i == 0 {
dp[i][0] = grid[i][0]
} else {
dp[i][0] = grid[i][0] + dp[i-1][0]
}
}
// initFirstRow
for i := 0; i < len(dp[0]); i++ {
if i == 0 {
dp[0][i] = grid[0][i]
} else {
dp[0][i] = grid[0][i] + dp[0][i-1]
}
}
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
for j := 1; j < n; j++ {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) + grid[i][j]
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1]
}
65. Valid Number
题目
A valid number can be split up into these components (in order):
- A decimal number or an integer.
- (Optional) An ‘e’ or ‘E’, followed by an integer.
A decimal number can be split up into these components (in order):
- (Optional) A sign character (either ‘+’ or ‘-').
- One of the following formats:
- One or more digits, followed by a dot ‘.’.
- One or more digits, followed by a dot ‘.’, followed by one or more digits.
- A dot ‘.’, followed by one or more digits.
An integer can be split up into these components (in order):
- (Optional) A sign character (either ‘+’ or ‘-').
- One or more digits.
For example, all the following are valid numbers: ["2", "0089", "-0.1", "+3.14", "4.", "-.9", "2e10", "-90E3", "3e+7", "+6e-1", "53.5e93", "-123.456e789"], while the following are not valid numbers: ["abc", "1a", "1e", "e3", "99e2.5", "--6", "-+3", "95a54e53"].
Given a string s, return true if s is a valid number.
Example:
Input: s = "0"
Output: true
Input: s = "e"
Output: false
题目大意
给定一个字符串S,请根据以上的规则判断该字符串是否是一个有效的数字字符串。
解题思路
- 用三个变量分别标记是否出现过数字、是否出现过’.‘和 是否出现过 ‘e/E’
- 从左到右依次遍历字符串中的每一个元素
- 如果是数字,则标记数字出现过
- 如果是 ‘.’, 则需要 ‘.‘没有出现过,并且 ‘e/E’ 没有出现过,才会进行标记
- 如果是 ‘e/E’, 则需要 ‘e/E’没有出现过,并且前面出现过数字,才会进行标记
- 如果是 ‘+/-’, 则需要是第一个字符,或者前一个字符是 ‘e/E’,才会进行标记,并重置数字出现的标识
- 最后返回时,需要字符串中至少出现过数字,避免下列case: s == ‘.’ or ‘e/E’ or ‘+/e’ and etc…
代码
package leetcode
func isNumber(s string) bool {
numFlag, dotFlag, eFlag := false, false, false
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
if '0' <= s[i] && s[i] <= '9' {
numFlag = true
} else if s[i] == '.' && !dotFlag && !eFlag {
dotFlag = true
} else if (s[i] == 'e' || s[i] == 'E') && !eFlag && numFlag {
eFlag = true
numFlag = false // reJudge integer after 'e' or 'E'
} else if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-') && (i == 0 || s[i-1] == 'e' || s[i-1] == 'E') {
continue
} else {
return false
}
}
// avoid case: s == '.' or 'e/E' or '+/-' and etc...
// string s must have num
return numFlag
}
66. Plus One
题目
Given a non-empty array of digits representing a non-negative integer, plus one to the integer.
The digits are stored such that the most significant digit is at the head of the list, and each element in the array contain a single digit.
You may assume the integer does not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output: [1,2,4]
Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
Example 2:
Input: [4,3,2,1]
Output: [4,3,2,2]
Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
题目大意
给定一个由整数组成的非空数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。最高位数字存放在数组的首位, 数组中每个元素只存储单个数字。你可以假设除了整数 0 之外,这个整数不会以零开头。
解题思路
- 给出一个数组,代表一个十进制数,数组的 0 下标是十进制数的高位。要求计算这个十进制数加一以后的结果。
- 简单的模拟题。从数组尾部开始往前扫,逐位进位即可。最高位如果还有进位需要在数组里面第 0 位再插入一个 1 。
代码
package leetcode
func plusOne(digits []int) []int {
for i := len(digits) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
digits[i]++
if digits[i] != 10 {
// no carry
return digits
}
// carry
digits[i] = 0
}
// all carry
digits[0] = 1
digits = append(digits, 0)
return digits
}
67. Add Binary
题目
Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string).
The input strings are both non-empty and contains only characters 1 or 0.
Example 1:
Input: a = "11", b = "1"
Output: "100"
Example 2:
Input: a = "1010", b = "1011"
Output: "10101"
题目大意
给你两个二进制字符串,返回它们的和(用二进制表示)。输入为 非空 字符串且只包含数字 1 和 0。
解题思路
- 要求输出 2 个二进制数的和,结果也用二进制表示。
- 简单题。按照二进制的加法规则做加法即可。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"strconv"
"strings"
)
func addBinary(a string, b string) string {
if len(b) > len(a) {
a, b = b, a
}
res := make([]string, len(a)+1)
i, j, k, c := len(a)-1, len(b)-1, len(a), 0
for i >= 0 && j >= 0 {
ai, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(a[i]))
bj, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(b[j]))
res[k] = strconv.Itoa((ai + bj + c) % 2)
c = (ai + bj + c) / 2
i--
j--
k--
}
for i >= 0 {
ai, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(a[i]))
res[k] = strconv.Itoa((ai + c) % 2)
c = (ai + c) / 2
i--
k--
}
if c > 0 {
res[k] = strconv.Itoa(c)
}
return strings.Join(res, "")
}
69. Sqrt(x)
题目
Implement int sqrt(int x).
Compute and return the square root of x, where x is guaranteed to be a non-negative integer.
Since the return type is an integer, the decimal digits are truncated and only the integer part of the result is returned.
Example 1:
Input: 4
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: 8
Output: 2
Explanation: The square root of 8 is 2.82842..., and since
the decimal part is truncated, 2 is returned.
题目大意
实现 int sqrt(int x) 函数。计算并返回 x 的平方根,其中 x 是非负整数。由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留整数的部分,小数部分将被舍去。
解题思路
-
题目要求求出根号 x
-
根据题意,根号 x 的取值范围一定在
[0,x]之间,这个区间内的值是递增有序的,有边界的,可以用下标访问的,满足这三点正好也就满足了二分搜索的 3 大条件。所以解题思路一,二分搜索。 -
解题思路二,牛顿迭代法。求根号 x,即求满足
x^2 - n = 0方程的所有解。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 二分, 找到最后一个满足 n^2 <= x 的整数n
func mySqrt(x int) int {
l, r := 0, x
for l < r {
mid := (l + r + 1) / 2
if mid*mid > x {
r = mid - 1
} else {
l = mid
}
}
return l
}
// 解法二 牛顿迭代法 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integer_square_root
func mySqrt1(x int) int {
r := x
for r*r > x {
r = (r + x/r) / 2
}
return r
}
// 解法三 Quake III 游戏引擎中有一种比 STL 的 sqrt 快 4 倍的实现 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fast_inverse_square_root
// float Q_rsqrt( float number )
// {
// long i;
// float x2, y;
// const float threehalfs = 1.5F;
// x2 = number * 0.5F;
// y = number;
// i = * ( long * ) &y; // evil floating point bit level hacking
// i = 0x5f3759df - ( i >> 1 ); // what the fuck?
// y = * ( float * ) &i;
// y = y * ( threehalfs - ( x2 * y * y ) ); // 1st iteration
// // y = y * ( threehalfs - ( x2 * y * y ) ); // 2nd iteration, this can be removed
// return y;
// }
70. Climbing Stairs
题目
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
题目大意
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?注意:给定 n 是一个正整数
解题思路
- 简单的 DP,经典的爬楼梯问题。一个楼梯可以由
n-1和n-2的楼梯爬上来。 - 这一题求解的值就是斐波那契数列。
代码
package leetcode
func climbStairs(n int) int {
dp := make([]int, n+1)
dp[0], dp[1] = 1, 1
for i := 2; i <= n; i++ {
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]
}
return dp[n]
}
71. Simplify Path
题目
Given an absolute path for a file (Unix-style), simplify it. Or in other words, convert it to the canonical path.
In a UNIX-style file system, a period . refers to the current directory. Furthermore, a double period .. moves the directory up a level. For more information, see: Absolute path vs relative path in Linux/Unix
Note that the returned canonical path must always begin with a slash /, and there must be only a single slash / between two directory names. The last directory name (if it exists) must not end with a trailing /. Also, the canonical path must be the shortest string representing the absolute path.
Example 1:
Input: "/home/"
Output: "/home"
Explanation: Note that there is no trailing slash after the last directory name.
Example 2:
Input: "/../"
Output: "/"
Explanation: Going one level up from the root directory is a no-op, as the root level is the highest level you can go.
Example 3:
Input: "/home//foo/"
Output: "/home/foo"
Explanation: In the canonical path, multiple consecutive slashes are replaced by a single one.
Example 4:
Input: "/a/./b/../../c/"
Output: "/c"
Example 5:
Input: "/a/../../b/../c//.//"
Output: "/c"
Example 6:
Input: "/a//b////c/d//././/.."
Output: "/a/b/c"
题目大意
给出一个 Unix 的文件路径,要求简化这个路径。这道题也是考察栈的题目。
解题思路
这道题笔者提交了好多次才通过,并不是题目难,而是边界条件很多,没考虑全一种情况就会出错。有哪些边界情况就看笔者的 test 文件吧。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"path/filepath"
"strings"
)
// 解法一
func simplifyPath(path string) string {
arr := strings.Split(path, "/")
stack := make([]string, 0)
var res string
for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {
cur := arr[i]
//cur := strings.TrimSpace(arr[i]) 更加严谨的做法应该还要去掉末尾的空格
if cur == ".." {
if len(stack) > 0 {
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
}
} else if cur != "." && len(cur) > 0 {
stack = append(stack, arr[i])
}
}
if len(stack) == 0 {
return "/"
}
res = strings.Join(stack, "/")
return "/" + res
}
// 解法二 golang 的官方库 API
func simplifyPath1(path string) string {
return filepath.Clean(path)
}
73. Set Matrix Zeroes
题目
Given an *m* x *n* matrix. If an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0. Do it in-place.
Follow up:
- A straight forward solution using O(mn) space is probably a bad idea.
- A simple improvement uses O(m + n) space, but still not the best solution.
- Could you devise a constant space solution?
Example 1:
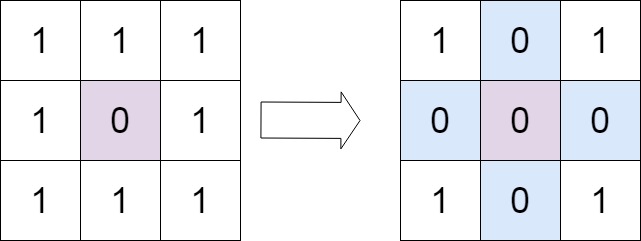
Input: matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
Example 2:
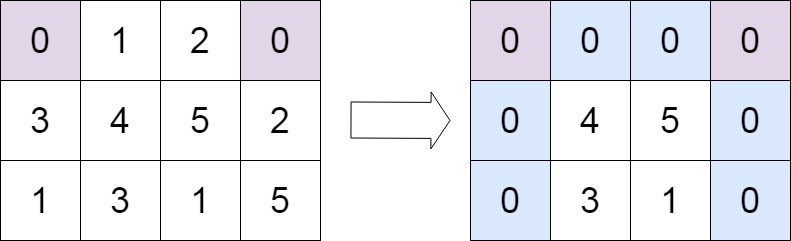
Input: matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]
Output: [[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[0].length1 <= m, n <= 2002^31 <= matrix[i][j] <= 2^31 - 1
题目大意
给定一个 m x n 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0。请使用原地算法。
解题思路
- 此题考查对程序的控制能力,无算法思想。题目要求采用原地的算法,所有修改即在原二维数组上进行。在二维数组中有 2 个特殊位置,一个是第一行,一个是第一列。它们的特殊性在于,它们之间只要有一个 0,它们都会变为全 0 。先用 2 个变量记录这一行和这一列中是否有 0,防止之后的修改覆盖了这 2 个地方。然后除去这一行和这一列以外的部分判断是否有 0,如果有 0,将它们所在的行第一个元素标记为 0,所在列的第一个元素标记为 0 。最后通过标记,将对应的行列置 0 即可。
代码
package leetcode
func setZeroes(matrix [][]int) {
if len(matrix) == 0 || len(matrix[0]) == 0 {
return
}
isFirstRowExistZero, isFirstColExistZero := false, false
for i := 0; i < len(matrix); i++ {
if matrix[i][0] == 0 {
isFirstColExistZero = true
break
}
}
for j := 0; j < len(matrix[0]); j++ {
if matrix[0][j] == 0 {
isFirstRowExistZero = true
break
}
}
for i := 1; i < len(matrix); i++ {
for j := 1; j < len(matrix[0]); j++ {
if matrix[i][j] == 0 {
matrix[i][0] = 0
matrix[0][j] = 0
}
}
}
// 处理[1:]行全部置 0
for i := 1; i < len(matrix); i++ {
if matrix[i][0] == 0 {
for j := 1; j < len(matrix[0]); j++ {
matrix[i][j] = 0
}
}
}
// 处理[1:]列全部置 0
for j := 1; j < len(matrix[0]); j++ {
if matrix[0][j] == 0 {
for i := 1; i < len(matrix); i++ {
matrix[i][j] = 0
}
}
}
if isFirstRowExistZero {
for j := 0; j < len(matrix[0]); j++ {
matrix[0][j] = 0
}
}
if isFirstColExistZero {
for i := 0; i < len(matrix); i++ {
matrix[i][0] = 0
}
}
}
74. Search a 2D Matrix
题目
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
- Integers in each row are sorted from left to right.
- The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
Example 1:
Input:
matrix = [
[1, 3, 5, 7],
[10, 11, 16, 20],
[23, 30, 34, 50]
]
target = 3
Output: true
Example 2:
Input:
matrix = [
[1, 3, 5, 7],
[10, 11, 16, 20],
[23, 30, 34, 50]
]
target = 13
Output: false
题目大意
编写一个高效的算法来判断 m x n 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值。该矩阵具有如下特性:
- 每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。
- 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
解题思路
- 给出一个二维矩阵,矩阵的特点是随着矩阵的下标增大而增大。要求设计一个算法能在这个矩阵中高效的找到一个数,如果找到就输出 true,找不到就输出 false。
- 虽然是一个二维矩阵,但是由于它特殊的有序性,所以完全可以按照下标把它看成一个一维矩阵,只不过需要行列坐标转换。最后利用二分搜索直接搜索即可。
代码
package leetcode
func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
if len(matrix) == 0 {
return false
}
m, low, high := len(matrix[0]), 0, len(matrix[0])*len(matrix)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if matrix[mid/m][mid%m] == target {
return true
} else if matrix[mid/m][mid%m] > target {
high = mid - 1
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
}
return false
}
75. Sort Colors
题目
Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white and blue.
Here, we will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue respectively.
Note: You are not suppose to use the library’s sort function for this problem.
Example 1:
Input: [2,0,2,1,1,0]
Output: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
Follow up:
- A rather straight forward solution is a two-pass algorithm using counting sort. First, iterate the array counting number of 0’s, 1’s, and 2’s, then overwrite array with total number of 0’s, then 1’s and followed by 2’s.
- Could you come up with a one-pass algorithm using only constant space?
题目大意
抽象题意其实就是排序。这题可以用快排一次通过。
解题思路
题目末尾的 Follow up 提出了一个更高的要求,能否用一次循环解决问题?这题由于数字只会出现 0,1,2 这三个数字,所以用游标移动来控制顺序也是可以的。具体做法:0 是排在最前面的,所以只要添加一个 0,就需要放置 1 和 2。1 排在 2 前面,所以添加 1 的时候也需要放置 2 。至于最后的 2,只用移动游标即可。
这道题可以用计数排序,适合待排序数字很少的题目。用一个 3 个容量的数组分别计数,记录 0,1,2 出现的个数。然后再根据个数排列 0,1,2 即可。时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(K)。这一题 K = 3。
这道题也可以用一次三路快排。数组分为 3 部分,第一个部分都是 0,中间部分都是 1,最后部分都是 2 。
代码
package leetcode
func sortColors(nums []int) {
zero, one := 0, 0
for i, n := range nums {
nums[i] = 2
if n <= 1 {
nums[one] = 1
one++
}
if n == 0 {
nums[zero] = 0
zero++
}
}
}
76. Minimum Window Substring
题目
Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain all the characters in T in complexity O(n).
Example:
Input: S = "ADOBECODEBANC", T = "ABC"
Output: "BANC"
Note:
- If there is no such window in S that covers all characters in T, return the empty string “”.
- If there is such window, you are guaranteed that there will always be only one unique minimum window in S.
题目大意
给定一个源字符串 s,再给一个字符串 T,要求在源字符串中找到一个窗口,这个窗口包含由字符串各种排列组合组成的,窗口中可以包含 T 中没有的字符,如果存在多个,在结果中输出最小的窗口,如果找不到这样的窗口,输出空字符串。
解题思路
这一题是滑动窗口的题目,在窗口滑动的过程中不断的包含字符串 T,直到完全包含字符串 T 的字符以后,记下左右窗口的位置和窗口大小。每次都不断更新这个符合条件的窗口和窗口大小的最小值。最后输出结果即可。
代码
package leetcode
func minWindow(s string, t string) string {
if s == "" || t == "" {
return ""
}
var tFreq, sFreq [256]int
result, left, right, finalLeft, finalRight, minW, count := "", 0, -1, -1, -1, len(s)+1, 0
for i := 0; i < len(t); i++ {
tFreq[t[i]-'a']++
}
for left < len(s) {
if right+1 < len(s) && count < len(t) {
sFreq[s[right+1]-'a']++
if sFreq[s[right+1]-'a'] <= tFreq[s[right+1]-'a'] {
count++
}
right++
} else {
if right-left+1 < minW && count == len(t) {
minW = right - left + 1
finalLeft = left
finalRight = right
}
if sFreq[s[left]-'a'] == tFreq[s[left]-'a'] {
count--
}
sFreq[s[left]-'a']--
left++
}
}
if finalLeft != -1 {
result = string(s[finalLeft : finalRight+1])
}
return result
}
77. Combinations
题目
Given two integers n and k, return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 … n.
Example:
Input: n = 4, k = 2
Output:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
题目大意
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 … n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
解题思路
- 计算排列组合中的组合,用 DFS 深搜即可,注意剪枝
代码
package leetcode
func combine(n int, k int) [][]int {
if n <= 0 || k <= 0 || k > n {
return [][]int{}
}
c, res := []int{}, [][]int{}
generateCombinations(n, k, 1, c, &res)
return res
}
func generateCombinations(n, k, start int, c []int, res *[][]int) {
if len(c) == k {
b := make([]int, len(c))
copy(b, c)
*res = append(*res, b)
return
}
// i will at most be n - (k - c.size()) + 1
for i := start; i <= n-(k-len(c))+1; i++ {
c = append(c, i)
generateCombinations(n, k, i+1, c, res)
c = c[:len(c)-1]
}
return
}
78. Subsets
题目
Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
题目大意
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
解题思路
- 找出一个集合中的所有子集,空集也算是子集。且数组中的数字不会出现重复。用 DFS 暴力枚举即可。
- 这一题和第 90 题,第 491 题类似,可以一起解答和复习。
代码
package leetcode
import "sort"
// 解法一
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
c, res := []int{}, [][]int{}
for k := 0; k <= len(nums); k++ {
generateSubsets(nums, k, 0, c, &res)
}
return res
}
func generateSubsets(nums []int, k, start int, c []int, res *[][]int) {
if len(c) == k {
b := make([]int, len(c))
copy(b, c)
*res = append(*res, b)
return
}
// i will at most be n - (k - c.size()) + 1
for i := start; i < len(nums)-(k-len(c))+1; i++ {
c = append(c, nums[i])
generateSubsets(nums, k, i+1, c, res)
c = c[:len(c)-1]
}
return
}
// 解法二
func subsets1(nums []int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 1)
sort.Ints(nums)
for i := range nums {
for _, org := range res {
clone := make([]int, len(org), len(org)+1)
copy(clone, org)
clone = append(clone, nums[i])
res = append(res, clone)
}
}
return res
}
// 解法三:位运算的方法
func subsets2(nums []int) [][]int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
res := [][]int{}
sum := 1 << uint(len(nums))
for i := 0; i < sum; i++ {
stack := []int{}
tmp := i // i 从 000...000 到 111...111
for j := len(nums) - 1; j >= 0; j-- { // 遍历 i 的每一位
if tmp & 1 == 1 {
stack = append([]int{nums[j]}, stack...)
}
tmp >>= 1
}
res = append(res, stack)
}
return res
}
79. Word Search
题目
Given a 2D board and a word, find if the word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cell, where “adjacent” cells are those horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example:
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
Given word = "ABCCED", return true.
Given word = "SEE", return true.
Given word = "ABCB", return false.
题目大意
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
解题思路
- 在地图上的任意一个起点开始,向 4 个方向分别 DFS 搜索,直到所有的单词字母都找到了就输出 true,否则输出 false。
代码
package leetcode
var dir = [][]int{
[]int{-1, 0},
[]int{0, 1},
[]int{1, 0},
[]int{0, -1},
}
func exist(board [][]byte, word string) bool {
visited := make([][]bool, len(board))
for i := 0; i < len(visited); i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, len(board[0]))
}
for i, v := range board {
for j := range v {
if searchWord(board, visited, word, 0, i, j) {
return true
}
}
}
return false
}
func isInBoard(board [][]byte, x, y int) bool {
return x >= 0 && x < len(board) && y >= 0 && y < len(board[0])
}
func searchWord(board [][]byte, visited [][]bool, word string, index, x, y int) bool {
if index == len(word)-1 {
return board[x][y] == word[index]
}
if board[x][y] == word[index] {
visited[x][y] = true
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
nx := x + dir[i][0]
ny := y + dir[i][1]
if isInBoard(board, nx, ny) && !visited[nx][ny] && searchWord(board, visited, word, index+1, nx, ny) {
return true
}
}
visited[x][y] = false
}
return false
}
80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
题目
Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that duplicates appeared at most twice and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3],
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 1, 1, 2, 2 and 3 respectively.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
Example 2:
Given nums = [0,0,1,1,1,1,2,3,3],
Your function should return length = 7, with the first seven elements of nums being modified to 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3 and 3 respectively.
It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
Clarification:
Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
Note that the input array is passed in by reference, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
Internally you can think of this:
// nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
// any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
// using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
题目大意
给定一个有序数组 nums,对数组中的元素进行去重,使得原数组中的每个元素最多暴露 2 个。最后返回去重以后数组的长度值。
解题思路
- 问题提示有序数组,一般最容易想到使用双指针的解法,双指针的关键点:移动两个指针的条件。
- 在该题中移动的条件:快指针从头遍历数组,慢指针指向修改后的数组的末端,当慢指针指向倒数第二个数与快指针指向的数不相等时,才移动慢指针,同时赋值慢指针。
- 处理边界条件:当数组小于两个元素时,不做处理。
代码
package leetcode
func removeDuplicates(nums []int) int {
slow := 0
for fast, v := range nums {
if fast < 2 || nums[slow-2] != v {
nums[slow] = v
slow++
}
}
return slow
}
81. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
题目
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., [0,0,1,2,2,5,6] might become [2,5,6,0,0,1,2]).
You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return true, otherwise return false.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: false
Follow up:
- This is a follow up problem to Search in Rotated Sorted Array, where
numsmay contain duplicates. - Would this affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
题目大意
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。( 例如,数组 [0,0,1,2,2,5,6] 可能变为 [2,5,6,0,0,1,2] )。
编写一个函数来判断给定的目标值是否存在于数组中。若存在返回 true,否则返回 false。
进阶:
- 这是搜索旋转排序数组 的延伸题目,本题中的 nums 可能包含重复元素。
- 这会影响到程序的时间复杂度吗?会有怎样的影响,为什么?
解题思路
- 给出一个数组,数组中本来是从小到大排列的,并且数组中有重复数字。但是现在把后面随机一段有序的放到数组前面,这样形成了前后两端有序的子序列。在这样的一个数组里面查找一个数,设计一个 O(log n) 的算法。如果找到就输出
true,如果没有找到,就输出false。 - 这一题是第 33 题的加强版,实现代码完全一样,只不过输出变了。这一题输出
true和false了。具体思路见第 33 题。
代码
package leetcode
func search(nums []int, target int) bool {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return false
}
low, high := 0, len(nums)-1
for low <= high {
mid := low + (high-low)>>1
if nums[mid] == target {
return true
} else if nums[mid] > nums[low] { // 在数值大的一部分区间里
if nums[low] <= target && target < nums[mid] {
high = mid - 1
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
} else if nums[mid] < nums[high] { // 在数值小的一部分区间里
if nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[high] {
low = mid + 1
} else {
high = mid - 1
}
} else {
if nums[low] == nums[mid] {
low++
}
if nums[high] == nums[mid] {
high--
}
}
}
return false
}
82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
题目
Given a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5
Output: 1->2->5
Example 2:
Input: 1->1->1->2->3
Output: 2->3
题目大意
删除链表中重复的结点,只要是有重复过的结点,全部删除。
解题思路
按照题意做即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
// 解法一
func deleteDuplicates1(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head.Next == nil {
return head
}
newHead := &ListNode{Next: head, Val: -999999}
cur := newHead
last := newHead
front := head
for front.Next != nil {
if front.Val == cur.Val {
// fmt.Printf("相同节点front = %v | cur = %v | last = %v\n", front.Val, cur.Val, last.Val)
front = front.Next
continue
} else {
if cur.Next != front {
// fmt.Printf("删除重复节点front = %v | cur = %v | last = %v\n", front.Val, cur.Val, last.Val)
last.Next = front
if front.Next != nil && front.Next.Val != front.Val {
last = front
}
cur = front
front = front.Next
} else {
// fmt.Printf("常规循环前front = %v | cur = %v | last = %v\n", front.Val, cur.Val, last.Val)
last = cur
cur = cur.Next
front = front.Next
// fmt.Printf("常规循环后front = %v | cur = %v | last = %v\n", front.Val, cur.Val, last.Val)
}
}
}
if front.Val == cur.Val {
// fmt.Printf("相同节点front = %v | cur = %v | last = %v\n", front.Val, cur.Val, last.Val)
last.Next = nil
} else {
if cur.Next != front {
last.Next = front
}
}
return newHead.Next
}
// 解法二
func deleteDuplicates2(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head.Next != nil && head.Val == head.Next.Val {
for head.Next != nil && head.Val == head.Next.Val {
head = head.Next
}
return deleteDuplicates(head.Next)
}
head.Next = deleteDuplicates(head.Next)
return head
}
func deleteDuplicates(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
cur := head
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head.Next == nil {
return head
}
for cur.Next != nil {
if cur.Next.Val == cur.Val {
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
} else {
cur = cur.Next
}
}
return head
}
// 解法三 双循环简单解法 O(n*m)
func deleteDuplicates3(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return head
}
nilNode := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: head}
head = nilNode
lastVal := 0
for head.Next != nil && head.Next.Next != nil {
if head.Next.Val == head.Next.Next.Val {
lastVal = head.Next.Val
for head.Next != nil && lastVal == head.Next.Val {
head.Next = head.Next.Next
}
} else {
head = head.Next
}
}
return nilNode.Next
}
// 解法四 双指针+删除标志位,单循环解法 O(n)
func deleteDuplicates4(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
nilNode := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: head}
// 上次遍历有删除操作的标志位
lastIsDel := false
// 虚拟空结点
head = nilNode
// 前后指针用于判断
pre, back := head.Next, head.Next.Next
// 每次只删除前面的一个重复的元素,留一个用于下次遍历判重
// pre, back 指针的更新位置和值比较重要和巧妙
for head.Next != nil && head.Next.Next != nil {
if pre.Val != back.Val && lastIsDel {
head.Next = head.Next.Next
pre, back = head.Next, head.Next.Next
lastIsDel = false
continue
}
if pre.Val == back.Val {
head.Next = head.Next.Next
pre, back = head.Next, head.Next.Next
lastIsDel = true
} else {
head = head.Next
pre, back = head.Next, head.Next.Next
lastIsDel = false
}
}
// 处理 [1,1] 这种删除还剩一个的情况
if lastIsDel && head.Next != nil {
head.Next = nil
}
return nilNode.Next
}
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
题目
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once.
Example 1:
Input: 1->1->2
Output: 1->2
Example 2:
Input: 1->1->2->3->3
Output: 1->2->3
题目大意
删除链表中重复的结点,以保障每个结点只出现一次。
解题思路
按照题意做即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func deleteDuplicates(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
cur := head
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head.Next == nil {
return head
}
for cur.Next != nil {
if cur.Next.Val == cur.Val {
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
} else {
cur = cur.Next
}
}
return head
}
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
题目
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.

Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].

The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
Example:
Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
题目大意
给出每个直方图的高度,要求在这些直方图之中找到面积最大的矩形,输出矩形的面积。
解题思路
用单调栈依次保存直方图的高度下标,一旦出现高度比栈顶元素小的情况就取出栈顶元素,单独计算一下这个栈顶元素的矩形的高度。然后停在这里(外层循环中的 i–,再 ++,就相当于停在这里了),继续取出当前最大栈顶的前一个元素,即连续弹出 2 个最大的,以稍小的一个作为矩形的边,宽就是 2 计算面积…………如果停在这里的下标代表的高度一直比栈里面的元素小,就一直弹出,取出最后一个比当前下标大的高度作为矩形的边。宽就是最后一个比当前下标大的高度和当前下标 i 的差值。计算出面积以后不断的更新 maxArea 即可。
代码
package leetcode
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
maxArea := 0
n := len(heights) + 2
// Add a sentry at the beginning and the end
getHeight := func(i int) int {
if i == 0 || n-1 == i {
return 0
}
return heights[i-1]
}
st := make([]int, 0, n/2)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for len(st) > 0 && getHeight(st[len(st)-1]) > getHeight(i) {
// pop stack
idx := st[len(st)-1]
st = st[:len(st)-1]
maxArea = max(maxArea, getHeight(idx)*(i-st[len(st)-1]-1))
}
// push stack
st = append(st, i)
}
return maxArea
}
func max(a int, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
86. Partition List
题目
Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Example:
Input: head = 1->4->3->2->5->2, x = 3
Output: 1->2->2->4->3->5
题目大意
给定一个数 x,比 x 大或等于的数字都要排列在比 x 小的数字后面,并且相对位置不能发生变化。由于相对位置不能发生变化,所以不能用类似冒泡排序的思想。
解题思路
这道题最简单的做法是构造双向链表,不过时间复杂度是 O(n^2)。
(以下描述定义,大于等于 x 的都属于比 x 大)
更优的方法是新构造 2 个链表,一个链表专门存储比 x 小的结点,另一个专门存储比 x 大的结点。在原链表头部开始扫描一边,依次把这两类点归类到 2 个新建链表中,有点入栈的意思。由于是从头开始扫描的原链表,所以原链表中的原有顺序会依旧被保存下来。最后 2 个新链表里面会存储好各自的结果,把这两个链表,比 x 小的链表拼接到 比 x 大的链表的前面,就能得到最后的答案了。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
// 解法一 单链表
func partition(head *ListNode, x int) *ListNode {
beforeHead := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: nil}
before := beforeHead
afterHead := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: nil}
after := afterHead
for head != nil {
if head.Val < x {
before.Next = head
before = before.Next
} else {
after.Next = head
after = after.Next
}
head = head.Next
}
after.Next = nil
before.Next = afterHead.Next
return beforeHead.Next
}
// DoublyListNode define
type DoublyListNode struct {
Val int
Prev *DoublyListNode
Next *DoublyListNode
}
// 解法二 双链表
func partition1(head *ListNode, x int) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
DLNHead := genDoublyListNode(head)
cur := DLNHead
for cur != nil {
if cur.Val < x {
tmp := &DoublyListNode{Val: cur.Val, Prev: nil, Next: nil}
compareNode := cur
for compareNode.Prev != nil {
if compareNode.Val >= x && compareNode.Prev.Val < x {
break
}
compareNode = compareNode.Prev
}
if compareNode == DLNHead {
if compareNode.Val < x {
cur = cur.Next
continue
} else {
tmp.Next = DLNHead
DLNHead.Prev = tmp
DLNHead = tmp
}
} else {
tmp.Next = compareNode
tmp.Prev = compareNode.Prev
compareNode.Prev.Next = tmp
compareNode.Prev = tmp
}
deleteNode := cur
if cur.Prev != nil {
deleteNode.Prev.Next = deleteNode.Next
}
if cur.Next != nil {
deleteNode.Next.Prev = deleteNode.Prev
}
}
cur = cur.Next
}
return genListNode(DLNHead)
}
func genDoublyListNode(head *ListNode) *DoublyListNode {
cur := head.Next
DLNHead := &DoublyListNode{Val: head.Val, Prev: nil, Next: nil}
curDLN := DLNHead
for cur != nil {
tmp := &DoublyListNode{Val: cur.Val, Prev: curDLN, Next: nil}
curDLN.Next = tmp
curDLN = tmp
cur = cur.Next
}
return DLNHead
}
func genListNode(head *DoublyListNode) *ListNode {
cur := head.Next
LNHead := &ListNode{Val: head.Val, Next: nil}
curLN := LNHead
for cur != nil {
tmp := &ListNode{Val: cur.Val, Next: nil}
curLN.Next = tmp
curLN = tmp
cur = cur.Next
}
return LNHead
}
88. Merge Sorted Array
题目
Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
Note:
- The number of elements initialized in nums1 and nums2 are m and n respectively.
- You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is equal to m + n) to hold additional elements from nums2.
Example:
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
Constraints:
- -10^9 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^9
- nums1.length == m + n
- nums2.length == n
题目大意
合并两个已经有序的数组,结果放在第一个数组中,第一个数组假设空间足够大。要求算法时间复杂度足够低。
解题思路
为了不大量移动元素,就要从2个数组长度之和的最后一个位置开始,依次选取两个数组中大的数,从第一个数组的尾巴开始往头放,只要循环一次以后,就生成了合并以后的数组了。
代码
package leetcode
func merge(nums1 []int, m int, nums2 []int, n int) {
for p := m + n; m > 0 && n > 0; p-- {
if nums1[m-1] <= nums2[n-1] {
nums1[p-1] = nums2[n-1]
n--
} else {
nums1[p-1] = nums1[m-1]
m--
}
}
for ; n > 0; n-- {
nums1[n-1] = nums2[n-1]
}
}
89. Gray Code
题目
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: [0,1,3,2]
Explanation:
00 - 0
01 - 1
11 - 3
10 - 2
For a given n, a gray code sequence may not be uniquely defined.
For example, [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence.
00 - 0
10 - 2
11 - 3
01 - 1
Example 2:
Input: 0
Output: [0]
Explanation: We define the gray code sequence to begin with 0.
A gray code sequence of n has size = 2n, which for n = 0 the size is 20 = 1.
Therefore, for n = 0 the gray code sequence is [0].
题目大意
格雷编码是一个二进制数字系统,在该系统中,两个连续的数值仅有一个位数的差异。给定一个代表编码总位数的非负整数 n,打印其格雷编码序列。格雷编码序列必须以 0 开头。
解题思路
- 输出 n 位格雷码
- 格雷码生成规则:以二进制为0值的格雷码为第零项,第一次改变最右边的位元,第二次改变右起第一个为1的位元的左边位元,第三、四次方法同第一、二次,如此反复,即可排列出 n 个位元的格雷码。
- 可以直接模拟,也可以用递归求解。
代码
package leetcode
// 解法一 递归方法,时间复杂度和空间复杂度都较优
func grayCode(n int) []int {
if n == 0 {
return []int{0}
}
res := []int{}
num := make([]int, n)
generateGrayCode(int(1<<uint(n)), 0, &num, &res)
return res
}
func generateGrayCode(n, step int, num *[]int, res *[]int) {
if n == 0 {
return
}
*res = append(*res, convertBinary(*num))
if step%2 == 0 {
(*num)[len(*num)-1] = flipGrayCode((*num)[len(*num)-1])
} else {
index := len(*num) - 1
for ; index >= 0; index-- {
if (*num)[index] == 1 {
break
}
}
if index == 0 {
(*num)[len(*num)-1] = flipGrayCode((*num)[len(*num)-1])
} else {
(*num)[index-1] = flipGrayCode((*num)[index-1])
}
}
generateGrayCode(n-1, step+1, num, res)
return
}
func convertBinary(num []int) int {
res, rad := 0, 1
for i := len(num) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
res += num[i] * rad
rad *= 2
}
return res
}
func flipGrayCode(num int) int {
if num == 0 {
return 1
}
return 0
}
// 解法二 直译
func grayCode1(n int) []int {
var l uint = 1 << uint(n)
out := make([]int, l)
for i := uint(0); i < l; i++ {
out[i] = int((i >> 1) ^ i)
}
return out
}
90. Subsets II
题目
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example:
Input: [1,2,2]
Output:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
题目大意
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
解题思路
- 这一题是第 78 题的加强版,比第 78 题多了一个条件,数组中的数字会出现重复。
- 解题方法依旧是 DFS,需要在回溯的过程中加上一些判断。
- 这一题和第 78 题,第 491 题类似,可以一起解答和复习。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func subsetsWithDup(nums []int) [][]int {
c, res := []int{}, [][]int{}
sort.Ints(nums) // 这里是去重的关键逻辑
for k := 0; k <= len(nums); k++ {
generateSubsetsWithDup(nums, k, 0, c, &res)
}
return res
}
func generateSubsetsWithDup(nums []int, k, start int, c []int, res *[][]int) {
if len(c) == k {
b := make([]int, len(c))
copy(b, c)
*res = append(*res, b)
return
}
// i will at most be n - (k - c.size()) + 1
for i := start; i < len(nums)-(k-len(c))+1; i++ {
fmt.Printf("i = %v start = %v c = %v\n", i, start, c)
if i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-1] { // 这里是去重的关键逻辑,本次不取重复数字,下次循环可能会取重复数字
continue
}
c = append(c, nums[i])
generateSubsetsWithDup(nums, k, i+1, c, res)
c = c[:len(c)-1]
}
return
}
91. Decode Ways
题目
A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
Given a non-empty string containing only digits, determine the total number of ways to decode it.
Example 1:
Input: "12"
Output: 2
Explanation: It could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12).
Example 2:
Input: "226"
Output: 3
Explanation: It could be decoded as "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), or "BBF" (2 2 6).
题目大意
一条包含字母 A-Z 的消息通过以下方式进行了编码:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
给定一个只包含数字的非空字符串,请计算解码方法的总数。
解题思路
- 给出一个数字字符串,题目要求把数字映射成 26 个字母,映射以后问有多少种可能的翻译方法。
- 这题思路也是 DP。
dp[n]代表翻译长度为 n 个字符的字符串的方法总数。由于题目中的数字可能出现 0,0 不能翻译成任何字母,所以出现 0 要跳过。dp[0] 代表空字符串,只有一种翻译方法,dp[0] = 1。dp[1] 需要考虑原字符串是否是 0 开头的,如果是 0 开头的,dp[1] = 0,如果不是 0 开头的,dp[1] = 1。状态转移方程是dp[i] += dp[i-1] (当 1 ≤ s[i-1 : i] ≤ 9);dp[i] += dp[i-2] (当 10 ≤ s[i-2 : i] ≤ 26)。最终结果是dp[n]。
代码
package leetcode
func numDecodings(s string) int {
n := len(s)
dp := make([]int, n+1)
dp[0] = 1
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
if s[i-1] != '0' {
dp[i] += dp[i-1]
}
if i > 1 && s[i-2] != '0' && (s[i-2]-'0')*10+(s[i-1]-'0') <= 26 {
dp[i] += dp[i-2]
}
}
return dp[n]
}
92. Reverse Linked List II
题目
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
题目大意
给定 2 个链表中结点的位置 m, n,反转这个两个位置区间内的所有结点。
解题思路
由于有可能整个链表都被反转,所以构造一个新的头结点指向当前的头。之后的处理方法是:找到第一个需要反转的结点的前一个结点 p,从这个结点开始,依次把后面的结点用“头插”法,插入到 p 结点的后面。循环次数用 n-m 来控制。
这一题结点可以原地变化,更改各个结点的 next 指针就可以。不需要游标 p 指针。因为每次逆序以后,原有结点的相对位置就发生了变化,相当于游标指针已经移动了,所以不需要再有游标 p = p.Next 的操作了。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func reverseBetween(head *ListNode, m int, n int) *ListNode {
if head == nil || m >= n {
return head
}
newHead := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: head}
pre := newHead
for count := 0; pre.Next != nil && count < m-1; count++ {
pre = pre.Next
}
if pre.Next == nil {
return head
}
cur := pre.Next
for i := 0; i < n-m; i++ {
tmp := pre.Next
pre.Next = cur.Next
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
pre.Next.Next = tmp
}
return newHead.Next
}
93. Restore IP Addresses
题目
Given a string containing only digits, restore it by returning all possible valid IP address combinations.
Example:
Input: "25525511135"
Output: ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]
题目大意
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。
解题思路
- DFS 深搜
- 需要注意的点是 IP 的规则,以 0 开头的数字和超过 255 的数字都为非法的。
代码
package leetcode
import (
"strconv"
)
func restoreIPAddresses(s string) []string {
if s == "" {
return []string{}
}
res, ip := []string{}, []int{}
dfs(s, 0, ip, &res)
return res
}
func dfs(s string, index int, ip []int, res *[]string) {
if index == len(s) {
if len(ip) == 4 {
*res = append(*res, getString(ip))
}
return
}
if index == 0 {
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(s[0]))
ip = append(ip, num)
dfs(s, index+1, ip, res)
} else {
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(s[index]))
next := ip[len(ip)-1]*10 + num
if next <= 255 && ip[len(ip)-1] != 0 {
ip[len(ip)-1] = next
dfs(s, index+1, ip, res)
ip[len(ip)-1] /= 10
}
if len(ip) < 4 {
ip = append(ip, num)
dfs(s, index+1, ip, res)
ip = ip[:len(ip)-1]
}
}
}
func getString(ip []int) string {
res := strconv.Itoa(ip[0])
for i := 1; i < len(ip); i++ {
res += "." + strconv.Itoa(ip[i])
}
return res
}
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
题目
Given a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example:
Input: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
Output: [1,3,2]
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
题目大意
中根遍历一颗树。
解题思路
递归的实现方法,见代码。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
var result []int
inorder(root, &result)
return result
}
func inorder(root *TreeNode, output *[]int) {
if root != nil {
inorder(root.Left, output)
*output = append(*output, root.Val)
inorder(root.Right, output)
}
}
95. Unique Binary Search Trees II
题目
Given an integer n, generate all structurally unique BST’s (binary search trees) that store values 1 … n.
Example:
Input: 3
Output:
[
[1,null,3,2],
[3,2,null,1],
[3,1,null,null,2],
[2,1,3],
[1,null,2,null,3]
]
Explanation:
The above output corresponds to the 5 unique BST's shown below:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
题目大意
给定一个整数 n,生成所有由 1 … n 为节点所组成的二叉搜索树。
解题思路
- 输出 1
n 元素组成的 BST 所有解。这一题递归求解即可。外层循环遍历 1n 所有结点,作为根结点,内层双层递归分别求出左子树和右子树。
代码
Go
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func generateTrees(n int) []*TreeNode {
if n == 0 {
return []*TreeNode{}
}
return generateBSTree(1, n)
}
func generateBSTree(start, end int) []*TreeNode {
tree := []*TreeNode{}
if start > end {
tree = append(tree, nil)
return tree
}
for i := start; i <= end; i++ {
left := generateBSTree(start, i-1)
right := generateBSTree(i+1, end)
for _, l := range left {
for _, r := range right {
root := &TreeNode{Val: i, Left: l, Right: r}
tree = append(tree, root)
}
}
}
return tree
}
96. Unique Binary Search Trees
题目
Given n, how many structurally unique BST’s (binary search trees) that store values 1 … n?
Example:
Input: 3
Output: 5
Explanation:
Given n = 3, there are a total of 5 unique BST's:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
题目大意
给定一个整数 n,求以 1 … n 为节点组成的二叉搜索树有多少种?
解题思路
- 给出 n,要求利用 1-n 这些数字组成二叉排序树,有多少种不同的树的形态,输出这个个数。
- 这题的解题思路是 DP。
dp[n]代表 1-n 个数能组成多少个不同的二叉排序树,F(i,n)代表以i为根节点,1-n 个数组成的二叉排序树的不同的个数。由于题意,我们可以得到这个等式:dp[n] = F(1,n) + F(2,n) + F(3,n) + …… + F(n,n)。初始值dp[0] = 1,dp[1] = 1。分析dp和F(i,n)的关系又可以得到下面这个等式F(i,n) = dp[i-1] * dp[n-i]。举例,[1,2,3,4,…, i ,…,n-1,n],以i为 根节点,那么左半边 [1,2,3,……,i-1] 和 右半边 [i+1,i+2,……,n-1,n] 分别能组成二叉排序树的不同个数相乘,即为以i为根节点,1-n 个数组成的二叉排序树的不同的个数,也即F(i,n)。
注意,由于二叉排序树本身的性质,右边的子树一定比左边的子树,值都要大。所以这里只需要根节点把树分成左右,不需要再关心左右两边数字的大小,只需要关心数字的个数。
- 所以状态转移方程是
dp[i] = dp[0] * dp[n-1] + dp[1] * dp[n-2] + …… + dp[n-1] * dp[0],最终要求的结果是dp[n]。
代码
package leetcode
func numTrees(n int) int {
dp := make([]int, n+1)
dp[0], dp[1] = 1, 1
for i := 2; i <= n; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= i; j++ {
dp[i] += dp[j-1] * dp[i-j]
}
}
return dp[n]
}
97. Interleaving String
题目
Given strings s1, s2, and s3, find whether s3 is formed by an interleaving of s1 and s2.
An interleaving of two strings s and t is a configuration where they are divided into non-empty substrings such that:
s = s1 + s2 + ... + snt = t1 + t2 + ... + tm|n - m| <= 1- The interleaving is
s1 + t1 + s2 + t2 + s3 + t3 + ...ort1 + s1 + t2 + s2 + t3 + s3 + ...
Note: a + b is the concatenation of strings a and b.
Example 1:
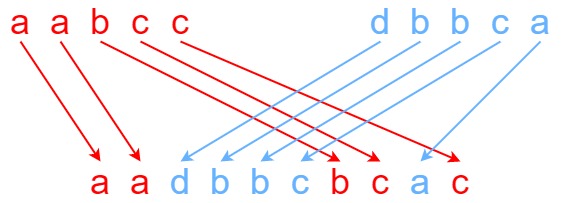
Input: s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbcbcac"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbbaccc"
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: s1 = "", s2 = "", s3 = ""
Output: true
Constraints:
0 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 1000 <= s3.length <= 200s1,s2, ands3consist of lowercase English letters.
Follow up: Could you solve it using only O(s2.length) additional memory space?
题目大意
给定三个字符串 s1、s2、s3,请你帮忙验证 s3 是否是由 s1 和 s2 交错 组成的。两个字符串 s 和 t 交错 的定义与过程如下,其中每个字符串都会被分割成若干 非空 子字符串:
- s = s1 + s2 + … + sn
- t = t1 + t2 + … + tm
|n - m| <= 1- 交错 是 s1 + t1 + s2 + t2 + s3 + t3 + … 或者 t1 + s1 + t2 + s2 + t3 + s3 + …
提示:a + b 意味着字符串 a 和 b 连接。
解题思路
- 深搜或者广搜暴力解题。笔者用深搜实现的。记录 s1 和 s2 串当前比较的位置 p1 和 p2。如果 s3[p1+p2] 的位置上等于 s1[p1] 或者 s2[p2] 代表能匹配上,那么继续往后移动 p1 和 p2 相应的位置。因为是交错字符串,所以判断匹配的位置是 s3[p1+p2] 的位置。如果仅仅这么写,会超时,s1 和 s2 两个字符串重复交叉判断的位置太多了。需要加上记忆化搜索。可以用 visited[i][j] 这样的二维数组来记录是否搜索过了。笔者为了压缩空间,将 i 和 j 编码压缩到一维数组了。i * len(s3) + j 是唯一下标,所以可以用这种方式存储是否搜索过。具体代码见下面的实现。
代码
Go
package leetcode
func isInterleave(s1 string, s2 string, s3 string) bool {
if len(s1)+len(s2) != len(s3) {
return false
}
visited := make(map[int]bool)
return dfs(s1, s2, s3, 0, 0, visited)
}
func dfs(s1, s2, s3 string, p1, p2 int, visited map[int]bool) bool {
if p1+p2 == len(s3) {
return true
}
if _, ok := visited[(p1*len(s3))+p2]; ok {
return false
}
visited[(p1*len(s3))+p2] = true
var match1, match2 bool
if p1 < len(s1) && s3[p1+p2] == s1[p1] {
match1 = true
}
if p2 < len(s2) && s3[p1+p2] == s2[p2] {
match2 = true
}
if match1 && match2 {
return dfs(s1, s2, s3, p1+1, p2, visited) || dfs(s1, s2, s3, p1, p2+1, visited)
} else if match1 {
return dfs(s1, s2, s3, p1+1, p2, visited)
} else if match2 {
return dfs(s1, s2, s3, p1, p2+1, visited)
} else {
return false
}
}
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
题目
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
2
/ \
1 3
Input: [2,1,3]
Output: true
Example 2:
5
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 6
Input: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
Output: false
Explanation: The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.
题目大意
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
解题思路
- 判断一个树是否是 BST,按照定义递归判断即可
代码
Go
package leetcode
import "math"
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
// 解法一,直接按照定义比较大小,比 root 节点小的都在左边,比 root 节点大的都在右边
func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
return isValidbst(root, math.Inf(-1), math.Inf(1))
}
func isValidbst(root *TreeNode, min, max float64) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
v := float64(root.Val)
return v < max && v > min && isValidbst(root.Left, min, v) && isValidbst(root.Right, v, max)
}
// 解法二,把 BST 按照左中右的顺序输出到数组中,如果是 BST,则数组中的数字是从小到大有序的,如果出现逆序就不是 BST
func isValidBST1(root *TreeNode) bool {
arr := []int{}
inOrder(root, &arr)
for i := 1; i < len(arr); i++ {
if arr[i-1] >= arr[i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func inOrder(root *TreeNode, arr *[]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
inOrder(root.Left, arr)
*arr = append(*arr, root.Val)
inOrder(root.Right, arr)
}
99. Recover Binary Search Tree
题目
Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped by mistake.
Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:
Input: [1,3,null,null,2]
1
/
3
\
2
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
3
/
1
\
2
Example 2:
Input: [3,1,4,null,null,2]
3
/ \
1 4
/
2
Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3]
2
/ \
1 4
/
3
Follow up:
- A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward.
- Could you devise a constant space solution?
题目大意
二叉搜索树中的两个节点被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树。
解题思路
- 在二叉搜索树中,有 2 个结点的值出错了,要求修复这两个结点。
- 这一题按照先根遍历 1 次就可以找到这两个出问题的结点,因为先访问根节点,然后左孩子,右孩子。用先根遍历二叉搜索树的时候,根结点比左子树都要大,根结点比右子树都要小。所以
左子树比根结点大的话,就是出现了乱序;根节点比右子树大的话,就是出现了乱序。遍历过程中在左子树中如果出现了前一次遍历的结点的值大于此次根节点的值,这就出现了出错结点了,记录下来。继续遍历直到找到第二个这样的结点。最后交换这两个结点的时候,只是交换他们的值就可以了,而不是交换这两个结点相应的指针指向。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func recoverTree(root *TreeNode) {
var prev, target1, target2 *TreeNode
_, target1, target2 = inOrderTraverse(root, prev, target1, target2)
if target1 != nil && target2 != nil {
target1.Val, target2.Val = target2.Val, target1.Val
}
}
func inOrderTraverse(root, prev, target1, target2 *TreeNode) (*TreeNode, *TreeNode, *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return prev, target1, target2
}
prev, target1, target2 = inOrderTraverse(root.Left, prev, target1, target2)
if prev != nil && prev.Val > root.Val {
if target1 == nil {
target1 = prev
}
target2 = root
}
prev = root
prev, target1, target2 = inOrderTraverse(root.Right, prev, target1, target2)
return prev, target1, target2
}
100. Same Tree
题目
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1:
Input: 1 1
/ \ / \
2 3 2 3
[1,2,3], [1,2,3]
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: 1 1
/ \
2 2
[1,2], [1,null,2]
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: 1 1
/ \ / \
2 1 1 2
[1,2,1], [1,1,2]
Output: false
题目大意
这一题要求判断 2 颗树是否是完全相等的。
解题思路
递归判断即可。
代码
package leetcode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
} else if p != nil && q != nil {
if p.Val != q.Val {
return false
}
return isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left) && isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
} else {
return false
}
}